Notice
of
Use
Copyright
Notice,
License
and
Disclosure
Disclaimer
Copyright
©
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
(2021).
(2021-2023).
All
rights
reserved.
This
The
information
within
this
document
is
the
property
of
the
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
and
its
use
and
disclosure
are
restricted.
restricted,
except
as
expressly
set
forth
herein.
Elements
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
hereby
grants
you
a
fully-paid,
non-exclusive,
nontransferable,
worldwide,
limited
and
revocable
license
(without
the
right
to
sublicense),
under
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance’s
applicable
copyright
rights,
to
view,
download,
save,
reproduce
and
use
the
document
solely
for
your
own
internal
purposes
and
in
accordance
with
the
terms
of
the
license
set
forth
herein.
This
license
does
not
authorize
you
to,
and
you
expressly
warrant
that
you
shall
not:
(a)
permit
others
(outside
your
organization)
to
use
this
document;
(b)
post
or
publish
this
document;
(c)
modify,
adapt,
translate,
or
otherwise
change
this
document
in
any
manner
or
create
any
derivative
work
based
on
this
document;
(d)
remove
or
modify
any
notice
or
label
on
this
document,
including
this
Copyright
Notice,
License
and
Disclaimer.
The
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
specifications
does
not
grant
you
any
license
hereunder
other
than
as
expressly
stated
herein.
Elements
of
this
document
may
be
subject
to
third
party
intellectual
property
rights,
including
without
limitation,
patent,
copyright
or
trademark
rights
(such
a
rights,
and
any
such
third
party
may
or
may
not
be
a
member
of
the
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance).
Alliance.
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
members
grant
other
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
members
certain
intellectual
property
rights
as
set
forth
in
the
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
IPR
Policy.
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
members
do
not
grant
you
any
rights
under
this
license.
The
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
is
not
responsible
for,
and
shall
not
be
held
responsible
in
any
manner
for
for,
identifying
or
failing
to
identify
any
or
all
such
third
party
intellectual
property
rights.
Please
visit
www.csa-iot.org
for
more
information
on
how
to
become
a
member
of
the
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance.
This
document
and
the
information
contained
herein
are
provided
on
an
"AS
IS"
“AS
IS”
basis
and
the
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
DISCLAIMS
ALL
WARRANTIES
EXPRESS
OR
IMPLIED,
INCLUDING
BUT
NOT
LIMITED
TO
(A)
ANY
WARRANTY
THAT
THE
USE
OF
THE
INFORMATION
HEREIN
WILL
NOT
INFRINGE
ANY
RIGHTS
OF
THIRD
PARTIES
(INCLUDING
WITHOUT
LIMITATION
ANY
INTELLECTUAL
PROPERTY
RIGHTS
INCLUDING
PATENT,
COPYRIGHT
OR
TRADEMARK
RIGHTS)
RIGHTS);
OR
(B)
ANY
IMPLIED
WARRANTIES
OF
MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS
FOR
A
PARTICULAR
PURPOSE,
TITLE
OR
NON-INFRINGEMENT.
NONINFRINGEMENT.
IN
NO
EVENT
WILL
THE
CONNECTIVITY
STANDARDS
ALLIANCE
BE
LIABLE
FOR
ANY
LOSS
OF
PROFITS,
LOSS
OF
BUSINESS,
LOSS
OF
USE
OF
DATA,
INTERRUPTION
OF
BUSINESS,
OR
FOR
ANY
OTHER
DIRECT,
INDIRECT,
SPECIAL
OR
EXEMPLARY,
INCIDENTAL,
PUNITIVE
OR
CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES
OF
ANY
KIND,
IN
CONTRACT
OR
IN
TORT,
IN
CONNECTION
WITH
THIS
DOCUMENT
OR
THE
INFORMATION
CONTAINED
HEREIN,
EVEN
IF
ADVISED
OF
THE
POSSIBILITY
OF
SUCH
LOSS
OR
DAMAGE.
All company, brand and product names in this document may be trademarks that are the sole property of their respective owners.
This
legal
notice
and
disclaimer
must
be
included
on
all
copies
of
this
document
that
are
made.
document.
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
508
Second
Street,
Suite
206
Davis,
CA
95616,
USA
Revision History
| Revision | Date | Details | Editor |
|---|---|---|---|
01 | September 23, 2022 | Version 1.0 | Robert Szewczyk |
02 | May 17, 2023 | Version 1.1 | Robert Szewczyk |
03 | October 18, 2023 | Version 1.2 | Robert Szewczyk |
Introduction
The Matter Application Cluster specification defines generic interfaces that are sufficiently general to be of use across a wide range of application domains.
Scope and Purpose
This document specifies the Matter Application Cluster Library (MACL). The MACL is a repository for cluster functionality that is developed by the Connectivity Standards Alliance, and is a working library with regular updates as new functionality is added. A developer constructing a new application should use the MACL to find relevant cluster functionality that can be incorporated into the new application. Correspondingly, new clusters that are defined for applications should be considered for inclusion in the MACL.
The MACL consists of a number of sets of clusters. Clusters that are generally useful across many application domains are included in the General set. Clusters that are intended for use mainly in specific application domains are grouped together in domain oriented sets.
References
The following standards and specifications contain provisions, which through reference in this document constitute provisions of this specification. All the standards and specifications listed are normative references. At the time of publication, the editions indicated were valid. All standards and specifications are subject to revision, and parties to agreements based on this specification are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions of the standards and specifications indicated below.
CSA Reference Documents
| Reference | Reference Location/URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
https://github.com/CHIP-Specifications/connectedhomeip-spec/raw/build-sample/pdf/main.pdf |
Matter Core Specification - Under development |
|
|
https://github.com/CHIP-Specifications/connectedhomeip-spec/raw/build-sample/pdf/device_library.pdf |
Matter Device Library Specification - Under development |
|
|
Organizational Processes and Procedures, 13-0625, revision 8, November 2021 |
External Reference Documents
| Reference | Reference Location/URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
http://www.dial-multiscreen.org/dial-registry/namespace-database |
DIAL Registry |
|
|
https://hdmiforum.org/hdmi-forum-releases-version-2-1-hdmi-specification/ |
HDMI CEC specification |
|
|
Wake on LAN Magic Packet specification |
Provisional
Per
[CSA-PNP]
[CSA-PNP]
,
when
a
specification
is
completed
there
may
be
sections
of
specification
text
(or
smaller
pieces
of
a
section)
that
are
not
certifiable
at
this
stage.
These
sections
(or
smaller
pieces
of
a
section)
are
marked
as
provisional
prior
to
publishing
the
specification.
This
specification
uses
well-defined
notation
to
mark
Provisional
Conformance
(see
[MatterCore]
[MatterCore]
,
Section
7.3)
or
notes
a
section
of
text
with
the
term
"provisional".
List of Provisional Items
The following is a list of provisional items:
-
Support for Scenes cluster is provisional.
-
Support for Pulse Width Modulation cluster and for the Frequency feature of the Level control cluster is provisional
-
Support for Ballast Configuration Cluster is provisional.
-
Support for Fan Control cluster is provisional.
-
Support for InflowError, DrainError, TempTooLow, TempTooHigh, and WaterLevelError alarms in Dishwasher Alarm Cluster is provisional.
1. General
The Cluster Library is made of individual chapters such as this one. See Document Control in the Cluster Library for a list of all chapters and documents. References between chapters are made using a X.Y notation where X is the chapter and Y is the sub-section within that chapter. References to external documents are contained in Chapter 1 and are made using [ Rn ] notation.
1.1. General Description
1.1.1. Introduction
The clusters specified in this document are generic interfaces that are sufficiently general to be of use across a wide range of application domains.
1.1.2. Cluster List
This section lists the general clusters as specified in this chapter.
| ID | Cluster Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0x0003 |
Attributes and commands for putting a device into Identification mode (e.g., flashing a light) |
|
|
0x0004 |
Cluster to manage the associated endpoint’s membership into one or more groups to support groupcast interactions. |
|
|
0x0005 |
Attributes and commands for setting up and recalling a number of scenes for a device. Each scene corresponds to a set of stored values of specified device attributes. |
|
|
0x0006 |
Attributes
and
commands
for
switching
devices
between
|
|
|
0x0008 |
|
Attributes
and
commands
for
controlling
a
characteristic
of
devices
that
can
be
set
to
a
level
between
fully
|
|
0x0045 |
Attribute and event for a boolean state variable |
|
|
0x0050 |
Allows a user to choose one mode option from several predefined values |
|
|
n/a | Allows a user to choose one mode option from several predefined values | |
0x0508 |
This cluster provides an interface for managing low power mode on a device. |
|
|
0x0503 |
This cluster provides an interface for managing low power mode on a device that supports the Wake On LAN protocol. |
|
|
|
Attributes and events for various types of switch devices. |
|
|
0x0060 | Commands and attributes for defining a device’s operational state | |
n/a | Base alarm cluster from which all alarms are derived |
1.2. Identify Cluster
This cluster supports an endpoint identification state (e.g., flashing a light), that indicates to an observer (e.g., an installer) which of several nodes and/or endpoints it is. It also supports a multicast request that any endpoint that is identifying itself to respond to the initiator.
The state of this cluster MAY be shared on more than one endpoint on a node.
1.2.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
CCB 2808 |
|
3 |
All Hubs changes |
|
4 |
|
1.2.4. Features
This
cluster
SHALL
support
the
Feature
Map
global
FeatureMap
bitmap
attribute
with
these
bits
defined:
as
defined
below.
| Bit | Code | Name |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
QRY |
Query |
Multicast query for identification state |
1.2.5. Data Types
1.2.5.1. IdentifyTypeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | None | No presentation. | M |
0x01 | LightOutput | Light output of a lighting product. | M |
0x02 | VisibleIndicator | Typically a small LED. | M |
0x03 | AudibleBeep | M | |
0x04 | Display | Presentation will be visible on display screen. | M |
0x05 | Actuator | Presentation will be conveyed by actuator functionality such as through a window blind operation or in-wall relay. | M |
1.2.5.2. EffectIdentifierEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | Blink | e.g., Light is turned on/off once. | M |
0x01 | Breathe | e.g., Light is turned on/off over 1 second and repeated 15 times. | M |
0x02 | Okay | e.g., Colored light turns green for 1 second; non-colored light flashes twice. | M |
0x0B | ChannelChange | e.g., Colored light turns orange for 8 seconds; non-colored light switches to the maximum brightness for 0.5s and then minimum brightness for 7.5s. | M |
0xFE | FinishEffect | Complete the current effect sequence before terminating. e.g., if in the middle of a breathe effect (as above), first complete the current 1s breathe effect and then terminate the effect. | M |
0xFF | StopEffect | Terminate the effect as soon as possible. | M |
1.2.5.
1.2.6.
Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
IdentifyTime |
uint16 |
all |
0 |
RW VO |
M |
|
|
0x0001 |
IdentifyType |
|
desc |
|
R V |
M * |
* IdentifyType represents a mandatory attribute that was previously not present or optional. Implementers should be aware that older devices may not implement it.
1.2.5.1.
1.2.6.1.
IdentifyTime
Attribute
This attribute specifies the remaining length of time, in seconds, that the endpoint will continue to identify itself.
If this attribute is set to a value other than 0 then the device SHALL enter its identification state, in order to indicate to an observer which of several nodes and/or endpoints it is. It is RECOMMENDED that this state consists of flashing a light with a period of 0.5 seconds. The IdentifyTime attribute SHALL be decremented every second while in this state.
If this attribute reaches or is set to the value 0 then the device SHALL terminate its identification state.
1.2.5.2.
1.2.6.2.
IdentifyType
Attribute
This attribute specifies how the identification state is presented to the user.
This
field
SHALL
contain
one
of
the
values
listed
below:
Table
2.
Values
of
the
IdentifyType
attribute
Value
Presentation
Notes
0x00
defined
in
IdentifyTypeEnum
.
The
value
None
No
presentation.
0x01
Light
output
Light
output
of
a
lighting
product.
0x02
Visible
indicator
Typically
a
small
LED.
0x03
Audible
beep
0x04
Display
Presentation
will
be
visible
on
display
screen.
0x05
Actuator
Presentation
will
SHALL
NOT
be
conveyed
by
actuator
functionality
such
as
through
a
window
blind
operation
or
in-wall
relay.
used
if
the
device
is
capable
of
presenting
its
identification
state
using
one
of
the
other
methods
defined
in
IdentifyTypeEnum
.
1.2.6.
1.2.7.
Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
Identify |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
M |
M |
|
0x01 |
IdentifyQuery |
client ⇒ server |
IdentifyQueryResponse |
M |
QRY |
|
0x40 |
TriggerEffect |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
M |
O |
|
0x00 |
IdentifyQueryResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
QRY |
1.2.6.1.
1.2.7.1.
Identify
Command
This command starts or stops the receiving device identifying itself.
This command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
IdentifyTime |
uint16 |
all |
M |
1.2.6.1.1.
1.2.7.1.1.
Effect
on
Receipt
On receipt of this command, the device SHALL set the IdentifyTime attribute to the value of the IdentifyTime field. This then starts, continues, or stops the device’s identification state as detailed in IdentifyTime Attribute .
1.2.6.2.
1.2.7.2.
IdentifyQuery
Command
This command allows the sending device to request the target or targets to respond if they are currently identifying themselves.
1.2.6.2.1.
1.2.7.2.1.
Effect
on
Receipt
On receipt of this command, if the IdentifyTime attribute is not zero, then it SHALL generate a response in the form of an IdentifyQueryResponse command, see IdentifyQueryResponse Command . Otherwise it SHALL take no further action.
1.2.6.3.
1.2.7.3.
TriggerEffect
Command
This command allows the support of feedback to the user, such as a certain light effect. It is used to allow an implementation to provide visual feedback to the user under certain circumstances such as a color light turning green when it has successfully connected to a network. The use of this command and the effects themselves are entirely up to the implementer to use whenever a visual feedback is useful but it is not the same as and does not replace the identify mechanism used during commissioning.
The
TriggerEffect
This
command
SHALL
have
the
following
data
fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
EffectIdentifier |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
EffectVariant |
|
desc |
M |
1.2.6.3.1.
1.2.7.3.1.
EffectIdentifier
Field
This
field
specifies
the
identify
effect
to
use.
use
and
SHALL
contain
one
of
the
non-reserved
values
in
EffectIdentifierEnum
.
All
values
of
the
EffectIdentifier
EffectIdentifierEnum
SHALL
be
supported.
Implementors
MAY
deviate
from
the
example
light
effects
in
the
table
below,
EffectIdentifierEnum
,
but
they
SHOULD
indicate
during
testing
how
they
handle
each
effect.
1.2.6.3.2.
1.2.7.3.2.
EffectVariant
Field
This
field
is
used
to
indicate
which
variant
of
the
effect,
indicated
in
the
EffectIdentifier
field,
SHOULD
be
triggered.
If
a
device
does
not
support
the
given
variant,
it
SHALL
use
the
default
variant.
This
field
SHALL
contain
one
of
the
values
listed
below:
in
EffectVariantEnum
.
1.2.6.4.
1.2.7.4.
IdentifyQueryResponse
Command
This
command
is
generated
in
response
to
receiving
an
IdentifyQuery
command,
see
IdentifyQuery
Command
,
in
the
case
that
the
device
is
currently
identifying
itself.
This command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Timeout |
uint16 |
all |
M |
1.2.6.4.1.
1.2.7.4.1.
Timeout
Field
This field contains the current value of the IdentifyTime attribute, and specifies the length of time, in seconds, that the device will continue to identify itself.
1.2.6.4.2.
1.2.7.4.2.
Effect
on
Receipt
On receipt of this command, the device is informed of a device in the network which is currently identifying itself. This information MAY be particularly beneficial in situations where there is no commissioning tool. Note that there MAY be multiple responses in case the IdentifyQuery command was sent as a groupcast or multicast, even from a single node in case multiple endpoints on that node are currently identifying themselves.
1.3. Groups Cluster
The Groups cluster manages, per endpoint, the content of the node-wide Group Table that is part of the underlying interaction layer.
In a network supporting fabrics, group IDs referenced by attributes or other elements of this cluster are scoped to the accessing fabric.
The Groups cluster is scoped to the endpoint. Groups cluster commands support discovering the endpoint membership in a group, adding the endpoint to a group, removing the endpoint from a group, removing endpoint membership from all groups. All commands defined in this cluster SHALL only affect groups scoped to the accessing fabric.
When group names are supported, the server stores a name string, which is set by the client for each assigned group and indicated in response to a client request.
Note that configuration of group addresses for outgoing commands is achieved using the Message Layer mechanisms where the Group Table is not involved. Hence this cluster does not play a part in that.
1.3.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
CCB 2289 |
|
3 |
CCB 2310 2704 |
|
4 |
|
1.3.4. Features
This
cluster
SHALL
support
the
FeatureMap
global
attribute:
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
| Bit | Code |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
The ability to store a name for a group. |
1.3.5.
Dependencies
Data
Types
1.3.5.1. NameSupportBitmap Type
For
correct
operation
of
the
AddGroupIfIdentifying
command,
any
endpoint
that
supports
the
Groups
server
cluster
SHALL
also
support
the
Identify
server
cluster.
This
data
type
is
derived
from
map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
7 |
GroupNames | The ability to store a name for a group. |
1.3.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
NameSupport |
|
desc |
F |
0 |
R V |
M |
1.3.6.1. NameSupport Attribute
This
attribute
provides
legacy,
read-only
access
to
whether
the
Group
Names
feature
is
supported.
The
most
significant
bit,
bit
7,
7
(GroupNames),
SHALL
be
equal
to
bit
0
of
the
FeatureMap
attribute.
attribute
(GN
Feature).
All
other
bits
SHALL
be
0.
1.3.7. Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
AddGroup |
client ⇒ server |
AddGroupResponse |
F M |
M |
|
0x01 |
ViewGroup |
client ⇒ server |
ViewGroupResponse |
F O |
M |
|
0x02 |
GetGroupMembership |
client ⇒ server |
GetGroupMembershipResponse |
F O |
M |
|
0x03 |
RemoveGroup |
client ⇒ server |
RemoveGroupResponse |
F M |
M |
|
0x04 |
RemoveAllGroups |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
F M |
M |
|
0x05 |
AddGroupIfIdentifying |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
F M |
M |
|
0x00 |
AddGroupResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x01 |
ViewGroupResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x02 |
GetGroupMembershipResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x03 |
RemoveGroupResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
1.3.7.1. AddGroup Command
The AddGroup command allows a client to add group membership in a particular group for the server endpoint.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
1 to max |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupName |
string |
max 16 |
M |
1.3.7.1.1.
When
Generated
GroupID
Field
The
GroupID
This
field
SHALL
be
used
to
identify
the
group
and
any
associated
key
material
to
which
the
server
endpoint
is
to
be
added.
The
1.3.7.1.2. GroupName Field
This field MAY be set to a human-readable name for the group. If the client has no name for the group, the GroupName field SHALL be set to the empty string.
Support of group names is optional and is indicated by the FeatureMap and NameSupport attribute.
1.3.7.1.2.
1.3.7.1.3.
Effect
on
Receipt
If the server does not support group names, the GroupName field SHALL be ignored.
On receipt of the AddGroup command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the command fields are not within constraints, the status SHALL be CONSTRAINT_ERROR, and the server continues from step 6.
-
If the receiving node requires security material to support the group ID and that material does not exist for this group ID, the status SHALL be UNSUPPORTED_ACCESS and the server continues from step 6.
-
If the server endpoint is a member of the group indicated by the GroupID, the group name SHALL be updated (if supported) to GroupName, the status SHALL be SUCCESS, and the server continues from step 6.
-
If there are no available resources to add the membership for the server endpoint, the status SHALL be RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED, and the server continues from step 6.
-
The server SHALL add the server endpoint as a member of the group indicated by the GroupID, the group name SHALL be updated (if supported) to GroupName, and the status SHALL be SUCCESS.
-
If the GroupID had already been added to the Group Table because of a previous AddGroup or AddGroupIfIdentifying command and a GroupName is provided and the server supports GroupName storage, then the GroupName associated with the GroupID in the Group Table SHALL be updated to reflect the new GroupName provided for the Group, such that subsequent ViewGroup commands yield the same name for all endpoints which have a group association to the given GroupID.
-
-
If the AddGroup command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL generate an AddGroupResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the AddGroup command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate an AddGroupResponse command.
See
AddGroupResponse
Command
for
a
description
of
the
AddGroupResponse
response
command.
1.3.7.2. ViewGroup Command
The ViewGroup command allows a client to request that the server responds with a ViewGroupResponse command containing the name string for a particular group.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
1 to max |
M |
1.3.7.2.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the ViewGroup command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the command fields are not within constraints, the status SHALL be CONSTRAINT_ERROR and the server continues from step 4.
-
If the server endpoint is a member of the group indicated by the GroupID, the status SHALL be SUCCESS, and the server continues from step 4.
-
Else the status SHALL be NOT_FOUND.
-
If the ViewGroup command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL generate a ViewGroupResponse command for the group, and the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the ViewGroup command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate a ViewGroupResponse command.
See
ViewGroupResponse
Command
for
a
description
of
the
ViewGroupResponse
response
command.
1.3.7.3. GetGroupMembership Command
The GetGroupMembership command allows a client to inquire about the group membership of the server endpoint, in a number of ways.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupList |
list[group-id] |
all[1 to max] |
M |
1.3.7.3.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the GetGroupMembership command, the server SHALL respond with group membership information using the GetGroupMembershipResponse command as follows:
If the GroupList field is empty, the server SHALL respond with all group IDs indicating the groups of which the server endpoint is a member.
If the GroupList field contains at least one group ID indicating a group of which the server endpoint is a member, the server SHALL respond with each group ID indicating a group of which the server endpoint is a member that matches a group in the GroupList field.
If the GroupList field contains one or more group IDs but does not contain any group ID indicating a group of which the server endpoint is a member, the server SHALL only respond if the command is unicast. The response SHALL return with an empty GroupList field.
1.3.7.4. RemoveGroup Command
The RemoveGroup command allows a client to request that the server removes the membership for the server endpoint, if any, in a particular group.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
1 to max |
M |
1.3.7.4.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the RemoveGroup command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the command fields are not within constraints, the status SHALL be CONSTRAINT_ERROR and the server continues from step 4.
-
If the server endpoint is a member of the group indicated by the GroupID, the server SHALL remove the server endpoint membership in the group, the status SHALL be SUCCESS, and the server continues from step 4.
-
Else the status SHALL be NOT_FOUND.
-
If the RemoveGroup command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL generate a RemoveGroupResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the RemoveGroup command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate a RemoveGroupResponse command.
See
RemoveGroupResponse
Command
for
a
description
of
the
RemoveGroupResponse
response
command.
Additionally, if the Scenes cluster is supported on the same endpoint, scenes associated with the indicated group SHALL be removed on that endpoint.
1.3.7.5. RemoveAllGroups Command
The RemoveAllGroups command allows a client to direct the server to remove all group associations for the server endpoint.
1.3.7.5.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, the server SHALL remove all group memberships for the server endpoint from the Group Table. If the RemoveAllGroups command was received as unicast and a response is not suppressed, the server SHALL generate a response with the Status field set to SUCCESS.
Additionally, if the Scenes cluster is supported on the same endpoint, all scenes, except for scenes associated with group ID 0, SHALL be removed on that endpoint.
1.3.7.6. AddGroupIfIdentifying Command
The AddGroupIfIdentifying command allows a client to add group membership in a particular group for the server endpoint, on condition that the endpoint is identifying itself. Identifying functionality is controlled using the Identify cluster, (see Identify Cluster ).
For correct operation of the AddGroupIfIdentifying command, any endpoint that supports the Groups server cluster SHALL also support the Identify server cluster.
This command might be used to assist configuring group membership in the absence of a commissioning tool.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
1 to max |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupName |
string |
max 16 |
M |
1.3.7.6.1.
When
Generated
GroupID
Field
The
GroupID
This
field
SHALL
be
used
to
identify
the
group
and
any
associated
key
material
to
which
the
server
endpoint
is
to
be
added.
The
1.3.7.6.2. GroupName Field
This field MAY be set to a human-readable name for the group. If the client has no name for the group, the GroupName field SHALL be set to the empty string.
Support of group names is optional and is indicated by the FeatureMap and NameSupport attribute.
1.3.7.6.2.
1.3.7.6.3.
Effect
on
Receipt
If the server does not support group names, the GroupName field SHALL be ignored.
On receipt of the AddGroupIfIdentifying command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
The server verifies that it is currently identifying itself. If the server it not currently identifying itself, the status SHALL be SUCCESS, and the server continues from step 7.
-
If the command fields are not within constraints, the status SHALL be CONSTRAINT_ERROR and the server continues from step 7.
-
If the receiving node requires security material to support the group ID, and that material does not exist for this group ID, the status SHALL be UNSUPPORTED_ACCESS and the server continues from step 7.
-
If the server endpoint is a member of the group indicated by the GroupID, the status SHALL be SUCCESS and the server continues from step 7.
-
If there are no available resources to add the membership for the server endpoint, the status SHALL be RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED and the server continues from step 7.
-
The server SHALL add the server endpoint as a member of the group indicated by the GroupID, the group name SHALL be updated (if supported) to GroupName, and the status SHALL be SUCCESS.
-
If the GroupID had already been added to the Group Table because of a previous AddGroup or AddGroupIfIdentifying command and a GroupName is provided and the server supports GroupName storage, then the GroupName associated with the GroupID in the Group Table SHALL be updated to reflect the new GroupName provided for the Group, such that subsequent ViewGroup commands yield the same name for all endpoints which have a group association to the given GroupID.
-
-
If the AddGroupIfIdentifying command was received as unicast and the evaluated status is not SUCCESS, or if the AddGroupIfIdentifying command was received as unicast and the evaluated status is SUCCESS and a response is not suppressed, the server SHALL generate a response with the Status field set to the evaluated status.
1.3.7.7. AddGroupResponse Command
The AddGroupResponse is sent by the Groups cluster server in response to an AddGroup command.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupID |
group-id |
1 to max |
M |
1.3.7.8. ViewGroupResponse Command
The ViewGroupResponse command is sent by the Groups cluster server in response to a ViewGroup command.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupID |
group-id |
1 to max |
M |
||
|
2 |
GroupName |
string |
max 16 |
M |
1.3.7.9. GetGroupMembershipResponse Command
The GetGroupMembershipResponse command is sent by the Groups cluster server in response to a GetGroupMembership command.
The GetGroupMembershipResponse command SHALL have the following data fields:
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Capacity |
uint8 |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
1 |
GroupList |
list[group-id] |
all[1 to max] |
M |
1.3.7.9.1. Capacity Field
The
fields
of
the
GetGroupMembershipResponse
command
have
the
following
semantics:
The
Capacity
This
field
SHALL
contain
the
remaining
capacity
of
the
Group
Table
of
the
node.
The
following
values
apply:
-
0 - No further groups MAY be added.
-
0 < Capacity <
0xfe0xFE - Capacity holds the number of groups that MAY be added. -
0xfe0xFE - At least 1 further group MAY be added (exact number is unknown). -
null - It is unknown if any further groups MAY be added.
1.3.7.9.2. GroupList Field
The
GroupList
field
SHALL
contain
either
the
group
IDs
of
all
the
groups
in
the
Group
Table
for
which
the
server
endpoint
is
a
member
of
the
group
(in
the
case
where
the
GroupList
field
of
the
received
GetGroupMembership
command
was
empty),
or
the
group
IDs
of
all
the
groups
in
the
Group
Table
for
which
the
server
endpoint
is
a
member
of
the
group
and
for
which
the
group
ID
was
included
in
the
the
GroupList
field
of
the
received
GetGroupMembership
command
(in
the
case
where
the
GroupList
field
of
the
received
GetGroupMembership
command
was
not
empty).
Zigbee:
If
the
total
number
of
groups
will
cause
the
maximum
payload
length
of
a
frame
to
be
exceeded,
then
the
GroupList
field
SHALL
contain
only
as
many
groups
as
will
fit.
1.3.7.10. RemoveGroupResponse Command
The RemoveGroupResponse command is generated by the server in response to the receipt of a RemoveGroup command.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupID |
group-id |
1 to max |
M |
1.4. Scenes
The Scenes cluster provides attributes and commands for setting up and recalling scenes. Each scene corresponds to a set of stored values of specified attributes for one or more clusters on the same end point as the Scenes cluster.
In most cases scenes are associated with a particular group identifier. Scenes MAY also exist without a group, in which case the value 0 replaces the group identifier. Note that extra care is required in these cases to avoid a scene identifier collision, and that commands related to scenes without a group MAY only be unicast, i.e., they MAY not be multicast or broadcast.
|
Note
|
Support for Scenes cluster is provisional. |
1.4.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Rev | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
global mandatory ClusterRevision attribute added; CCB 1745 |
|
2 |
TransitionTime field added to the RecallScene command |
|
3 |
CCB 2427 3026 |
|
4 |
new
data
model
format
and
|
5 | not provisional; Explicit, TableSize and FabricScenes features; support multi-fabric environment; adding attributes SceneTableSize and RemainingCapacity; add fabric-scoped scene information list |
1.4.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role | PICS Code | Primary Transaction |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
S |
Type 1 (client to server) |
1.4.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap global attribute:
| Bit | Code |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
SN |
|
|
The ability to store a name for a scene. |
|
1 | EX | Explicit | M | Use explicit attribute IDs, not implicit based on order |
2 | TS | TableSize | M | Table size and remaining capacity supported |
3 | FS | FabricScenes | M | Supports current scene, count, group etc, as fabric-scoped. |
The following sections describe each feature in some detail. Further details are found within the specification.
1.4.5. Dependencies
Any endpoint that implements the Scenes server cluster SHALL also implement the Groups server cluster.
Note that the RemoveGroup command and the RemoveAllGroups command of the Groups cluster also remove scenes.
1.4.6. Handling of fabric-scoping
To retain semantic equivalence to earlier versions of the Scenes cluster which were designed prior to the introduction of multiple fabrics, the behavior of fabric-scoping in this cluster replaces use of explicit fabric-scoped access quality with an implicit method.
In nodes supporting fabrics, attributes and commands for this cluster are scoped to the accessing fabric and SHALL only affect or reflect data related to the accessing fabric.
In nodes supporting fabrics, the following constraints apply in addition to any other stated requirements in individual data model elements:
Any attribute read, attribute write or command invoked on the server when no accessing fabric is available SHALL fail with a status code of UNSUPPORTED_ACCESS returned to the client.
When accessing scene information, implementations SHALL ensure that scenes with identical Group ID and Scene ID across fabrics will only access the data for the accessing fabric, so that the same identifier values used by different accessing fabrics do not cause mixing or overwriting of another fabric’s scenes.
Upon leaving a fabric with the RemoveFabric command of the Operational Credentials Cluster, all scenes data for the associated fabric SHALL be removed from the Scene Table.
The Scene Table capacity for a given fabric SHALL be less than half (rounded down towards 0) of the Scene Table entries (as indicated in the SceneTableSize attribute), with a maximum of 253 entries (to allow expressing it in the GetSceneMembershipResponse command). If the Scene Table capacity is about to be exceeded by adding or storing a scene, then the resource exhaustion behavior of the associated command SHALL apply.
1.4.7. Data Types
1.4.6.1.
AttributeValuePair
1.4.7.1.
SceneInfoStruct
Type
Except for RemainingCapacity, the fields in this struct are used in place of the attributes of the same name to indicate the current state on the scene on the server, when the FabricScenes feature is supported. A reference to one of the attributes with the same name in behavior text, is synonymous with a reference to the field with the same name.
| Access Quality: Fabric Scoped | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
0 | SceneCount | uint8 | all | 0 | R V | M | |
1 | CurrentScene | uint8 | all | 0 | R V S | M | |
2 | CurrentGroup | group-id | all | 0 | R V S | M | |
3 | SceneValid | bool | all | False | R V S | M | |
4 | RemainingCapacity | uint8 | max 253 | MS | R V | TS | |
1.4.7.1.5. RemainingCapacity Field
This field SHALL indicate the remaining capacity of the Scene Table on this endpoint for the accessing fabric. Note that this value may change between reads even if no entries are added or deleted on the accessing fabric due to other clients associated with other fabrics adding or deleting entries that impact the resource usage on the device.
1.4.7.2. CopyModeMap Type
The CopyModeMap type is used in the CopyScene command. The data type of the CopyModeMap is derived from map8.
| Bit | Description | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | CopyAllScenes | 0 | M |
1.4.7.3. AttributeValuePairStruct Type
This data type indicates a combination of an identifier and the value of an attribute.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Access | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
AttributeID |
attribute-id |
all |
RW |
|
||
|
1 |
|
uint8 |
RW | O.a | |||
2 | ValueSigned8 |
int8 |
RW |
| |||
3 | ValueUnsigned16 | uint16 | RW | O.a | |||
4 | ValueSigned16 | int16 | RW | O.a | |||
5 | ValueUnsigned32 | uint32 | RW | O.a | |||
6 | ValueSigned32 | int32 | RW | O.a | |||
7 | ValueUnsigned64 | uint64 | RW | O.a | |||
8 | ValueSigned64 | int64 | RW | O.a |
1.4.6.1.1.
1.4.7.3.1.
AttributeID
Field
This
field
SHALL
be
present
for
all
instances
in
a
given
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
(explicit
list)
or
not
present,
SHALL
be
absent
for
all
instances
in
the
Scenes
cluster.
a
given
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
(implicit
list).
If
this
field
is
not
present,
then
the
data
type
of
AttributeValue
SHALL
be
determined
by
the
order
and
data
type
defined
in
the
cluster
specification.
specification
for
the
ClusterID
present
in
an
ExtensionFieldSetStruct.
Otherwise
the
data
type
of
AttributeValue
SHALL
be
the
data
type
of
the
attribute
indicated
by
AttributeID.
The AttributeID field SHALL NOT refer to an attribute without the Scenes ("S") designation in the Quality column of the cluster specification.
1.4.6.1.2.
AttributeValue
1.4.7.3.2.
ValueUnsigned8,
ValueSigned8,
ValueUnsigned16,
ValueSigned16,
ValueUnsigned32,
ValueSigned32,
ValueUnsigned64,
ValueSigned64
Fields
This
is
the
attribute
value
as
part
of
an
extension
field
set.
See
set,
associated
with
a
given
AttributeID
under
an
ExtensionFieldSetStruct’s
ClusterID.
The
proper
field
SHALL
be
present
that
maps
to
determine
the
data
type
of
the
attribute
indicated
(implicit
or
explicit).
Data types bool, map8, and uint8 SHALL map to ValueUnsigned8.
Data types int8 SHALL map to ValueSigned8.
Data types map16 and uint16 SHALL map to ValueUnsigned16.
Data types int16 SHALL map to ValueSigned16.
Data types map32, uint24, and uint32 SHALL map to ValueUnsigned32.
Data types int24 and int32 SHALL map to ValueSigned32.
Data types map64, uint48, uint56 and uint64 SHALL map to ValueUnsigned64.
Data types int48, int56 and int64 SHALL map to ValueSigned64.
For nullable attributes, any value that is not a valid numeric value for
this field.the attribute’s type after accounting for range reductions due to being nullable and constraints SHALL be considered to have the null value for the type.For non-nullable attributes, any value that is not a valid numeric value for the attribute’s type after accounting for constraints SHALL be considered to have the maximum legal value in the attribute’s constrained range.
Examples of processing are:
ColorControl cluster CurrentX (AttributeID 0x0003) has a type of uint16 and is not nullable.
AttributeValue of 0xAB12 would be used as-is, as it is in range.
AttributeValue of 0xAA0011 is outside of the range of uint16, and would be saturated to the maximum of the attribute’s constraint range: 0xFEFF.
LevelControl cluster CurrentLevel (AttributeID 0x0000) has a type of uint8 and is nullable.
AttributeValue of 0xA1 would be used as-is, as it is in range.
AttributeValue of 0xBB12 is outside the range of nullable uint8, and would be considered as the null value.
1.4.6.2.
ExtensionFieldSet
1.4.7.4.
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
Type
This
data
type
indicates
for
a
given
cluster
a
set
of
attributes
and
their
values.
Only
attributes
which
have
the
"S"
designation
in
the
Quality
column
of
the
cluster
specification
SHALL
be
used
in
the
AttributeValueList
field.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Access | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
ClusterID |
cluster-id |
all |
RW |
M |
||
|
1 |
AttributeValueList |
|
desc |
RW |
M |
1.4.7.4.1. ClusterID Field
This field SHALL indicate the cluster-id of the cluster whose attributes are in the AttributeValueList field.
1.4.7.4.2. AttributeValueList Field
This field SHALL indicate a set of attributes and their values which are stored as part of a scene.
Attributes which do not have the Scenes ("S") designation in the Quality column of their cluster specification SHALL NOT be used in the AttributeValueList field.
The ExtensionFieldSetStruct can appear in an implicit form and an explicit form.
1.4.7.4.3. Implicit Form of ExtensionFieldSetStruct
In the implicit form, the AttributeValuePairStructs in AttributeValueList SHALL NOT have an AttributeID and the order of items in the AttributeValueList SHALL match the Scene Table order defined in the specification of the cluster identified by ClusterID. Note that the specified order of attributes in an AttributeValueList may not be the same as the order of attribute IDs.
The AttributeValueList SHOULD contain all the attributes with the Scenes ("S") quality as the specification of the cluster identified by ClusterID describes, but trailing AttributeValuePairStruct MAY be omitted. However, this restricts which AttributeValuePairStruct can be left out, imposing a problem for clusters that have attributes that have the Scenes ("S") quality but are not implemented, or for attributes which are a 'don’t care' in the given AttributeValueList. For these situations, the specification of the cluster identified by ClusterID also defines default values for these attributes.
An example using the Color Control cluster using positional indices:
Index 0: maps to Attribute 0x0003, CurrentX
Index 1: maps to Attribute 0x0004, CurrentY
Index 2: maps to Attribute 0x4000, EnhancedCurrentHue
Index 3: maps to Attribute 0x0001, CurrentSaturation
Index 4: maps to Attribute 0x4002, ColorLoopActive
Index 5: maps to Attribute 0x4003, ColorLoopDirection
Index 6: maps to Attribute 0x4004, ColorLoopTime
Index 7: maps to Attribute 0x0007, ColorTemperatureMireds
Index 8: maps to Attribute 0x4001, EnhancedColorMode
1.4.7.4.4. Explicit Form of ExtensionFieldSetStruct
In the explicit form, the AttributeValuePairStructs in AttributeValueList SHALL have an AttributeID and the items in the AttributeValueList MAY be in any order.
The AttributeValueList SHOULD contain all the attributes with the Scenes ("S") quality as the specification of the cluster identified by ClusterID describes, but AttributeValuePairStruct MAY be omitted.
An example using the Color Control cluster:
Attribute 0x0001, CurrentSaturation, S quality, optional, implemented
Attribute 0x0003, CurrentX, S quality, optional based on feature, implemented
Attribute 0x0004, CurrentY, S quality, optional based on feature, implemented
Attribute 0x0007, ColorTemperatureMireds, S quality, optional based on feature, implemented
Attribute 0x4000, EnhancedCurrentHue, S quality, optional based on feature, implemented
Attribute 0x4001, EnhancedColorMode, S quality, mandatory, implemented
Attribute 0x4002, ColorLoopActive, S quality, optional based on feature, NOT implemented
Attribute 0x4003, ColorLoopDirection, S quality, optional based on feature, NOT implemented
Attribute 0x4004, ColorLoopTime, S quality, optional based on feature, NOT implemented
1.4.7.
1.4.8.
Attributes
The attribute IDs for the Scene cluster are listed in the table below.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
SceneCount |
uint8 |
all |
0 |
R V |
!FS |
|
|
0x0001 |
CurrentScene |
uint8 |
all |
0 |
R V |
!FS |
|
|
0x0002 |
CurrentGroup |
group-id |
all |
0 |
R V |
!FS |
|
|
0x0003 |
SceneValid |
bool |
all |
|
R V |
!FS |
|
|
0x0004 |
NameSupport |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0005 |
LastConfiguredBy |
node-id |
|
X |
null |
R V |
O |
|
0x0006 | SceneTableSize | uint16 | desc | F | 16 | R V | TS |
0x0007 | FabricSceneInfo | list[SceneInfoStruct] | R V F | FS |
1.4.7.1.
1.4.8.1.
SceneCount
Attribute
The
SceneCount
attribute
specifies
the
number
of
scenes
currently
used
in
the
server’s
Scene
Table.
Table
on
the
endpoint
where
the
Scenes
cluster
appears.
For nodes supporting fabrics, this only includes the count for the accessing fabric.
1.4.7.2.
1.4.8.2.
CurrentScene
Attribute
The CurrentScene attribute holds the scene identifier of the scene last invoked.
1.4.7.3.
1.4.8.3.
CurrentGroup
Attribute
The CurrentGroup attribute holds the group identifier of the scene last invoked, or 0 if the scene last invoked is not associated with a group.
1.4.7.4.
1.4.8.4.
SceneValid
Attribute
The SceneValid attribute indicates whether the state of the server corresponds to that associated with the CurrentScene and CurrentGroup attributes. TRUE indicates that these attributes are valid, FALSE indicates that they are not valid.
Before a scene has been stored or recalled, this attribute is set to FALSE. After a successful StoreScene or RecallScene command it is set to TRUE. If, after a scene is stored or recalled, the state of the server is modified, this attribute is set to FALSE.
1.4.7.5.
1.4.8.5.
NameSupport
Attribute
This attribute provides legacy, read-only access to whether the Scene Names feature is supported. The most significant bit, bit 7, SHALL be equal to bit 0 of the FeatureMap attribute. All other bits SHALL be 0.
| Bit | Code | Name | Def | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
7 |
SN |
Scene Names |
0 |
The ability to store a name for a scene. |
1.4.7.6.
1.4.8.6.
LastConfiguredBy
Attribute
The
LastConfiguredBy
attribute
holds
the
Node
ID
(the
IEEE
address
in
case
of
Zigbee)
of
the
node
that
last
configured
the
Scene
Table.
The null value indicates that the server has not been configured, or that the identifier of the node that last configured the Scenes cluster is not known.
For nodes supporting fabrics, the Node ID is scoped to the accessing fabric.
1.4.8.
1.4.8.7.
SceneTableSize
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the number of entries in the Scene Table on this endpoint. For nodes supporting fabrics, this is the total across all fabrics; note that a single fabric cannot use all those entries (see Handling of fabric-scoping ). The minimum size of this table, (i.e., the minimum number of scenes to support across all fabrics per endpoint) SHALL be 16, unless a device type in which this cluster is used, defines a larger value in the device type definition.
1.4.8.8. FabricSceneInfo Attribute
This attribute indicates a list of fabric scoped information about scenes on this endpoint.
1.4.8.9. Logical Scene Table
The Scene Table is used to store information for each scene capable of being invoked on the server. Each scene is defined for a particular group. The Scene Table is defined here as a conceptual illustration to assist in understanding the underlying data to be stored when scenes are defined. Though the Scene Table is defined here using the data model architecture rules and format, the design is not normative.
The
fields
of
each
Scene
Table
entry
consist
of
table
is
logically
a
number
list
of
sets.
fabric-scoped
structs.
The
base
set
consists
of
the
first
four
logical
fields
of
Fields
of
a
each
Scene
Table
Entry
.
A
set
of
extension
fields
can
entry
struct
are
illustrated
below.
An
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
MAY
be
added
by
present
for
each
additional
Scenes-supporting
cluster
implemented
on
the
same
endpoint.
| Quality: Fabric-Scoped | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
0 | SceneGroupID |
group-id |
all |
|
|||
|
1 | SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
|
|||
|
2 | SceneName |
string |
|
|
|||
|
3 | SceneTransitionTime |
uint16 |
all |
| M |
||
|
|
|
|
| M |
|||
|
5 | TransitionTime100ms |
uint8 |
|
| M |
||
1.4.8.1.
Scene
Names
1.4.8.9.1.
SceneGroupID
Field
Scene
names
are
between
This
field
is
the
group
identifier
for
which
this
scene
applies,
or
0
and
16
bytes
long.
Support
of
if
the
scene
names
is
optional,
and
not
associated
with
a
group.
1.4.8.9.2. SceneID Field
This field is unique within this group, which is used to identify this scene.
1.4.8.9.3. SceneName Field
The
field
is
indicated
by
the
NameSupport
attribute.
name
of
the
scene.
If
scene
names
are
not
supported,
any
commands
that
write
a
scene
name
SHALL
simply
discard
the
name,
and
any
command
that
returns
a
scene
names
name
SHALL
return
an
empty
string.
Zigbee:
Note
older
implementations
before
revision
5
may
return
the
null
string.
1.4.8.2.
Maximum
Number
of
Scenes
1.4.8.9.4.
SceneTransitionTime
Field
The
number
of
scenes
capable
This
field
is
the
amount
of
being
stored
time,
in
seconds,
it
will
take
for
a
cluster
to
change
from
its
current
state
to
the
requested
state.
1.4.8.9.5. ExtensionFields Field
See
the
Scene
Table
is
defined
by
Extensions
subsections
of
individual
clusters.
A
Scene
Table
Extension
SHALL
only
use
attributes
with
the
profile
in
which
this
Scene
quality.
Each
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
holds
a
set
of
values
of
these
attributes
for
a
cluster
is
used.
The
default
maximum,
implemented
on
the
same
endpoint
where
the
Scene
("S")
designation
appears
in
the
absence
quality
column.
A
scene
is
the
aggregate
of
specification
by
all
such
fields
across
all
clusters
on
the
profile,
is
16.
endpoint.
1.4.9. Commands
The command IDs for the Scenes cluster are listed in the table below.
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
AddScene |
client ⇒ server |
AddSceneResponse |
M |
M |
|
0x01 |
ViewScene |
client ⇒ server |
ViewSceneResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x02 |
RemoveScene |
client ⇒ server |
RemoveSceneResponse |
M |
M |
|
0x03 |
RemoveAllScenes |
client ⇒ server |
RemoveAllScenesResponse |
M |
M |
|
0x04 |
StoreScene |
client ⇒ server |
StoreSceneResponse |
M |
M |
|
0x05 |
RecallScene |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x06 |
GetSceneMembership |
client ⇒ server |
GetSceneMembershipResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x40 |
EnhancedAddScene |
client ⇒ server |
EnhancedAddSceneResponse |
M |
O |
|
0x41 |
EnhancedViewScene |
client ⇒ server |
EnhancedViewSceneResponse |
O |
O |
|
0x42 |
CopyScene |
client ⇒ server |
CopySceneResponse |
M |
O |
|
0x00 |
AddSceneResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x01 |
ViewSceneResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x02 |
RemoveSceneResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x03 |
RemoveAllScenesResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x04 |
StoreSceneResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x06 |
GetSceneMembershipResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x40 |
EnhancedAddSceneResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
|
|
|
0x41 |
EnhancedViewSceneResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
|
|
|
0x42 |
CopySceneResponse |
server ⇒ client |
N |
|
1.4.9.1. Generic Usage Notes
Scene
identifier
0,
along
when
used
with
group
identifier
0,
is
reserved
for
the
global
scene
used
by
the
On/Off
cluster.
On receipt of the AddScene command, the SceneTransitionTime field of the Scene Table SHALL be updated with the value of the TransitionTime field and the TransitionTime100ms field SHALL be set to zero.
1.4.9.2. AddScene Command
The AddScene command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
|
M |
||
|
3 |
SceneName |
string |
max 16 |
M |
||
|
4 |
|
|
desc |
M |
It is not mandatory for an extension field set to be included in the command for every cluster on that endpoint that has a defined extension field set. Extension field sets MAY be omitted, including the case of no extension field sets at all.
1.4.9.2.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the AddScene command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step4.5. -
The server verifies that it has free entries in its Scene Table.If the ExtensionFieldSetStructs list is formatted in a way deemed invalid according to the ExtensionFieldSetStruct structure definition (see ExtensionFieldSetStruct Type ), then the status SHALL be INVALID_COMMAND in the AddSceneResponse, and the serverhas no further free entriescontinues from step 5. If a scene already exists under the same group/scene identifier pair, in
itsstep 4 the already existing scene entry SHALL be replaced with the new scene being added. Otherwise, if a scene cannot be created due to the lack of SceneTable,Table capacity for the given fabric, the status SHALL be RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED and the server continues from step4.5.-
The server adds the scene entry into its Scene Table with fields copied from the AddScene command data fields and the status SHALL be SUCCESS.
If there-
Any ExtensionFieldSetStruct referencing a ClusterID that is
alreadynot implemented on the endpoint MAY be omitted during processing. Any AttributeValuePairStruct referencing an AttributeID from the referenced cluster that is not implemented on the endpoint MAY be omitted during processing.
If the ExtensionFieldSetStructs list has multiple entries listing the same ClusterID, the last one within the list SHALL be the one recorded.
Within a
scene insingle entry of theScene Table withExtensionFieldSetStructs list, if the explicit form contains the samescene identifier and group identifier, itAttributeID more than once, the last one within the list SHALLoverwrite it.be the one recorded.
-
-
If the AddScene command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate an AddSceneResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the AddScene command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate an AddSceneResponse command.
See AddSceneResponse Command for a description of the AddSceneResponse command.
1.4.9.3. ViewScene Command
The ViewScene command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
1.4.9.3.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the ViewScene command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step 4. -
The server verifies that the scene entry corresponding to the GroupID and SceneID fields exists in its Scene Table. If there is no such entry in its Scene Table, the status SHALL be NOT_FOUND and the server continues from step 4.
-
The server retrieves the requested scene entry from its Scene Table and the status SHALL be SUCCESS.
-
If the ViewScene command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate a ViewSceneResponse command with the retrieved scene entry and the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the ViewScene command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate a ViewSceneResponse command.
Note: For the explicit form of ExtensionFieldSetStructs, the order of attributes within the ExtensionFieldSetStruct MAY differ in implementation-defined ways from any potential order given in a prior AddScene or EnhancedAddScene.
See ViewSceneResponse Command for a description of the ViewSceneResponse command.
1.4.9.4. RemoveScene Command
The RemoveScene command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
1.4.9.4.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the RemoveScene command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step 4. -
The server verifies that the scene entry corresponding to the GroupID and SceneID fields exists in its Scene Table. If there is no such entry in its Scene Table, the status SHALL be NOT_FOUND and the server continues from step 4.
-
The server removes the requested scene entry from its Scene Table and the status SHALL be SUCCESS.
-
If the RemoveScene command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate a RemoveSceneResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the RemoveScene command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate a RemoveSceneResponse command.
See RemoveSceneResponse Command for a description of the RemoveSceneResponse command.
1.4.9.5. RemoveAllScenes Command
The RemoveAllScenes command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
1.4.9.5.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the RemoveAllScenes command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step 3. -
The server SHALL remove all scenes, corresponding to the value of the GroupID field, from its Scene Table and the status SHALL be SUCCESS.
-
If the RemoveAllScenes command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate a RemoveAllScenesResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the RemoveAllScenes command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate a RemoveAllScenesResponse command.
See RemoveAllScenesResponse Command for a description of the RemoveAllScenesResponse command.
1.4.9.6. StoreScene Command
The StoreScene command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
1.4.9.6.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the StoreScene command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step 4. -
The server verifies that it has free entries in its Scene Table.If a scene already exists under theserver has no further free entriessame group/scene identifier pair, initsstep 3 the already existing scene entry SHALL be used to store the current state.
If a scene cannot be created due to the lack of SceneTable,Table capacity for the given fabric, the status SHALL be RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED and the server continues from step 4. -
The server addsIf a scene already exists under the same group/scene identifier pair, the ExtensionFieldSets of the stored sceneentry into its Scene Table alongSHALL be replaced withall extension field setsthe ExtensionFieldSets corresponding to the current state of other clusters on the same endpoint andwiththeSceneTransitionTime and SceneNameother fieldsset to 0 andof theempty string, respectively. If there is already ascenein the Scene Table with the same SceneID and GroupID, ittable entry SHALLoverwrite it, i.e., itremain unchanged.
Otherwise, a new entry SHALLfirst remove all information included inbe added to theoriginalsceneentry except fortable, using the provided GroupID and SceneID, with SceneTransitionTime and TransitionTime100ms set to 0, with SceneNamefields, which are left unaltered.set to the empty string, and with ExtensionFieldSets corresponding to the current state of other clusters on the same endpoint.
The status SHALL be SUCCESS. -
If the StoreScene command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate a StoreSceneResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status.
If the StoreScene command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate a StoreSceneResponse command.
Note that if a scene to be stored requires a TransitionTime field and/or a SceneName field, these must be set up by a prior AddScene command, e.g., with no scene extension field sets.
See StoreSceneResponse Command for a description of the StoreSceneResponse command.
1.4.9.7. RecallScene Command
The RecallScene command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
|
X |
O |
1.4.9.7.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the RecallScene command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step 4. -
The server verifies that the scene entry corresponding to the GroupID and SceneID fields exists in its Scene Table. If there is no such entry in its Scene Table, the status SHALL be NOT_FOUND and the server continues from step 4.
-
The server retrieves the requested scene entry from its Scene Table. For each other cluster implemented on the endpoint, it SHALL retrieve any corresponding extension
fieldsfield sets from the Scene Table and set the attributes and corresponding state of the cluster accordingly. If there is no extension field set for a cluster, the state of that cluster SHALL remain unchanged. If an extension field set omits the values of anytrailingattributes, the values of these attributes SHALL remain unchanged. If an extension field set would cause an unknown or missing attribute to be set for any reason, that attribute SHALL be skipped. The status SHALL be SUCCESS. -
The server SHALL then generate a response with the Status field set to the evaluated status.
If
the
TransitionTime
data
field
is
present
in
the
command
and
its
value
is
not
equal
to
null,
this
field
SHALL
indicate
the
transition
time
in
1/10ths
of
a
second.
In
all
other
cases
(command
data
field
not
present
or
value
equal
to
null),
the
SceneTransitionTime
field
of
the
Scene
Table
entry
SHALL
indicate
the
transition
time.
The
transition
time
determines
how
long
the
transition
takes
from
the
old
cluster
state
to
the
new
cluster
state.
It
is
recommended
that,
where
possible
(e.g.,
it
is
not
possible
for
attributes
with
Boolean
data
type),
a
gradual
transition
SHOULD
take
place
from
the
old
to
the
new
state
over
this
time.
However,
the
exact
transition
algorithm
is
manufacturer
dependent.
implementation-defined.
1.4.9.8. GetSceneMembership Command
The
GetSceneMembership
command
can
be
used
to
find
an
unused
scene
identifier
within
a
certain
group
when
no
commissioning
tool
is
in
the
network,
or
for
a
commissioning
tool
to
get
the
used
scene
identifiers
within
a
certain
group,
for
the
endpoint
that
implements
this
cluster.
The GetSceneMembership command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
1.4.9.8.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the GetSceneMembership command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step2.3.The status SHALL be SUCCESS.
-
If the GetSceneMembership command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate a GetSceneMembershipResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the GetSceneMembership command was not received as a unicast, the server SHALL only generate a GetSceneMembershipResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status if an entry within the Scene Table corresponds to the GroupID.
See GetSceneMembershipResponse Command for a description of the GetSceneMembershipResponse command.
1.4.9.9. EnhancedAddScene Command
The EnhancedAddScene command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | GroupID | group-id | all | M | ||
1 | SceneID | uint8 | all | M | ||
2 | TransitionTime | uint16 | max 60000 | M | ||
3 | SceneName | string | max 16 | M | ||
4 | ExtensionFieldSetStructs | list[ExtensionFieldSetStruct] | desc | M |
The EnhancedAddScene command allows a scene to be added using a finer scene transition time than the AddScene command.
This
The
meaning
of
the
data
fields
for
this
command
SHALL
have
be
the
same
data
fields
as
for
the
AddScene
command,
with
the
following
difference:
The TransitionTime data field SHALL be measured in tenths of a second rather than in seconds.
1.4.9.9.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the EnhancedAddScene command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step4.5. -
The server verifies that it has free entries in its Scene Table.If the ExtensionFieldSetStructs list is formatted in a way deemed invalid according to the ExtensionFieldSetStruct structure definition (see ExtensionFieldSetStruct Type ), then the status SHALL be INVALID_COMMAND in the AddSceneResponse, and the serverhas no further free entriescontinues from step 5. If a scene already exists under the same group/scene identifier pair, in
itsstep 4 the already existing scene entry SHALL be replaced with the new scene being added. Otherwise, if a scene cannot be created due to the lack of SceneTable,Table capacity for the given fabric, the status SHALL be RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED and the server continues from step4.5.-
The server adds the scene entry into its Scene Table with fields copied from the
EnhancedAddSceneAddScene command data fields and the status SHALL be SUCCESS.If there is already a scene in the Scene Table with the same SceneID and GroupID, it SHALL overwrite it, i.e., it SHALL first remove all information included in the original scene entry.The TransitionTime field (measured in tenths of a second) SHALL be separated into whole seconds for the SceneTransitionTime field and tenths of a second for the TransitionTime100ms field of the Scene Table entry, as specified.-
Any ExtensionFieldSetStruct referencing a ClusterID that is not implemented on the endpoint MAY be omitted during processing.
Any AttributeValuePairStruct referencing an AttributeID from the referenced cluster that is not implemented on the endpoint MAY be omitted during processing.
If the ExtensionFieldSetStructs list has multiple entries listing the same ClusterID, the last one within the list SHALL be the one recorded.
Within a single entry of the ExtensionFieldSetStructs list, if the explicit form contains the same AttributeID more than once, the last one within the list SHALL be the one recorded.
-
-
If the EnhancedAddScene command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate an EnhancedAddSceneResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the EnhancedAddScene command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate an EnhancedAddSceneResponse command.
See EnhancedAddSceneResponse Command for a description of the EnhancedAddSceneResponse command.
1.4.9.10. EnhancedViewScene Command
The EnhancedViewScene command allows a scene to be retrieved using a finer scene transition time than the ViewScene command.
This command SHALL have the same data fields as the ViewScene command.
1.4.9.10.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the EnhancedViewScene command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of the GroupID field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for that GroupID in the Group Table. If there is no such entry in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step 4. -
The server verifies that the scene entry corresponding to the GroupID and SceneID fields exists in its Scene Table. If there is no such entry in its Scene Table, the status SHALL be NOT_FOUND and the server continues from step 4.
-
The server retrieves the requested scene entry from its Scene Table and the status SHALL be SUCCESS.
-
If the EnhancedViewScene command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate an EnhancedViewSceneResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the EnhancedViewScene command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate an EnhancedViewSceneResponse command.
Note: For the explicit form of ExtensionFieldSetStructs, the order of attributes within the ExtensionFieldSetStruct MAY differ in implementation-defined ways from any potential order given in a prior AddScene or EnhancedAddScene.
See EnhancedViewSceneResponse Command for a description of the EnhancedViewSceneResponse command.
1.4.9.11. CopyScene Command
The CopyScene command allows a client to efficiently copy scenes from one group/scene identifier pair to another group/scene identifier pair.
The CopyScene command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Mode |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupIdentifierFrom |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
SceneIdentifierFrom |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
3 |
GroupIdentifierTo |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
4 |
SceneIdentifierTo |
uint8 |
all |
M |
1.4.9.11.1. Mode Field
The
Mode
field
contains
information
of
how
the
scene
copy
is
to
proceed.
This
field
SHALL
be
formatted
as
illustrated
in
Format
of
the
Mode
Field
of
the
CopyScene
Command
.
The
CopyAllScenes
subfield
is
1-bit
in
length
and
bit
of
the
Mode
indicates
whether
all
scenes
are
to
be
copied.
If
this
value
is
set
to
1,
all
scenes
are
to
be
copied
and
the
SceneIdentifierFrom
and
SceneIdentifierTo
fields
SHALL
be
ignored.
Otherwise
this
field
bit
is
set
to
0.
1.4.9.11.2. GroupIdentifierFrom Field
The GroupIdentifierFrom field specifies the identifier of the group from which the scene is to be copied. Together with the SceneIdentifierFrom field, this field uniquely identifies the scene to copy from the Scene Table.
1.4.9.11.3. SceneIdentifierFrom Field
The SceneIdentifierFrom field specifies the identifier of the scene from which the scene is to be copied. Together with the GroupIdentifierFrom field, this field uniquely identifies the scene to copy from the Scene Table.
1.4.9.11.4. GroupIdentifierTo Field
The GroupIdentifierTo field specifies the identifier of the group to which the scene is to be copied. Together with the SceneIdentifierTo field, this field uniquely identifies the scene to copy to the Scene Table.
1.4.9.11.5. SceneIdentifierTo Field
The SceneIdentifierTo field specifies the identifier of the scene to which the scene is to be copied. Together with the GroupIdentifierTo field, this field uniquely identifies the scene to copy to the Scene Table.
1.4.9.11.6. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the CopyScene command, the server SHALL perform the following procedure:
-
If the value of either the GroupIdentifierFrom field or the Group Identifier To field is non-zero, the server verifies that the endpoint has an entry for these non-zero group identifiers in the Group Table. If there are no such entries in the Group Table, the status SHALL be
ILLEGAL_COMMANDINVALID_COMMAND and the server continues from step 5. -
TheIf the CopyAllScenes sub-field of the Mode field is set to 0, the server verifies that the scene entry corresponding to theGroup Identifier FromGroupIdentifierFrom and SceneIdentifierFrom fields exists in its Scene Table. If there is no such entry in its Scene Table, the status SHALL be NOT_FOUND and the server continues from step 5. -
If the CopyAllScenes sub-field of the Mode field is set to
1 or the scene entry corresponding to the GroupIdentifierTo and SceneIdentifierTo fields does not exist in the Scene Table and if the server has no further free entries in its Scene Table, the status SHALL be RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED and the server continues from step 5. The status SHALL be SUCCESS. If the CopyAllScenes sub-field of the Mode field is set to1, the server SHALL copy all its available scenes with group identifier equal to the GroupIdentifierFrom field under the group identifier specified in the GroupIdentifierTo field, leaving the scene identifiers the same. In this case, the SceneIdentifierFrom and SceneIdentifierTo fieldsareSHALL be ignored.
If the CopyAllScenes sub-field of the Mode field is set to 0, the server SHALL copy the Scene Table entry corresponding to the GroupIdentifierFrom and SceneIdentifierFrom fields to the Scene Table entry corresponding to the GroupIdentifierTo and SceneIdentifierTo fields.If
Regardless of the value of the CopyAllScenes subfield, if a scene already exists under the same group/scene identifier pair, it SHALL beoverwritten.replaced with the scene being copied.
Regardless of the value of the CopyAllScenes subfield, if a scene cannot be copied due to the lack of Scene Table capacity for the given fabric, the status SHALL be RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED and the server continues from step 5. In this case, scenes already copied SHALL be kept. The status SHALL be SUCCESS.
-
If the CopyScene command was received as a unicast, the server SHALL then generate a CopySceneResponse command with the Status field set to the evaluated status. If the CopyScene command was received as a groupcast, the server SHALL NOT generate
ana CopySceneResponse command.
See CopySceneResponse Command for a description of the CopySceneResponse command.
1.4.9.12. AddSceneResponse Command
The AddSceneResponse command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
1.4.9.12.1. When Generated
This command is generated in response to a received AddScene command, see AddScene Command . The Status field is set according to the Effect on Receipt section for AddScene. The GroupID and SceneID fields are set to the corresponding fields of the received AddScene command.
1.4.9.13. ViewSceneResponse Command
The ViewSceneResponse command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
3 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
|
desc |
||
|
4 |
SceneName |
string |
max 16 |
desc |
||
|
5 |
|
|
desc |
1.4.9.13.1. When Generated
This command is generated in response to a received ViewScene command, see ViewScene Command .
The entry in the Scene Table with SceneID and GroupID given in the received ViewScene command is located (if possible). The Status field is set according to the Effect on Receipt section for ViewScene. The GroupID and SceneID fields are set to the corresponding fields in the received ViewScene command.
If
the
status
is
SUCCESS,
the
TransitionTime,
SceneName
and
ExtensionFieldSets
ExtensionFieldSetStructs
fields
are
copied
from
the
corresponding
fields
in
the
Scene
Table
entry,
otherwise
they
are
omitted.
1.4.9.14. RemoveSceneResponse Command
The RemoveSceneResponse command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
1.4.9.14.1. When Generated
This command is generated in response to a received RemoveScene command, see RemoveScene Command . The Status field is set according to the Effect on Receipt section for RemoveScene. The GroupID and SceneID fields are set to the corresponding fields of the received RemoveScene command.
1.4.9.15. RemoveAllScenesResponse Command
The RemoveAllScenesResponse command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
1.4.9.15.1. When Generated
This command is generated in response to a received RemoveAllScenes command, see RemoveAllScenes Command . The Status field is according to the Effect on Receipt section for RemoveAllScenes. The GroupID field is set to the corresponding field of the received RemoveAllScenes command.
1.4.9.16. StoreSceneResponse Command
The StoreSceneResponse command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
SceneID |
uint8 |
all |
M |
1.4.9.16.1. When Generated
This
command
is
generated
in
response
to
a
received
StoreScene
command,
see
StoreScene
Command
.
The
Status
field
is
set
to
SUCCESS,
RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED
or
ILLEGAL_COMMAND
INVALID_COMMAND
(the
endpoint
is
not
a
member
of
the
group)
as
appropriate.
The
GroupID
and
SceneID
fields
are
set
to
the
corresponding
fields
of
the
received
StoreScene
command.
1.4.9.17. GetSceneMembershipResponse Command
The GetSceneMembershipResponse command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Capacity |
uint8 |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
2 |
GroupID |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
3 |
SceneList |
list[uint8] |
|
The fields of the get scene membership response command have the following semantics:
The Capacity field SHALL contain the remaining capacity of the Scene Table of the server (for all groups). The following values apply:
-
0 - No further scenes MAY be added.
-
0 < Capacity <
0xfe0xFE - Capacity holds the number of scenes that MAY be added. -
0xfe0xFE - At least 1 further scene MAY be added (exact number is unknown). -
null - It is unknown if any further scenes MAY be added.
The
Status
field
SHALL
contain
SUCCESS
or
ILLEGAL_COMMAND
INVALID_COMMAND
(the
endpoint
is
not
a
member
of
the
group)
as
appropriate.
The GroupID field SHALL be set to the corresponding field of the received GetSceneMembership command.
If
the
status
is
not
SUCCESS
then
the
SceneList
field
SHALL
be
omitted,
else
the
SceneList
field
SHALL
contain
the
identifiers
of
all
the
scenes
in
the
Scene
Table
with
the
corresponding
Group
ID.
Zigbee:
If
the
total
number
of
scenes
associated
with
this
Group
ID
will
cause
the
maximum
payload
length
of
a
frame
to
be
exceeded,
then
the
SceneList
field
SHALL
contain
only
as
many
scenes
as
will
fit.
1.4.9.17.1. When Generated
This command is generated in response to a received GetSceneMembership command, see GetSceneMembership Command .
1.4.9.18. EnhancedAddSceneResponse Command
The EnhancedAddSceneResponse command allows a server to respond to an EnhancedAddScene command, see EnhancedAddScene Command .
This command SHALL have the same data fields as the AddSceneResponse command.
1.4.9.19. EnhancedViewSceneResponse Command
The EnhancedViewSceneResponse command allows a server to respond to an EnhancedViewScene command using a finer scene transition time.
This
The
EnhancedViewSceneResponse
command
SHALL
have
the
same
data
fields
as
the
ViewSceneResponse
command,
with
the
following
difference:
data
fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Status | status | desc | M | ||
1 | GroupID | group-id | all | M | ||
2 | SceneID | uint8 | all | M | ||
3 | TransitionTime | uint16 | max 60000 | desc | ||
4 | SceneName | string | max 16 | desc | ||
5 | ExtensionFieldSetStructs | list[ExtensionFieldSetStruct] | desc |
The
TransitionTime
field
meaning
of
the
data
fields
for
this
command
SHALL
be
measured
in
tenths
the
same
as
for
the
ViewSceneResponse
command,
except
that
the
resolution
of
TransitionTime
is
1/10ths
of
a
second
rather
than
in
seconds.
second.
1.4.9.19.1. When Generated
The
EnhancedViewSceneResponse
command
is
generated
in
response
to
a
received
EnhancedViewScene
command.
The
entry
in
the
Scene
Table
with
scene
identifier
and
group
identifier
given
in
the
received
EnhancedViewScene
command
is
located
(if
possible).
The
Status
field
is
set
to
SUCCESS,
CONSTRAINT_ERROR
(the
group
identifier
is
not
in
range),
NOT_FOUND
(the
scene
is
not
present
in
the
Scene
Table)
or
ILLEGAL_COMMAND
INVALID_COMMAND
(the
endpoint
is
not
a
member
of
the
group)
as
appropriate.
The
GroupID
and
SceneID
fields
are
set
to
the
corresponding
fields
in
the
received
EnhancedViewScene
command.
If
the
status
is
SUCCESS,
the
TransitionTime,
SceneName
and
ExtensionFieldSets
fields
are
copied
from
the
corresponding
ExtensionFieldSetStructs
fields
in
the
Scene
Table
entry,
SHALL
be
present,
otherwise
they
are
omitted.
The
If
present,
the
TransitionTime
field
(measured
in
tenths
of
a
second)
SHALL
be
calculated
from
the
SceneTransitionTime
field
(measured
in
seconds)
and
the
TransitionTime100ms
field
of
the
Scene
Table
entry,
as
specified.
and
the
SceneName
and
ExtensionFieldSetStructs
fields
SHALL
be
copied
from
the
corresponding
fields
of
the
Scene
Table
entry.
1.4.9.20. CopySceneResponse Command
The CopySceneResponse command allows a server to respond to a CopyScene command.
The CopySceneResponse command SHALL have the following data fields:
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
GroupIdentifierFrom |
group-id |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
SceneIdentifierFrom |
uint8 |
all |
M |
1.4.9.20.1.
Status
field
The
Status
field
contains
the
status
of
the
copy
scene
attempt.
This
field
SHALL
be
set
to
one
of
the
non-reserved
values
listed
in
Values
of
the
Status
Field
of
the
CopySceneResponse
Command
.
Table
11.
Values
of
the
Status
Field
of
the
CopySceneResponse
Command
Status
Field
Value
Description
SUCCESS
Success
ILLEGAL_COMMAND
Invalid
scene
specified
RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED
Insufficient
space
in
the
Scene
Table
1.4.9.20.2.
GroupIdentifierFrom
Field
The
GroupIdentifierFrom
field
specifies
the
identifier
of
the
group
from
which
the
scene
was
copied,
as
specified
in
the
CopyScene
command.
Together
with
the
SceneIdentifierFrom
field,
this
field
uniquely
identifies
the
scene
that
was
copied
from
the
Scene
Table.
1.4.9.20.3.
SceneIdentifierFrom
Field
The
SceneIdentifierFrom
field
is
specifies
the
identifier
of
the
scene
from
which
the
scene
was
copied,
as
specified
in
the
CopyScene
command.
Together
with
the
GroupIdentifierFrom
field,
this
field
uniquely
identifies
the
scene
that
was
copied
from
the
Scene
Table.
1.4.9.20.4.
When
Generated
The
CopySceneResponse
command
is
generated
in
response
to
a
received
CopyScene
command,
see
CopyScene
Command
.
If,
during
the
copy,
there
is
no
more
space
in
the
Scene
Table
for
the
entire
next
scene
to
be
copied,
the
Status
field
SHALL
be
set
to
RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED
and
the
scenes
already
copied
SHALL
be
kept.
If
either
the
GroupIdentifierFrom
field
or
the
GroupIdentifierTo
field
are
not
in
the
correct
range,
the
Status
field
SHALL
be
set
to
CONSTRAINT_ERROR.
If
the
GroupIdentifierFrom
and
SceneIdentifierFrom
fields
do
not
specify
a
scene
that
exists
in
the
Scene
Table,
the
The
Status
field
SHALL
be
is
set
according
to
ILLEGAL_COMMAND.
Otherwise,
if
the
copy
was
successful,
Effect
on
Receipt
section
for
the
Status
field
SHALL
be
set
to
SUCCESS.
CopyScene
command.
The
GroupIdentifierFrom
and
SceneIdentifierFrom
fields
SHALL
be
set
to
the
same
values
as
in
the
corresponding
fields
of
the
received
CopyScene
command.
1.5. On/Off Cluster
Attributes and commands for turning devices on and off.
1.5.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
ZLO 1.0: StartUpOnOff |
|
3 |
FeatureMap global attribute support with Level Control and Lighting feature |
|
4 |
|
|
5 | Addition of Dead Front behavior and associated FeatureMap entry |
1.5.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
|
1.5.4. Features
This
cluster
SHALL
support
the
FeatureMap
global
attribute.
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
| Bit | Code | Feature |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
LT |
|
Behavior that supports lighting applications. |
|
1 | DF | DeadFrontBehaviour | Device has Dead Front behavior |
1.5.4.1.
Level
Control
for
Lighting
Feature
This cluster is used for a lighting application.
On receipt of a Level Control cluster command that causes the OnOff attribute to be set to FALSE, the OnTime attribute SHALL be set to 0.
On receipt of a Level Control cluster command that causes the OnOff attribute to be set to TRUE, if the value of the OnTime attribute is equal to 0, the server SHALL set the OffWaitTime attribute to 0.
1.5.4.2. DeadFrontBehaviour Feature
When this feature is supported, the device exposing this server cluster exhibits "dead front" behavior when the "OnOff" attribute is FALSE (Off). This "dead front" behavior includes:
clusters other than this cluster that are also exposed MAY respond with failures to Invoke and Write interactions. Such failure responses when in a "dead front" SHALL be with an INVALID_IN_STATE status code.
clusters other than this cluster MAY change the values of their attributes to best-effort values, due to the actual values not being defined or available in this state. Device type specifications that require support for the DF feature SHOULD define what these best-effort values are.
Report Transactions SHALL continue to be generated. Such transactions MAY include best-effort values as noted above.
Event generation logic for clusters other than this cluster is unchanged (noting possible use of best-effort attribute values as in the preceding bullets).
When this feature is supported and the OnOff attribute changes from TRUE to FALSE (e.g. when receiving an Off Command, or due to a manual interaction on the device), it SHALL start executing this "dead front" behavior.
When this feature is supported and the OnOff attribute changes from FALSE to TRUE (e.g. when receiving an On Command, or due to a manual interaction on the device), it SHALL stop executing this "dead front" behavior.
When this feature is supported, and any change of the "dead front" state leads to changes in attributes of other clusters due to the "dead front" feature, these attribute changes SHALL NOT be skipped or omitted from the usual processing associated with attribute changes. For example, if an attribute changes from value 4 to null on "dead front" behavior due to an Off command being received, this change SHALL be processed for reporting and subscriptions.
1.5.5. Data Types
1.5.5.1.
StartUpOnOffEnum
OnOffControlBitmap
Type
The
This
data
type
StartUpOnOffEnum
is
derived
from
enum8.
The
values
of
the
StartUpOnOffEnum
data
type
are
listed
below.
map8.
|
|
Name |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
Indicates a command is only accepted when in On state. | M |
1.5.5.2. StartUpOnOffEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Off |
Set the OnOff attribute to FALSE |
M |
|
1 |
On |
|
M |
|
2 |
Toggle |
|
M |
1.5.5.3. EffectIdentifierEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 | DelayedAllOff | Delayed All Off | M |
0x01 | DyingLight | Dying Light | M |
1.5.6.
Attributes
1.5.5.4.
DelayedAllOffEffectVariantEnum
Type
The
server
supports
the
attributes
shown
This
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
0x00 | DelayedOffFastFade |
Fade
to
off
in
| M |
0x01 | NoFade | No fade | M |
0x02 | DelayedOffSlowFade |
50% dim down in 0.8 seconds then fade to off in 12 seconds | M |
1.5.6.
Attributes
of
the
On/Off
Server
Cluster
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
OnOff |
bool |
all |
SN |
FALSE |
R V |
M |
|
0x4000 |
GlobalSceneControl |
bool |
all |
TRUE |
R V |
LT |
|
|
0x4001 |
OnTime |
uint16 |
all |
|
0 |
RW VO |
LT |
|
0x4002 |
OffWaitTime |
uint16 |
all |
|
0 |
RW VO |
LT |
|
0x4003 |
StartUpOnOff |
desc |
XN |
MS |
RW VM |
LT |
1.5.6.1. Scene Table Extensions
If
the
Scenes
server
cluster
is
implemented
on
the
same
endpoint,
the
following
extension
field
attribute
SHALL
be
added
to
part
of
the
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
of
the
Scene
Table:
Table.
-
OnOff
1.5.6.1.
1.5.6.2.
OnOff
Attribute
The
OnOff
This
attribute
indicates
whether
the
device
type
implemented
on
the
endpoint
is
turned
off
or
turned
on,
in
these
cases
the
value
of
the
OnOff
attribute
equals
FALSE,
or
TRUE
respectively.
1.5.6.2.
1.5.6.3.
GlobalSceneControl
Attribute
In order to support the use case where the user gets back the last setting of a set of devices (e.g. level settings for lights), a global scene is introduced which is stored when the devices are turned off and recalled when the devices are turned on. The global scene is defined as the scene that is stored with group identifier 0 and scene identifier 0.
The
GlobalSceneControl
This
attribute
is
defined
in
order
to
prevent
a
second
Off
command
storing
the
all-devices-off
situation
as
a
global
scene,
and
to
prevent
a
second
On
command
destroying
the
current
settings
by
going
back
to
the
global
scene.
The
GlobalSceneControl
This
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
TRUE
after
the
reception
of
a
command
which
causes
the
OnOff
attribute
to
be
set
to
TRUE,
such
as
a
standard
On
command,
a
MoveToLevel(WithOnOff)
command,
a
RecallScene
command
or
a
OnWithRecallGlobalScene
command
(see
OnWithRecallGlobalScene
Command
).
command.
The
GlobalSceneControl
This
attribute
is
set
to
FALSE
after
reception
of
a
OffWithEffect
command.
These concepts are illustrated in Explanation of the Behavior of Store and Recall Global Scene functionality using a State Diagram .

1.5.6.3.
1.5.6.4.
OnTime
Attribute
The
OnTime
This
attribute
specifies
the
length
of
time
(in
1/10ths
second)
that
the
‘On’
On
state
SHALL
be
maintained
before
automatically
transitioning
to
the
‘Off’
Off
state
when
using
the
OnWithTimedOff
command.
This
attribute
can
be
written
at
any
time,
but
writing
a
value
only
has
effect
when
in
the
‘Timed
On’
Timed
On
state.
See
OnWithTimedOff
Command
for
more
details.
1.5.6.4.
1.5.6.5.
OffWaitTime
Attribute
The
OffWaitTime
This
attribute
specifies
the
length
of
time
(in
1/10ths
second)
that
the
‘Off’
Off
state
SHALL
be
guarded
to
prevent
another
OnWithTimedOff
command
turning
the
server
back
to
its
‘On’
On
state
(e.g.,
when
leaving
a
room,
the
lights
are
turned
off
but
an
occupancy
sensor
detects
the
leaving
person
and
attempts
to
turn
the
lights
back
on).
This
attribute
can
be
written
at
any
time,
but
writing
a
value
only
has
an
effect
when
in
the
‘Timed
On’
Timed
On
state
followed
by
a
transition
to
the
‘Delayed
Off'
Delayed
Off
state,
or
in
the
‘Delayed
Off’
Delayed
Off
state.
See
OnWithTimedOff
Command
for
more
details.
1.5.6.5.
1.5.6.6.
StartUpOnOff
Attribute
The
StartUpOnOff
This
attribute
SHALL
define
the
desired
startup
behavior
of
a
device
when
it
is
supplied
with
power
and
this
state
SHALL
be
reflected
in
the
OnOff
attribute.
If
the
value
is
null,
the
OnOff
attribute
is
set
to
its
previous
value.
Otherwise,
the
behavior
is
defined
in
the
table
defining
StartUpOnOffEnum
.
This
behavior
does
not
apply
to
reboots
associated
with
OTA.
After
an
OTA
restart,
the
OnOff
attribute
shall
SHALL
return
to
its
value
prior
to
the
restart.
1.5.7. Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
Off |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
On |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x02 |
Toggle |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x40 |
OffWithEffect |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
LT |
|
0x41 |
OnWithRecallGlobalScene |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
LT |
|
0x42 |
OnWithTimedOff |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
LT |
1.5.7.3. Toggle Command
1.5.7.3.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the Toggle command, if the value of the OnOff attribute is equal to FALSE, the server SHALL set the OnOff attribute to TRUE, otherwise, the server SHALL set the OnOff attribute to FALSE.
Additionally, when the OnTime and OffWaitTime attributes are both supported, if the value of the OnOff attribute is equal to FALSE and if the value of the OnTime attribute is equal to 0, the server SHALL set the OffWaitTime attribute to 0. If the value of the OnOff attribute is equal to TRUE, the server SHALL set the OnTime attribute to 0.
1.5.7.4. OffWithEffect Command
The OffWithEffect command allows devices to be turned off using enhanced ways of fading.
The OffWithEffect command SHALL have the following data fields:
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
EffectIdentifier |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
EffectVariant |
|
desc |
0 |
M |
1.5.7.4.1. EffectIdentifier Field
The
EffectIdentifier
This
field
specifies
the
fading
effect
to
use
when
turning
the
device
off.
This
field
SHALL
contain
one
of
the
non-reserved
values
listed
in
Values
of
the
EffectIdentifier
Field
of
the
OffWithEffect
Command
EffectIdentifierEnum
.
1.5.7.4.2. EffectVariant Field
The
EffectVariant
This
field
is
used
to
indicate
which
variant
of
the
effect,
indicated
in
the
EffectIdentifier
field,
SHOULD
be
triggered.
If
the
server
does
not
support
the
given
variant,
it
SHALL
use
the
default
variant.
This
field
is
dependent
on
the
value
of
the
EffectIdentifier
field
and
SHALL
contain
one
of
the
non-reserved
values
listed
in
Values
of
the
EffectVariant
Field
of
the
OffWithEffect
Command
either
DelayedAllOffEffectVariantEnum
or
DyingLightEffectVariantEnum
.
1.5.7.4.3. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the OffWithEffect command the server SHALL check the value of the GlobalSceneControl attribute.
If the GlobalSceneControl attribute is equal to TRUE, the server SHALL store its settings in its global scene then set the GlobalSceneControl attribute to FALSE, then set the OnOff attribute to FALSE and if the OnTime attribute is supported set the OnTime attribute to 0.
If the GlobalSceneControl attribute is equal to FALSE, the server SHALL only set the OnOff attribute to FALSE.
1.5.7.5. OnWithRecallGlobalScene Command
The
OnWithRecallGlobalScene
This
command
allows
the
recall
of
the
settings
when
the
device
was
turned
off.
1.5.7.5.1. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of the OnWithRecallGlobalScene command, if the GlobalSceneControl attribute is equal to TRUE, the server SHALL discard the command.
If the GlobalSceneControl attribute is equal to FALSE, the Scene cluster server on the same endpoint SHALL recall its global scene, updating the OnOff attribute accordingly. The OnOff server SHALL then set the GlobalSceneControl attribute to TRUE.
Additionally, when the OnTime and OffWaitTime attributes are both supported, if the value of the OnTime attribute is equal to 0, the server SHALL set the OffWaitTime attribute to 0.
1.5.7.6. OnWithTimedOff Command
The
OnWithTimedOff
This
command
allows
devices
to
be
turned
on
for
a
specific
duration
with
a
guarded
off
duration
so
that
SHOULD
the
device
be
subsequently
turned
off,
further
OnWithTimedOff
commands,
received
during
this
time,
are
prevented
from
turning
the
devices
back
on.
Further
OnWithTimedOff
commands
received
while
the
server
is
turned
on,
will
update
the
period
that
the
device
is
turned
on.
The OnWithTimedOff command SHALL have the following data fields:
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
OnOffControl |
|
|
M |
||
|
1 |
OnTime |
uint16 |
|
|
M |
|
|
2 |
OffWaitTime |
uint16 |
|
|
M |
1.5.7.6.1. OnOffControl Field
The
OnOffControl
This
field
contains
information
on
how
the
server
is
to
be
operated.
This
field
SHALL
be
formatted
as
illustrated
in
Format
of
the
OnOffControl
Field
of
the
OnWithTimedOff
Command
.
The
AcceptOnlyWhenOn
sub-field
is
1
This
bit
in
length
and
specifies
whether
the
OnWithTimedOff
command
is
to
be
processed
unconditionally
or
only
when
the
OnOff
attribute
is
equal
to
TRUE.
If
this
sub-field
is
set
to
1,
the
OnWithTimedOff
command
SHALL
only
be
accepted
if
the
OnOff
attribute
is
equal
to
TRUE.
If
this
sub-field
is
set
to
0,
the
OnWithTimedOff
command
SHALL
be
processed
unconditionally.
1.5.7.6.3. OffWaitTime Field
The
OffWaitTime
This
field
is
used
to
adjust
the
value
of
the
OffWaitTime
attribute.
1.5.7.6.4. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, if the AcceptOnlyWhenOn sub-field of the OnOffControl field is set to 1, and the value of the OnOff attribute is equal to FALSE, the command SHALL be discarded.
If the value of the OffWaitTime attribute is greater than zero and the value of the OnOff attribute is equal to FALSE, then the server SHALL set the OffWaitTime attribute to the minimum of the OffWaitTime attribute and the value specified in the OffWaitTime field.
In all other cases, the server SHALL set the OnTime attribute to the maximum of the OnTime attribute and the value specified in the OnTime field, set the OffWaitTime attribute to the value specified in the OffWaitTime field and set the OnOff attribute to TRUE.
If
the
values
of
the
OnTime
and
OffWaitTime
attributes
are
both
not
equal
to
null,
0xFFFF,
the
server
SHALL
then
update
these
attributes
every
1/10
th
second
until
both
the
OnTime
and
OffWaitTime
attributes
are
equal
to
0,
as
follows:
-
If the value of the OnOff attribute is equal to TRUE and the value of the OnTime attribute is greater than zero, the server SHALL decrement the value of the OnTime attribute. If the value of the OnTime attribute reaches 0, the server SHALL set the OffWaitTime and OnOff attributes to 0 and FALSE, respectively.
-
If the value of the OnOff attribute is equal to FALSE and the value of the OffWaitTime attribute is greater than zero, the server SHALL decrement the value of the OffWaitTime attribute. If the value of the OffWaitTime attribute reaches 0, the server SHALL terminate the update.
1.5.8. State Description
The
operation
of
the
On/Off
cluster
with
respect
to
the
On,
Off,
and
OnWithTimedOff
commands
is
illustrated
in
On/Off
Cluster
Operation
State
Machine
.
In
this
diagram,
the
values
X
and
Y
correspond
to
the
OnTime
and
OffWaitTime
fields,
respectively,
of
the
OnWithTimedOff
command.
In
the
‘Timed
On’
Timed
On
state,
the
OnTime
attribute
is
decremented
every
1/10
th
second,
unless
its
value
equals
null.
0xFFFF.
Similarly,
in
the
‘Delayed
Off’
Delayed
Off
state,
the
OffWaitTime
attribute
is
decremented
every
1/10
th
second,
unless
its
value
equals
null.
0xFFFF.

1.6. Level Control Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for controlling a characteristic of a device that can be set to a level, for example the brightness of a light, the degree of closure of a door, or the power output of a heater.
1.6.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
CCB 2574 2616 2659 2702 2814 2818 2819 2898 |
|
4 |
FeatureMap support with On/Off, Lighting and Frequency features |
|
5 |
|
1.6.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
|
1.6.3.
Cluster
Identifiers
ID
Derived cluster specifications are defined elsewhere. This base cluster specification MAY be used for generic level control; however, it is recommended to derive another cluster to better define the application and domain requirements. If one of more derived cluster identifiers and the base identifier exists on a device endpoint, then they SHALL all represent a single instance of the device level control.
|
|
Hierarchy | Name |
|---|---|---|
|
0x0008 |
Base |
Level
|
|
|
Derived |
Pulse Width Modulation |
|
Note
|
Pulse Width Modulation cluster is provisional. |
1.6.4. Features
This
cluster
SHALL
support
the
FeatureMap
global
attribute:
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
| Bit | Code |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
OO |
|
1 |
Dependency with the On/Off cluster |
|
1 |
LT |
Lighting |
0 |
Behavior that supports lighting applications |
|
2 |
FQ |
Frequency |
0 |
Supports frequency attributes and behavior. The Pulse Width Modulation cluster was created for frequency control. |
The following sections describe each feature in some detail. Further details are found within the specification.
1.6.4.1. On/Off Feature
For many applications, a close relationship between this cluster and the On/Off cluster is needed. This section describes the dependencies that are required when an endpoint that implements this server cluster and also implements the On/Off server cluster. Before the On/Off feature bit in the FeatureMap existed, there was a dependency between this cluster and the On/Off cluster.
The OnOff attribute of the On/Off cluster and the CurrentLevel attribute of the Level Control cluster are intrinsically independent variables, as they are on different clusters. However, when both clusters are implemented on the same endpoint, dependencies MAY be introduced between them. Facilities are provided to introduce dependencies if required.
1.6.4.1.1. Effect of On/Off Commands on the CurrentLevel Attribute
The
attribute
OnLevel
(see
OnLevel
Attribute
)
attribute
determines
whether
commands
of
the
On/Off
cluster
have
a
permanent
effect
on
the
CurrentLevel
attribute
or
not.
If
this
attribute
is
defined
(i.e.,
implemented
and
not
equal
to
null)
they
do
have
a
permanent
effect,
otherwise
they
do
not.
There
is
always
a
temporary
effect,
due
to
fading
up
/
down.
The
effect
on
the
Level
Control
cluster
on
receipt
of
the
various
commands
of
the
On/Off
cluster
are
as
detailed
in
Actions
on
Receipt
for
the
Effect
of
On/Off
Commands,
Commands
when
Associated
associated
with
Level
Control
.
table.
In
this
table,
and
throughout
this
cluster
specification,
'level'
means
the
value
of
the
CurrentLevel
attribute.
| Command | Action On Receipt |
|---|---|
|
On |
Temporarily
store
CurrentLevel.
|
|
Off |
Temporarily
store
CurrentLevel.
|
|
Toggle |
If the OnOff attribute has the value FALSE, proceed as for the On command. Otherwise proceed as for the Off command. |
Intention of the actions described in the table above is that CurrentLevel, which was in effect before any of the On, Off or Toggle commands were issued, SHALL be restored, after the transition is completed. If another of these commands is received, before the transition is completed, the originally stored CurrentLevel SHALL be preserved and restored.
1.6.4.1.2. Effect of Level Control Commands on the OnOff Attribute
There are two sets of commands provided in the Level Control cluster. These are identical, except that the first set (MoveToLevel, Move and Step commands) SHALL NOT affect the OnOff attribute, whereas the second set ('with On/Off' variants) SHALL.
The first set is used to maintain independence between the CurrentLevel and OnOff attributes, so changing CurrentLevel has no effect on the OnOff attribute. As examples, this represents the behavior of a volume control with a separate mute button, or a 'turn to set level and press to turn on/off' light dimmer.
The second set is used to link the CurrentLevel and OnOff attributes. When the level is reduced to its minimum the OnOff attribute is automatically turned to FALSE, and when the level is increased above its minimum the OnOff attribute is automatically turned to TRUE. As an example, this represents the behavior of a light dimmer with no independent on/off switch.
For the Stop command, the StopWithOnOff is included solely for symmetry, to allow easy choice of one or other set of commands – both Stop commands are identical, because the dependency on On/Off is determined by the original command that is being stopped.
1.6.4.1.3. Effect of Level Control Commands Depends on OnOff
Before the Options attribute was introduced, all commands except those postfixed with ‘with On/Off’, had no effect if the OnOff attribute of the On/Off cluster, on the same endpoint, was FALSE. Even if the On/Off (OO) feature set bit is set to zero, this is still true. To allow such commands to function, please see the Options attribute below.
1.6.4.1.4. GlobalSceneControl and Commands with On/Off
If
a
MoveToLevel(WithOnOff),
Move(WithOnOff)
or
Step(WithOnOff)
command
is
received
that
causes
a
change
to
the
value
of
the
OnOff
attribute
of
the
On/Off
cluster,
the
value
of
the
GlobalSceneControl
attribute
of
the
On/Off
cluster
SHALL
be
updated
according
to
section
GlobalSceneControl
Attribute
.
1.6.4.2. Lighting Feature
This feature supports an interface for controlling the level of a light source.
For the CurrentLevel attribute:
-
A value of 0x00 SHALL NOT be used.
-
A value of 0x01 SHALL indicate the minimum level that can be attained on a device.
-
A value of
0xfe0xFE SHALL indicate the maximum level that can be attained on a device. -
A value of null SHALL represent an undefined value.
-
All other values are application specific gradations from the minimum to the maximum level.
1.6.5.
Attributes
Data
Types
1.6.5.1. OptionsBitmap Type
The
attributes
of
the
Level
This
data
type
is
derived
from
map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | ExecuteIfOff | Dependency on On/Off cluster | LT | OO |
1 | CoupleColorTempToLevel |
Dependency
on
Color
Control
|
LT |
1.6.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
CurrentLevel |
uint8 |
MinLevel to MaxLevel |
SNX |
null |
R V |
M |
|
0x0001 |
RemainingTime |
uint16 |
all |
0 |
R V |
LT |
|
|
0x0002 |
MinLevel |
uint8 |
1
to
MaxLevel
|
1 |
R V | [LT] | |
0x0002 | MinLevel | uint8 | 0 to MaxLevel |
0
|
R V |
|
|
|
0x0003 |
MaxLevel |
uint8 |
MinLevel to 254 |
254 |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0004 |
CurrentFrequency |
uint16 |
MinFrequency to MaxFrequency |
PS |
0 |
R V |
FQ |
|
0x0005 |
MinFrequency |
uint16 |
0 to MaxFrequency |
0 |
R V |
FQ |
|
|
0x0006 |
MaxFrequency |
uint16 |
MinFrequency to max |
0 |
R V |
FQ |
|
|
0x0010 |
OnOffTransitionTime |
uint16 |
all |
0 |
RW VO |
O |
|
|
0x0011 |
OnLevel |
uint8 |
MinLevel to MaxLevel |
X |
null |
RW VO |
M |
|
0x0012 |
OnTransitionTime |
uint16 |
all |
X |
null |
RW VO |
O |
|
0x0013 |
OffTransitionTime |
uint16 |
all |
X |
null |
RW VO |
O |
|
0x0014 |
DefaultMoveRate |
uint8 |
all |
X |
MS |
RW VO |
O |
|
0x000F |
Options |
|
desc |
0 |
RW VO |
M |
|
|
0x4000 |
StartUpCurrentLevel |
uint8 |
desc |
XN |
MS |
RW VM |
LT |
1.6.6.1. Scene Table Extensions
If
the
Scenes
server
cluster
is
implemented
on
the
same
endpoint,
the
following
extension
fields
attributes
SHALL
be
added
to
part
of
the
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
of
the
Scene
Table
Table.
If
the
implicit
form
of
the
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
is
used,
the
order
of
the
attributes
in
the
AttributeValueList
is
in
the
given
order,
i.e.,
the
attribute
listed
as
1
is
added
first:
-
CurrentLevel
-
CurrentFrequency
Attributes in the scene table that are not supported by the device (according to the FeatureMap attribute) SHALL be present in the scene table but ignored.
OnLevel represents a mandatory field that was previously not present or optional. Implementers should be aware that older devices may not implement it.
1.6.5.1.
1.6.6.2.
CurrentLevel
Attribute
The CurrentLevel attribute represents the current level of this device. The meaning of 'level' is device dependent.
1.6.5.2.
1.6.6.3.
RemainingTime
Attribute
The RemainingTime attribute represents the time remaining until the current command is complete - it is specified in 1/10ths of a second.
1.6.5.3.
1.6.6.4.
MinLevel
Attribute
The MinLevel attribute indicates the minimum value of CurrentLevel that is capable of being assigned.
1.6.5.4.
1.6.6.5.
MaxLevel
Attribute
The MaxLevel attribute indicates the maximum value of CurrentLevel that is capable of being assigned.
1.6.5.5.
1.6.6.6.
CurrentFrequency
Attribute
The CurrentFrequency attribute represents the frequency at which the device is at CurrentLevel. A CurrentFrequency of 0 is unknown.
1.6.5.6.
1.6.6.7.
MinFrequency
Attribute
The MinFrequency attribute indicates the minimum value of CurrentFrequency that is capable of being assigned. MinFrequency SHALL be less than or equal to MaxFrequency. A value of 0 indicates undefined.
1.6.5.7.
1.6.6.8.
MaxFrequency
Attribute
The MaxFrequency attribute indicates the maximum value of CurrentFrequency that is capable of being assigned. MaxFrequency SHALL be greater than or equal to MinFrequency. A value of 0 indicates undefined.
1.6.5.8.
1.6.6.9.
Options
Attribute
The Options attribute is meant to be changed only during commissioning. The Options attribute is a bitmap that determines the default behavior of some cluster commands. Each command that is dependent on the Options attribute SHALL first construct a temporary Options bitmap that is in effect during the command processing. The temporary Options bitmap has the same format and meaning as the Options attribute, but includes any bits that may be overridden by command fields.
Below
is
the
format
and
description
of
the
Options
attribute
and
temporary
Options
bitmap
and
the
effect
on
dependent
commands.
Table
19.
Options
Attribute
Bit
Name
Summary
Description
Conformance
0
ExecuteIfOff
Dependency
on
On/Off
cluster
LT
|
OO
1
CoupleColorTempToLevel
Dependency
on
Color
Control
cluster
LT
1.6.5.8.1.
ExecuteIfOff
Options
Bit
Command
execution
SHALL
NOT
continue
beyond
the
Options
processing
if
all
of
these
criteria
are
true:
-
The command is one of the ‘without On/Off’ commands: Move, Move to Level, Step, or Stop.
-
The On/Off cluster exists on the same endpoint as this cluster.
-
The OnOff attribute of the On/Off cluster, on this endpoint, is FALSE.
-
The value of the ExecuteIfOff bit is 0.
1.6.5.8.2.
CoupleColorTempToLevel
Options
1.6.6.9.1.
ExecuteIfOff
Bit
Valid
values
are:
0
-
Do
not
couple
changes
to
If
this
bit
is
set,
commands
in
this
cluster
are
executed
and
potentially
change
the
CurrentLevel
attribute
with
when
the
color
temperature.
OnOff
attribute
of
the
On/Off
cluster
is
FALSE.
1.6.5.9.
1.6.6.10.
OnOffTransitionTime
Attribute
The OnOffTransitionTime attribute represents the time taken to move to or from the target level when On or Off commands are received by an On/Off cluster on the same endpoint. It is specified in 1/10ths of a second.
The actual time taken SHOULD be as close to OnOffTransitionTime as the device is able. Please note that if the device is not able to move at a variable rate, the OnOffTransitionTime attribute SHOULD NOT be implemented.
1.6.5.10.
1.6.6.11.
OnLevel
Attribute
The OnLevel attribute determines the value that the CurrentLevel attribute is set to when the OnOff attribute of an On/Off cluster on the same endpoint is set to TRUE, as a result of processing an On/Off cluster command. If the OnLevel attribute is not implemented, or is set to the null value, it has no effect. For more details see Effect of On/Off Commands on the CurrentLevel Attribute .
1.6.5.11.
1.6.6.12.
OnTransitionTime
Attribute
The OnTransitionTime attribute represents the time taken to move the current level from the minimum level to the maximum level when an On command is received by an On/Off cluster on the same endpoint. It is specified in 10ths of a second. If this attribute is not implemented, or contains a null value, the OnOffTransitionTime will be used instead.
1.6.5.12.
1.6.6.13.
OffTransitionTime
Attribute
The OffTransitionTime attribute represents the time taken to move the current level from the maximum level to the minimum level when an Off command is received by an On/Off cluster on the same endpoint. It is specified in 10ths of a second. If this attribute is not implemented, or contains a null value, the OnOffTransitionTime will be used instead.
1.6.5.13.
1.6.6.14.
DefaultMoveRate
Attribute
The DefaultMoveRate attribute determines the movement rate, in units per second, when a Move command is received with a null value Rate parameter.
1.6.5.14.
1.6.6.15.
StartUpCurrentLevel
Attribute
The StartUpCurrentLevel attribute SHALL define the desired startup level for a device when it is supplied with power and this level SHALL be reflected in the CurrentLevel attribute. The values of the StartUpCurrentLevel attribute are listed below:
| Value | Action on power up |
|---|---|
|
|
Set the CurrentLevel attribute to the minimum value permitted on the device |
|
null |
Set the CurrentLevel attribute to its previous value |
|
other values |
Set the CurrentLevel attribute to this value |
This behavior does not apply to reboots associated with OTA. After an OTA restart, the CurrentLevel attribute SHALL return to its value prior to the restart.
1.6.6.
1.6.7.
Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
MoveToLevel |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
Move |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x02 |
Step |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x03 |
Stop |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x04 |
MoveToLevelWithOnOff |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x05 |
MoveWithOnOff |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x06 |
StepWithOnOff |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x07 |
StopWithOnOff |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x08 |
MoveToClosestFrequency |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
FQ |
1.6.6.1.
1.6.7.1.
MoveToLevel
Command
The
MoveToLevel
This
command
SHALL
have
the
following
data
fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Level |
uint8 |
0 to 254 |
M |
||
|
1 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
2 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsOverride |
|
desc |
0 |
M |
1.6.6.1.1.
1.6.7.1.1.
Effect
on
Receipt
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL both be present. Default values are provided to interpret missing fields from legacy devices. A temporary Options bitmap SHALL be created from the Options attribute, using the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields. Each bit of the temporary Options bitmap SHALL be determined as follows:
Each bit in the Options attribute SHALL determine the corresponding bit in the temporary Options bitmap, unless the OptionsMask field is present and has the corresponding bit set to 1, in which case the corresponding bit in the OptionsOverride field SHALL determine the corresponding bit in the temporary Options bitmap.
The
resulting
temporary
Options
bitmap
SHALL
then
be
processed
as
defined
in
section
the
Options
Attribute
.
attribute.
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL move from its current level to the value given in the Level field. The meaning of ‘level’ is device dependent – e.g., for a light it MAY mean brightness level.
The movement SHALL be as continuous as technically practical, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new level SHALL be equal to the value of the TransitionTime field, in tenths of a second, or as close to this as the device is able.
If the TransitionTime field takes the value null then the time taken to move to the new level SHALL instead be determined by the OnOffTransitionTime attribute. If OnOffTransitionTime, which is an optional attribute, is not present, the device SHALL move to its new level as fast as it is able.
If the device is not able to move at a variable rate, the TransitionTime field MAY be disregarded.
1.6.6.2.
1.6.7.2.
Move
Command
The Move command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
MoveMode |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Rate |
uint8 |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
2 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsOverride |
|
desc |
0 |
M |
1.6.6.2.1.
1.6.7.2.1.
MoveMode
Field
The
MoveMode
This
field
SHALL
be
one
of
the
non-reserved
values
in
Values
of
the
MoveMode
Field
MoveModeEnum
.
1.6.6.2.2.
1.6.7.2.2.
Rate
Field
The
Rate
This
field
specifies
the
rate
of
movement
in
units
per
second.
The
actual
rate
of
movement
SHOULD
be
as
close
to
this
rate
as
the
device
is
able.
If
the
Rate
field
is
equal
to
null,
then
the
value
in
DefaultMoveRate
attribute
SHALL
be
used.
However,
if
the
Rate
field
is
equal
to
null
and
the
DefaultMoveRate
attribute
is
not
supported,
or
if
the
Rate
field
is
equal
to
null
and
the
value
of
the
DefaultMoveRate
attribute
is
equal
to
null,
then
the
device
SHOULD
move
as
fast
as
it
is
able.
If
the
device
is
not
able
to
move
at
a
variable
rate,
this
field
MAY
be
disregarded.
1.6.6.2.3.
1.6.7.2.3.
Effect
on
Receipt
On
receipt
of
this
command,
a
device
SHALL
first
create
and
process
a
temporary
Options
bitmap
as
described
in
section
Effect
on
Receipt
.
the
MoveToLevel
command.
On
receipt
of
this
command,
a
device
SHALL
move
from
its
current
level
in
an
up
or
down
direction
in
a
continuous
fashion,
as
detailed
in
Actions
on
Receipt
for
Move
Command
.
below.
| MoveMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Up |
Increase the device’s level at the rate given in the Rate field. If the level reaches the maximum allowed for the device, stop. |
|
Down |
Decrease the device’s level at the rate given in the Rate field. If the level reaches the minimum allowed for the device, stop. |
1.6.6.3.
1.6.7.3.
Step
Command
The Step command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
StepMode |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
StepSize |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
|
desc |
0 |
M |
1.6.7.3.1. StepMode Field
The
StepMode
This
field
SHALL
be
one
of
the
non-reserved
values
in
Values
of
the
StepMode
Field
MoveModeEnum
.
0x01
1.6.7.3.2.
StepSize
Field
This field SHALL indicate the change to CurrentLevel.
Down
1.6.7.3.3.
TransitionTime
Field
The
TransitionTime
This
field
specifies
the
time
that
SHALL
be
taken
to
perform
the
step,
in
tenths
of
a
second.
A
step
is
a
change
in
the
CurrentLevel
of
StepSize
units.
The
actual
time
taken
SHOULD
be
as
close
to
this
as
the
device
is
able.
If
the
TransitionTime
field
is
equal
to
null,
the
device
SHOULD
move
as
fast
as
it
is
able.
If the device is not able to move at a variable rate, the TransitionTime field MAY be disregarded.
1.6.6.3.1.
1.6.7.3.4.
Effect
on
Receipt
On
receipt
of
this
command,
a
device
SHALL
first
create
and
process
a
temporary
Options
bitmap
as
described
in
section
Effect
on
Receipt
.
the
MoveToLevel
command.
On
receipt
of
this
command,
a
device
SHALL
move
from
its
current
level
in
an
up
or
down
direction
as
detailed
in
Actions
on
Receipt
for
Step
Command
.
below.
| StepMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Up |
Increase CurrentLevel by StepSize units, or until it reaches the maximum level allowed for the device if this reached in the process. In the latter case, the transition time SHALL be proportionally reduced. |
|
Down |
Decrease CurrentLevel by StepSize units, or until it reaches the minimum level allowed for the device if this reached in the process. In the latter case, the transition time SHALL be proportionally reduced. |
1.6.6.4.
1.6.7.4.
Stop
Command
The Stop command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
1 |
OptionsOverride |
|
desc |
0 |
M |
1.6.6.4.1.
1.6.7.4.1.
Effect
of
Receipt
On
receipt
of
this
command,
a
device
SHALL
first
create
and
process
a
temporary
Options
bitmap
as
described
in
section
Effect
on
Receipt
.
the
MoveToLevel
command.
Upon receipt of this command, any MoveToLevel, Move or Step command (and their 'with On/Off' variants) currently in process SHALL be terminated. The value of CurrentLevel SHALL be left at its value upon receipt of the Stop command, and RemainingTime SHALL be set to zero.
This
command
has
two
entries
in
Command
IDs
for
the
Level
Control
Cluster
,
Commands
list,
one
for
the
MoveToLevel,
Move
and
Step
commands,
and
one
for
their
'with
On/Off'
counterparts.
This
is
solely
for
symmetry,
to
allow
easy
choice
of
one
or
other
set
of
commands
–
the
Stop
commands
are
identical,
because
the
dependency
on
On/Off
is
determined
by
the
original
command
that
is
being
stopped.
1.6.6.5.
1.6.7.5.
MoveToClosestFrequency
Command
The MoveToClosestFrequency command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Frequency |
uint16 |
all |
0 |
M |
1.6.6.5.1.
1.6.7.5.1.
Effect
of
Receipt
Upon receipt of this command, the device SHALL change its current frequency to the requested frequency, or to the closest frequency that it can generate. If the device cannot approximate the frequency, then it SHALL return a default response with an error code of CONSTRAINT_ERROR. Determining if a requested frequency can be approximated by a supported frequency is a manufacturer-specific decision.
1.6.6.6.
1.6.7.6.
'With
On/Off'
Commands
The MoveToLevelWithOnOff, MoveWithOnOff and StepWithOnOff commands have identical data fields compared to the MoveToLevel, Move and Step commands respectively. They also have the same effects, except for the following additions.
Before commencing any command that has the effect of setting the CurrentLevel attribute above the minimum level allowed by the device, the OnOff attribute of the On/Off cluster on the same endpoint, if implemented, SHALL be set to TRUE (‘On’).
If
any
command
that
has
the
effect
of
setting
the
CurrentLevel
attribute
to
the
minimum
level
allowed
by
the
device,
the
OnOff
attribute
of
the
On/Off
cluster
on
the
same
endpoint,
if
implemented,
SHALL
be
set
to
to
FALSE
(‘Off’).
The StopWithOnOff command has identical data fields compared to the Stop command. Both Stop commands are identical, because the dependency on On/Off is determined by the original command that is being stopped.
1.6.7.
1.6.8.
State
Change
Table
for
Lighting
Below is a table of examples of state changes when Level Control and On/Off clusters are on the same endpoint and the Lighting feature is set.
-
EiO - ExecuteIfOff field in the Options attribute
-
OnOff –
attributeAttribute value of On/Off cluster: FALSE=‘Off’, TRUE=‘On’ -
MIN - MinLevel
-
MAX - MaxLevel
-
MID –
midpointMidpoint between MinLevel and MaxLevel
1.6.8.1. Lighting Device State Change examples
| CurrentLevel | EiO | OnOff | Physical Device |
Command
Before After |
CurrentLevel | OnOff | Physical Device |
Device
Output
Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
any |
0 |
FALSE |
Off |
MoveToLevel(l= MID , t=2 sec) |
same |
FALSE |
Off |
|
|
any |
0 |
FALSE |
Off |
MoveToLevelWithOnOff(l= MID , t=2 sec |
MID |
TRUE |
On (mid-point brightness) |
|
|
any |
1 |
FALSE |
Off |
MoveToLevel(l= MID , t=2 sec) |
MID |
FALSE |
Off |
|
|
any |
1 |
FALSE |
Off |
MoveToLevelWithOnOff(l= MID , t=2 sec) |
MID |
TRUE |
On |
|
|
any |
1 |
FALSE |
Off |
Move(up, rate=64/s) |
MAX |
FALSE |
Off |
|
|
any |
1 |
FALSE |
Off |
MoveWithOnOff(up, rate=64/s) |
MAX |
TRUE |
On |
|
|
any |
1 |
FALSE |
Off |
MoveWithOnOff(down, rate=64/s) |
MIN |
FALSE |
Off |
|
|
any |
any |
TRUE |
On (any brightness) |
MoveToLevelWithOnOff(l= MID , t=2 sec) |
MID |
TRUE |
On (mid-point brightness) |
|
|
any |
any |
TRUE |
On (any brightness) |
MoveWithOnOff(up, rate=64/s) |
MAX |
TRUE |
On (full brightness) |
|
|
any |
any |
TRUE |
On (any brightness) |
Move(down, rate=64/s) |
MIN |
TRUE |
On (at minimum brightness) |
|
|
any |
any |
TRUE |
On (any brightness) |
MoveWithOnOff(down, rate=64/s) |
MIN |
FALSE |
Off |
|
1.7. Boolean State Cluster
This
cluster
provides
an
interface
to
a
boolean
state
called
StateValue.
state.
1.7.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial release |
1.7.3.
Cluster
Identifiers
ID
| ID | Name |
|---|---|
|
0x0045 |
Boolean State |
1.7.4. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
StateValue |
bool |
P |
R V |
M |
1.8. Mode Select Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for controlling a characteristic of a device that can be set to one of several predefined values. For example, the light pattern of a disco ball, the mode of a massage chair, or the wash cycle of a laundry machine.
The server allows the client to set a mode on the server. A mode is one of a list of options that may be presented by a client for a user choice, or understood by the client, via the semantic tags on the mode.
A semantic tag is either a standard tag within a standard category namespace, or a manufacturer specific tag, within the namespace of the vendor ID of the manufacturer. If there is no semantic tag, the mode is anonymous, and the selection is made by the user solely based on the Label string.
Each cluster ID that indicates this specification SHALL define a distinct purpose for the cluster instance. For example: A LightBlinking cluster ID supports blinking modes for a light (and is described that way).
An anonymous mode SHALL support the derived cluster purpose. A manufacturer specific semantic tag SHALL support the derived cluster purpose. An anonymous mode SHALL NOT replace the meaning of a standard semantic tag, when one exists, for the cluster purpose.
1.8.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial version |
|
2 | The MfgCode field was marked non-nullable. Updated the related text. Reorder sections. |
1.8.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
|
1.8.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap global attribute:
| ID | Code |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
DEPONOFF |
|
Dependency
with
the
|
1.8.4.1.
On/Off
OnOff
Feature
This
feature
creates
a
dependency
between
an
On/Off
OnOff
cluster
instance
and
this
cluster
instance
on
the
same
endpoint.
See
OnMode
Attribute
for
more
information.
1.8.5. Data Types
1.8.5.1. ModeOptionStruct
This is a struct representing a possible mode of the server.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Label | string | max 64 | F | MS | R | M |
1 | Mode | uint8 | F | MS | R | M | |
2 | SemanticTags | list[ SemanticTagStruct ] | max 64 | F | MS | R | M |
1.8.5.1.1. Label Field
This field is readable text that describes the mode option that can be used by a client to indicate to the user what this option means. This field is meant to be readable and understandable by the user.
1.8.5.1.2. Mode Field
The Mode field is used to identify the mode option. The value SHALL be unique for every item in the SupportedModes attribute.
1.8.5.1.3. SemanticTags Field
This field is a list of semantic tags that map to the mode option. This MAY be used by clients to determine the meaning of the mode option as defined in a standard or manufacturer specific namespace. Semantic tags can help clients look for options that meet certain criteria. A semantic tag SHALL be either a standard tag or manufacturer specific tag as defined in each SemanticTagStruct list entry.
A mode option MAY have more than one semantic tag. A mode option MAY be mapped to a mixture of standard and manufacturer specific semantic tags.
All standard semantic tags are from a single namespace indicated by the StandardNamespace attribute.
For
example:
A
mode
labeled
"100%"
can
have
both
the
HIGH
(MS)
and
MAX
(standard)
semantic
tag.
Clients
seeking
the
option
for
either
HIGH
or
MAX
will
find
the
same
option
in
this
case.
1.8.5.2. SemanticTagStruct
A Semantic Tag is meant to be interpreted by the client for the purpose the cluster serves.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | MfgCode | vendor-id | desc | F | R | M | |
1 | Value | enum16 | all | F | R | M |
1.8.5.2.1. Value Field
This field SHALL indicate the semantic tag within a semantic tag namespace which is either manufacturer specific or standard. For semantic tags in a standard namespace, see Standard Namespace .
1.8.5.2.2. MfgCode Field
This field SHALL indicate a manufacturer code (Vendor ID), and the Value field SHALL indicate a semantic tag defined by the manufacturer. Each manufacturer code supports a single namespace of values. The same manufacturer code and semantic tag value in separate cluster instances are part of the same namespace and have the same meaning. For example: a manufacturer tag meaning "pinch", has the same meaning in a cluster whose purpose is to choose the amount of sugar, or amount of salt.
1.8.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
Description |
string |
max 64 |
F |
MS |
R V |
M |
|
0x0001 |
StandardNamespace |
enum16 |
desc |
FX |
null |
R V |
M |
|
0x0002 |
SupportedModes |
list[ ModeOptionStruct ] |
max 255 |
F |
MS |
R V |
M |
|
0x0003 |
CurrentMode |
uint8 |
desc |
SN |
MS |
R V |
M |
|
0x0004 |
StartUpMode |
uint8 |
desc |
NX |
MS |
RW VO |
O |
|
0x0005 |
OnMode |
uint8 |
desc |
NX |
null |
RW VO |
DEPONOFF |
1.8.6.1. Scene Table Extensions
If
the
Scenes
server
cluster
is
implemented
on
the
same
endpoint,
the
following
extension
field
attribute
SHALL
be
added
to
part
of
the
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
of
the
Scene
Table:
Table.
-
CurrentMode
1.8.5.1.
1.8.6.2.
Description
Attribute
This attribute describes the purpose of the server, in readable text.
For
example,
a
coffee
machine
may
have
a
Mode
Select
cluster
for
the
amount
of
milk
to
add,
and
another
Mode
Select
cluster
for
the
amount
of
sugar
to
add.
In
this
case,
the
first
instance
can
have
the
description
Milk
and
the
second
instance
can
have
the
description
Sugar
.
This
allows
the
user
to
tell
the
purpose
of
each
of
the
instances.
1.8.5.2.
1.8.6.3.
StandardNamespace
Attribute
This attribute, when not null, SHALL indicate a single standard namespace for any standard semantic tag value supported in this or any other cluster instance with the same value of this attribute. A null value indicates no standard namespace, and therefore, no standard semantic tags are provided in this cluster instance. Each standard namespace and corresponding values and value meanings SHALL be defined in another document.
1.8.5.3.
1.8.6.4.
SupportedModes
Attribute
This attribute is the list of supported modes that may be selected for the CurrentMode attribute. Each item in this list represents a unique mode as indicated by the Mode field of the ModeOptionStruct. Each entry in this list SHALL have a unique value for the Mode field.
1.8.5.4.
1.8.6.5.
CurrentMode
Attribute
This attribute represents the current mode of the server.
The
value
of
this
field
must
match
the
Mode
field
of
one
of
the
entries
in
the
SupportedModes
attribute.
1.8.5.5.
1.8.6.6.
StartUpMode
Attribute
The StartUpMode attribute value indicates the desired startup mode for the server when it is supplied with power.
If
this
attribute
is
not
null,
the
CurrentMode
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
the
StartUpMode
value,
when
the
server
is
powered
up,
except
in
the
case
when
the
OnMode
attribute
overrides
the
StartUpMode
attribute
.
(see
OnModeWithPowerUp
).
This behavior does not apply to reboots associated with OTA. After an OTA restart, the CurrentMode attribute SHALL return to its value prior to the restart.
The
value
of
this
field
SHALL
match
the
Mode
field
of
one
of
the
entries
in
the
SupportedModes
attribute.
If this attribute is not implemented, or is set to the null value, it SHALL have no effect.
1.8.5.6.
1.8.6.7.
OnMode
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the value of CurrentMode that depends on the state of the On/Off cluster on the same endpoint. If this attribute is not present or is set to null, it SHALL NOT have an effect, otherwise the CurrentMode attribute SHALL depend on the OnOff attribute of the On/Off cluster as described in the table below:
| OnOff Change | CurrentMode Change |
|---|---|
|
ON → OFF |
No change |
|
OFF → ON |
Change CurrentMode to OnMode |
|
OFF → OFF |
No change |
|
ON → ON |
No change |
The value of this field SHALL match the Mode field of one of the entries in the SupportedModes attribute.
1.8.5.6.1.
1.8.6.7.1.
OnMode
with
Power
Up
If the On/Off feature is supported and the On/Off cluster attribute StartUpOnOff is present, with a value of On (turn on at power up), then the CurrentMode attribute SHALL be set to the OnMode attribute value when the server is supplied with power, except if the OnMode attribute is null.
1.8.6.
1.8.7.
Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
ChangeToMode |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
1.8.6.1.
1.8.7.1.
ChangeToMode
Command
On
receipt
of
this
command,
if
the
NewMode
field
matches
the
Mode
field
in
an
entry
of
indicates
a
valid
mode
transition
within
the
SupportedModes
supported
list,
the
server
SHALL
set
the
CurrentMode
attribute
to
the
NewMode
value,
otherwise,
the
server
SHALL
respond
with
an
INVALID_COMMAND
status
response.
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NewMode |
uint8 |
desc |
M |
1.9. Mode Base Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for controlling a characteristic of a device that can be set to one of several predefined values. For example, the light pattern of a disco ball, the mode of a massage chair, or the wash cycle of a laundry machine.
The server allows the client to set a mode on the server. A mode is one of a list of options that may be presented by a client for a user choice, or understood by the client, via the mode’s tags.
A mode tag is either a standard tag within a standard category namespace, or a manufacturer specific tag, within the namespace of the vendor ID of the manufacturer. If there are no mode tags for the mode or none that are known to the client, the mode is anonymous, and the selection by the user can be made solely based on the Label string.
Any derived cluster specification based on this cluster SHALL support the standard mode tag value definitions and command status definitions defined in this cluster and MAY define additional standard mode tag values and standard command status values that are supported in the respective derived cluster instances.
Each cluster ID that indicates this specification SHALL define a distinct purpose for the cluster instance. For example: A LightBlinking cluster ID supports blinking modes for a light (and is described that way).
An anonymous mode SHALL NOT replace the meaning of a standard mode tag, when one exists, for the cluster purpose.
1.8.7.
Events
1.9.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial version |
1.9.4. Features
This
cluster
has
no
events.
SHALL
support
the
FeatureMap
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | DEPONOFF | OnOff | Dependency with the OnOff cluster |
1.9.4.1. OnOff Feature
This feature creates a dependency between an OnOff cluster instance and this cluster instance on the same endpoint. See OnMode for more information.
1.8.8.
1.9.5.
Data
Types
1.8.8.1.
1.9.5.1.
ModeTagStruct
Type
A Mode Tag is meant to be interpreted by the client for the purpose the cluster serves.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | MfgCode | vendor-id | desc | R | O | ||
1 | Value | enum16 | all | R | M |
1.9.5.1.1. MfgCode Field
If the MfgCode field exists, the Value field SHALL be in the manufacturer-specific value range (see Mode Namespace ).
This field SHALL indicate the manufacturer’s VendorID and it SHALL determine the meaning of the Value field.
The same manufacturer code and mode tag value in separate cluster instances are part of the same namespace and have the same meaning. For example: a manufacturer tag meaning "pinch" can be used both in a cluster whose purpose is to choose the amount of sugar, or in a cluster whose purpose is to choose the amount of salt.
1.9.5.2. ModeOptionStruct Type
This is a struct representing a possible mode of the server.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality |
|
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Label |
string |
max 64 |
F |
|
|
M |
|
1 |
Mode |
uint8 |
F |
|
|
M |
|
|
2 |
|
list[
|
max
|
F |
|
|
M |
1.8.8.1.1.
1.9.5.2.1.
Label
Field
This
field
is
SHALL
indicate
readable
text
that
describes
the
mode
option
option,
so
that
can
be
used
by
a
client
to
indicate
can
provide
it
to
the
user
to
indicate
what
this
option
means.
This
field
is
meant
to
be
readable
and
understandable
by
the
user.
1.8.8.1.2.
1.9.5.2.2.
Mode
Field
The
Mode
This
field
is
used
to
identify
the
mode
option.
The
value
SHALL
be
unique
for
every
item
in
the
SupportedModes
attribute.
1.8.8.1.3.
SemanticTags
1.9.5.2.3.
ModeTags
Field
This
field
is
SHALL
contain
a
list
of
semantic
tags
that
map
to
are
associated
with
the
mode
option.
This
MAY
be
used
by
clients
to
determine
the
meaning
of
full
or
the
partial
semantics
of
a
certain
mode,
depending
on
which
tags
they
understand,
using
standard
definitions
and/or
manufacturer
specific
namespace
definitions.
The
standard
mode
option
as
tags
are
defined
in
this
cluster
specification.
For
the
derived
cluster
instances,
if
the
specification
of
the
derived
cluster
defines
a
namespace,
the
set
of
standard
or
manufacturer
specific
mode
tags
also
includes
the
mode
tag
values
from
that
namespace.
Semantic
Mode
tags
can
help
clients
look
for
options
that
meet
certain
criteria.
criteria,
render
the
user
interface,
use
the
mode
in
an
automation,
or
to
craft
help
text
their
voice-driven
interfaces.
A
semantic
mode
tag
SHALL
be
either
a
standard
tag
or
a
manufacturer
specific
tag
tag,
as
defined
in
each
SemanticTagStruct
ModeTagStruct
list
entry.
A
mode
option
MAY
have
more
than
one
semantic
mode
tag.
A
mode
option
MAY
be
mapped
to
associated
with
a
mixture
of
standard
and
manufacturer
specific
semantic
mode
tags.
All
standard
semantic
tags
A
few
examples
are
from
a
single
namespace
indicated
by
the
StandardNamespace
attribute.
provided
below.
-
For example:A modelabelednamed "100%" can have both theHIGH (MS)High (manufacturer specific) andMAXMax (standard)semanticmode tag. Clients seeking theoptionmode for eitherHIGHHigh orMAXMax will find the sameoptionmode in this case.1.8.8.2. SemanticTagStruct -
A
Semantic Tag is meant tomode that includes a LowEnergy tag can beinterpreteddisplayed by the client using a widget icon that shows a green leaf. A mode that includes a LowNoise tag may be used by the client when the user wishes for a lower level of audible sound, less likely to disturb the
purposehousehold’s activities.A mode that includes a LowEnergy tag (standard, defined in this cluster specification) and also a Delicate tag (standard, defined in the namespace of a Laundry Washer Mode derived cluster).
A mode that includes both a generic Quick tag (defined here), and Vacuum and Mop tags, (defined in the RVC Clean cluster
serves.that is a derivation of this cluster).
1.9.6. Attributes
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality |
|
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
F |
|
R V |
M |
|
|
|
|
desc |
|
|
R V |
M |
|
0x0002 | StartUpMode | uint8 | desc | NX | MS | RW VO | O |
0x0003 | OnMode | uint8 | desc | NX | null | RW VO | DEPONOFF |
1.8.8.2.1.
Value
Field
1.9.6.1.
Scene
Table
Extensions
If the Scenes server cluster is implemented on the same endpoint, the following attribute SHALL be part of the ExtensionFieldSetStruct of the Scene Table.
CurrentMode
1.9.6.2. SupportedModes Attribute
This attribute SHALL contain the list of supported modes that may be selected for the CurrentMode attribute. Each item in this list represents a unique mode as indicated by the Mode field of the ModeOptionStruct .
Each entry in this list SHALL have a unique value for the Mode field.
Each entry in this list SHALL have a unique value for the Label field.
1.9.6.3. CurrentMode Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
semantic
tag
within
current
mode
of
the
server.
The value of this field SHALL match the Mode field of one of the entries in the SupportedModes attribute.
The
value
of
this
attribute
may
change
at
any
time
via
an
out-of-band
interaction
outside
of
the
server,
such
as
interactions
with
a
semantic
tag
namespace
user
interface,
via
internal
mode
changes
due
to
autonomously
progressing
through
a
sequence
of
operations,
on
system
time-outs
or
idle
delays,
or
via
interactions
coming
from
a
fabric
other
than
the
one
which
last
executed
a
ChangeToMode.
1.9.6.4. StartUpMode Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
desired
startup
mode
for
the
server
when
it
is
either
manufacturer
specific
supplied
with
power.
If this attribute is not null, the CurrentMode attribute SHALL be set to the StartUpMode value, when the server is powered up, except in the case when the OnMode attribute overrides the StartUpMode attribute (see OnModeWithPowerUp ).
This behavior does not apply to reboots associated with OTA. After an OTA restart, the CurrentMode attribute SHALL return to its value prior to the restart.
The value of this field SHALL match the Mode field of one of the entries in the SupportedModes attribute.
If
this
attribute
is
not
implemented,
or
standard.
For
semantic
tags
is
set
to
the
null
value,
it
SHALL
have
no
effect.
1.9.6.5. OnMode Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate whether the value of CurrentMode depends on the state of the On/Off cluster on the same endpoint. If this attribute is not present or is set to null, there is no dependency, otherwise the CurrentMode attribute SHALL depend on the OnOff attribute in the On/Off cluster as described in the table below:
| OnOff Change | CurrentMode Change |
|---|---|
ON → OFF | No change |
OFF → ON | Change CurrentMode to OnMode |
OFF → OFF | No change |
ON → ON | No change |
The value of this field SHALL match the Mode field of one of the entries in the SupportedModes attribute.
1.9.6.5.1. OnMode with Power Up
If
the
On/Off
feature
is
supported
and
the
On/Off
cluster
attribute
StartUpOnOff
is
present,
with
a
standard
namespace,
see
Standard
Namespace
.
value
of
On
(turn
on
at
power
up),
then
the
CurrentMode
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
the
OnMode
attribute
value
when
the
server
is
supplied
with
power,
except
if
the
OnMode
attribute
is
null.
1.9.7. Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | ChangeToMode | client ⇒ server | ChangeToModeResponse | O | M |
0x01 | ChangeToModeResponse | client ⇐ server | N | O | M |
1.9.7.1. ChangeToMode Command
This command is used to change device modes.
On receipt of this command the device SHALL respond with a ChangeToModeResponse command.
This command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | NewMode | uint8 | desc | M |
1.8.8.2.2.
MfgCode
1.9.7.1.1.
NewMode
Field
If
this
the
NewMode
field
is
null,
doesn’t
match
the
Value
Mode
field
of
any
entry
of
the
SupportedModes
list,
the
ChangeToModeResponse
command’s
Status
field
SHALL
indicate
UnsupportedMode
and
the
StatusText
field
SHALL
be
defined
in
included
and
MAY
be
used
to
indicate
the
issue,
with
a
standard
namespace
human
readable
string,
or
include
an
empty
string.
If
the
NewMode
field
matches
the
Mode
field
of
one
entry
of
the
SupportedModes
list,
but
the
device
is
not
able
to
transition
as
indicated
by
requested,
the
StandardNamespace
attribute.
ChangeToModeResponse
command
SHALL:
Have the Status set to a product-specific Status value representing the error, or GenericFailure if a more specific error cannot be provided. See Status Field for details.
Provide a human readable string in the StatusText field.
If
this
the
NewMode
field
matches
the
Mode
field
of
one
entry
of
the
SupportedModes
list
and
the
device
is
not
null,
it
able
to
transition
as
requested,
the
server
SHALL
indicate
transition
into
the
mode
associated
with
NewMode,
the
ChangeToModeResponse
command
SHALL
have
the
Status
field
set
to
Success,
the
StatusText
field
MAY
be
supplied
with
a
manufacturer
code
(Vendor
ID),
human
readable
string
or
include
an
empty
string
and
the
Value
CurrentMode
field
SHALL
indicate
be
set
to
the
value
of
the
NewMode
field.
If
the
NewMode
field
is
the
same
as
the
value
of
the
CurrentMode
attribute
the
ChangeToModeResponse
command
SHALL
have
the
Status
field
set
to
Success
and
the
StatusText
field
MAY
be
supplied
with
a
semantic
tag
defined
human
readable
string
or
include
an
empty
string.
1.9.7.2. ChangeToModeResponse Command
This
command
is
sent
by
the
manufacturer.
Each
device
on
receipt
of
the
ChangeToMode
command.
This
command
SHALL
have
the
following
data
fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Status | enum8 | desc | M | ||
1 | StatusText | string | max 64 | [Status == Success], M |
1.9.7.2.1. Status Field
The following table defines the enumeration ranges for the ChangeToModeResponse command’s Status field values.
| Status Code Range | Range Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0x00 to 0x3F | CommonCodes | Common standard values defined in the generic Mode Base cluster specification. |
0x40 to 0x7F | DerivedClusterCodes | Derived cluster specific standard values defined in the derived Mode Base cluster specification. |
0x80 to 0xBF | MfgCodes |
Manufacturer
specific
values.
For
the
derived
Mode
Base
cluster
instances,
these
are
manufacturer
|
The set of Status field values defined in each of the generic or derived Mode Base cluster specifications is called StatusCode.
The following table defines the common StatusCode values.
| Status Code | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0x00 | Success | Switching to the mode indicated by the NewMode field is allowed and possible. The CurrentMode attribute is set to the value of the NewMode field. |
0x01 | UnsupportedMode | The value of the NewMode field doesn’t match any entries in the SupportedMode attribute list. |
0x02 | GenericFailure | Generic failure code, indicating that switching to the mode indicated by the NewMode field is not allowed or not possible. |
0x03 | InvalidInMode | The received request cannot be handled due to the current mode of the device |
The
derived
cluster
code
definitions
SHALL
NOT
duplicate
the
common
code
definitions.
For
example,
a
derived
cluster
specification
SHALL
NOT
define
a
status
code
with
the
same
manufacturer
semantic
as
the
common
code
of
0x01
(UnsupportedMode).
If the Status field is set to Success, the StatusText field is optional.
If the Status field is set to UnsupportedMode, the StatusText field SHALL be an empty string.
If the Status field is not set to Success or UnsupportedMode, the StatusText field SHALL include a vendor-defined error description which can be used to explain the error to the user.
If the Status field is set to InvalidInMode, the StatusText field SHALL be an empty string.
1.9.8. Mode Namespace
This
section
provides
the
definitions
of
the
mode
tag
ranges
and
semantic
of
the
common
standard
mode
tag
value
values
available
in
separate
cluster
the
instances
are
part
of
this
cluster.
The
following
table
defines
the
same
namespace
and
have
enumeration
ranges
for
the
same
meaning.
ModeTagStruct
Value
field
values.
| Mode Tag Value Range | Range Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0x0000 to 0x3FFF | CommonTags | Common standard values defined in this cluster specification. |
0x4000 to 0x7FFF | DerivedClusterTags | Derived cluster specific standard values defined in the derived cluster specification. |
0x8000 to 0xBFFF | MfgTags |
Manufacturer-specific
values.
For
|
The
derived
cluster
specific
standard
value
definitions
SHALL
not
duplicate
the
common
standard
value
definitions.
For
example,
a
derived
cluster
specification
can’t
define
a
mode
tag
meaning
"pinch",
has
value
with
the
same
meaning
mode
as
the
common
standard
tag
value
of
0x0001
(Quick).
The
set
of
ModeTagStruct
Value
field
values
defined
in
a
each
of
the
generic
or
derived
Mode
Base
cluster
whose
purpose
specifications
is
to
choose
called
ModeTag.
The
following
table
defines
the
amount
common
ModeTag
values.
| Mode Tag Value | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0x0000 | Auto | The device decides which options, features and setting values to use. |
0x0001 | Quick |
The
mode
of
|
0x0002 | Quiet |
The
device
is
silent
or
|
|
0x0003 | LowNoise | Either the mode is inherently low noise or the device optimizes for that. |
0x0004 | LowEnergy | The device is optimizing for lower energy usage in this mode. Sometimes called "Eco mode". |
0x0005 | Vacation | A mode suitable for use during vacations or other extended absences. |
0x0006 | Min | The mode uses the lowest available setting value. |
0x0007 | Max | The mode uses the highest available setting value. |
0x0008 | Night | The mode is recommended or suitable for use during night time. |
0x0009 | Day | The mode is recommended or suitable for use during day time. |
1.9.
1.10.
Low
Power
Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for managing low power mode on a device.
This cluster would be supported on an endpoint that represents a physical device with a low power mode. This cluster provides a sleep() command to allow clients to manually put the device into low power mode. There is no command here to wake up a sleeping device because that operation often involves other protocols such as Wake On LAN . Most devices automatically enter low power mode based upon inactivity.
The cluster server for Low Power is implemented by a device that supports a low power mode, such as a TV, Set-top box, or Smart Speaker.
|
Note
|
|
1.9.1.1.
1.10.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial Release |
1.9.1.2.
1.10.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
LOWPOWER |
1.10.
1.11.
Wake
On
LAN
Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for managing low power mode on a device that supports the Wake On LAN or Wake On Wireless LAN (WLAN) protocol (see [ Wake On LAN ]).
This cluster would be supported on IP devices that have a low power mode AND support the ability to be woken up using the Wake on LAN or Wake on WLAN protocol. This cluster provides the device MAC address which is a required input to the Wake on LAN protocol. Besides the MAC address, this cluster provides an optional link-local IPv6 address which is useful to support "Wake on Direct Packet" used by some Ethernet and Wi-Fi devices.
Acting
on
the
MAC
address
or
link-local
IPv6
address
information
does
require
the
caller
to
be
in
the
same
broadcast
domain
as
the
destination.
To
wake
the
destination
up,
the
caller
sends
a
multicast-based
magic
UDP
packet
that
contains
destination’s
MAC
address
in
the
UDP
payload
to
FF02::1,
the
IPv6
all-nodes
link-local
multicast
group
address.
If
the
optional
link-local
address
is
provided
by
the
destination
through
this
cluster,
the
caller
also
sends
the
magic
UDP
packet
in
unicast
to
that
link-local
address.
This
unicast-based
method
is
particularly
useful
for
Wi-Fi
devices,
since
due
to
lack
of
MAC
layer
retransmission
mechanism,
multicast
over
Wi-Fi
is
not
as
reliable
as
unicast.
If
a
device
provides
the
link-local
address
in
this
cluster,
its
Ethernet
controller
or
Wi-Fi
radio
shall
SHALL
respond
to
the
IPv6
neighbor
solicitation
message
for
the
link-local
address
without
the
need
to
wake
host
CPU
up.
In
order
to
receive
the
magic
or
neighbor
solicitation
packets
in
multicast,
the
Wi-Fi
devices
must
support
Group
Temporal
Key
(GTK)
rekey
operation
in
low
power
mode.
Most devices automatically enter low power mode based upon inactivity.
The cluster server for Wake on LAN or Wake on WLAN is implemented by a device that supports the Wake on LAN/WLAN protocol, such as a TV, Set-top Box, or Smart Speaker.
1.10.1.1.
1.11.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial Release |
1.10.1.2.
1.11.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
WAKEONLAN |
1.10.2.
1.11.4.
Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
MACAddress |
hwadr |
desc |
F |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0001 |
LinkLocalAddress |
ipv6adr |
desc |
F |
R V |
O |
1.10.2.1.
1.11.4.1.
MACAddress
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the current MAC address of the device. Only 48-bit MAC Addresses SHALL be used for this attribute as required by the Wake on LAN protocol.
1.10.2.2.
1.11.4.2.
LinkLocalAddress
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the current link-local address of the device. Only 128-bit IPv6 link-local addresses SHALL be used for this attribute.
|
Note
|
Some companies may consider MAC Address to be protected data subject to PII handling considerations and will therefore choose not to include it or read it. The MAC Address can often be determined using ARP in IPv4 or NDP in IPv6. |
1.11.
1.12.
Switch
Cluster
This
cluster
exposes
interactions
with
a
switch
device,
for
the
purpose
of
using
those
interactions
by
other
devices.
Two
types
of
switch
devices
are
supported:
latching
switch
(e.g.
rocker
switch)
and
momentary
switch
(e.g.
push
button),
distinguished
with
their
feature
flags.
Interactions
with
the
switch
device
are
exposed
as
attributes
(for
the
latching
switch)
and
as
events
(for
both
types
of
switches).
An
interested
client
MAY
subscribe
to
these
attributes/events
and
thus
be
informed
of
the
interactions,
and
can
perform
actions
based
on
this,
for
example
by
sending
commands
to
perform
an
action
such
as
controlling
a
light
or
a
window
shade.
1.11.1.
1.12.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial Release |
1.11.2.
1.12.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
SWTCH |
1.11.4.
1.12.4.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
These
feature
flags
SHALL
be
used
to
indicate
the
physics
as
well
as
the
detection/reporting
capabilities
of
the
device
represented
by
the
cluster,
and
hence
the
attributes
and
events
exposed.
cluster.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
Switch is latching |
|
1 |
|
|
|
Switch is momentary |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
MSL |
|
[MS & MSR] |
Switch supports long press |
|
4 |
MSM |
|
[MS & MSR] |
Switch supports multi-press |
1.11.4.1.
Latching
Switch
1.12.4.1.
LatchingSwitch
Feature
This feature is for a switch that maintains its position after being pressed (or turned).
1.11.4.2.
Momentary
Switch
1.12.4.2.
MomentarySwitch
Feature
This feature is for a switch that does not maintain its position after being pressed (or turned). After releasing, it goes back to its idle position.
1.11.4.3.
Momentary
Switch
Release
1.12.4.3.
MomentarySwitchRelease
Feature
This feature is for a momentary switch that can distinguish and report release events. When this feature flag MSR is present, MS SHALL be present as well.
1.11.4.4.
Momentary
Switch
LongPress
1.12.4.4.
MomentarySwitchLongPress
Feature
This feature is for a momentary switch that can distinguish and report long presses from short presses. When this feature flag MSL is present, MS and MSR SHALL be present as well.
1.11.4.5.
Momentary
Switch
MultiPress
1.12.4.5.
MomentarySwitchMultiPress
Feature
This feature is for a momentary switch that can distinguish and report double press and potentially multiple presses with more events, such as triple press, etc. When this feature flag MSM is present, MS and MSR SHALL be present as well.
1.11.5.
1.12.5.
Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
NumberOfPositions |
uint8 |
2 to max |
F |
2 |
R |
M |
|
0x0001 |
CurrentPosition |
uint8 |
0
to
|
N |
0 |
R |
M |
|
0x0002 |
MultiPressMax |
uint8 |
2 to max |
F |
2 |
R |
MSM |
1.11.5.1.
1.12.5.1.
NumberOfPositions
Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
number
of
positions
the
switch
has.
Any
kind
of
switch
has
a
minimum
of
2
positions.
Also
see
Section
1.11.10,
“NumberOfPositions
>
2”
Multi
Position
Details
for
the
case
NumberOfPositions>2.
1.11.5.2.
1.12.5.2.
CurrentPosition
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the position of the switch. The valid range is zero to NumberOfPositions-1. CurrentPosition value 0 SHALL be assigned to the default position of the switch: for example the "open" state of a rocker switch, or the "idle" state of a push button switch.
1.11.5.3.
1.12.5.3.
MultiPressMax
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate how many consecutive presses can be detected and reported by a momentary switch which supports multi-press (e.g. it will report the value 3 if it can detect single press, double press and triple press, but not quad press and beyond).
1.11.7.
1.12.6.
Events
| ID | Name | Priority | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
SwitchLatched |
INFO |
V |
LS |
|
|
InitialPress |
INFO |
V |
MS |
|
|
LongPress |
INFO |
V |
MSL |
|
|
ShortRelease |
INFO |
V |
MSR |
|
|
LongRelease |
INFO |
V |
MSL |
|
|
MultiPressOngoing |
INFO |
V |
MSM |
|
|
MultiPressComplete |
INFO |
V |
MSM |
1.11.7.1.
1.12.6.1.
SwitchLatched
Event
This
event
SHALL
be
generated,
when
the
latching
switch
is
moved
to
a
new
position.
It
MAY
have
been
delayed
by
debouncing
within
the
switch.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NewPosition |
uint8 |
0
to
|
M |
1.11.7.2.
1.12.6.2.
InitialPress
Event
This event SHALL be generated, when the momentary switch starts to be pressed (after debouncing).
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NewPosition |
uint8 |
0
to
|
M |
1.11.7.3.
1.12.6.3.
LongPress
Event
This event SHALL be generated, when the momentary switch has been pressed for a "long" time (this time interval is manufacturer determined (e.g. since it depends on the switch physics)).
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NewPosition |
uint8 |
0
to
|
M |
1.11.7.4.
1.12.6.4.
ShortRelease
Event
This event SHALL be generated, when the momentary switch has been released (after debouncing).
-
If the server supports the Momentary Switch LongPress (MSL) feature, this event SHALL be generated when the switch is released if no LongPress event had been generated since the previous InitialPress event.
-
If the server does not support the Momentary Switch LongPress (MSL) feature, this event SHALL be generated when the switch is released - even when the switch was pressed for a long time.
-
Also see Section
1.11.8,1.12.7, “Sequence of generated events” .
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PreviousPosition |
uint8 |
0
to
|
M |
1.11.7.5.
1.12.6.5.
LongRelease
Event
This
event
SHALL
be
generated,
when
the
momentary
switch
has
been
released
(after
debouncing)
and
after
having
been
pressed
for
a
long
time,
i.e.
this
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
the
switch
is
released
if
a
LongPress
event
has
been
generated
since
since
the
previous
InitialPress
event.
Also
see
Section
1.11.8,
1.12.7,
“Sequence
of
generated
events”
.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PreviousPosition |
uint8 |
0
to
|
M |
1.11.7.6.
1.12.6.6.
MultiPressOngoing
Event
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
to
indicate
how
many
times
the
momentary
switch
has
been
pressed
in
a
multi-press
sequence,
during
that
sequence.
See
Section
1.11.9,
“Sequence
of
events
for
MultiPress”
Multi
Press
Details
below.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NewPosition |
uint8 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
1 |
CurrentNumberOfPressesCounted |
uint8 |
2 to MultiPressMax |
M |
1.12.6.6.1. NewPosition Field
The
NewPosition
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
new
value
of
the
CurrentPosition
attribute,
i.e.
while
pressed.
1.12.6.6.2. CurrentNumberOfPressesCounted Field
The
CurrentNumberOfPressesCounted
This
field
SHALL
contain:
-
a value of 2 when the second press of a multi-press sequence has been detected,
-
a value of 3 when the third press of a multi-press sequence has been detected,
-
a value of N when the N th press of a multi-press sequence has been detected.
1.11.7.7.
1.12.6.7.
MultiPressComplete
Event
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
to
indicate
how
many
times
the
momentary
switch
has
been
pressed
in
a
multi-press
sequence,
after
it
has
been
detected
that
the
sequence
has
ended
.
See
Section
1.11.9,
“Sequence
of
events
for
MultiPress”
below.
Multi
Press
Details
.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PreviousPosition |
uint8 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
1 |
TotalNumberOfPressesCounted |
uint8 |
1 to MultiPressMax |
M |
The PreviousPosition field SHALL indicate the previous value of the CurrentPosition attribute, i.e. just prior to release.
The TotalNumberOfPressesCounted field SHALL contain:
-
a value of 1 when there was one press in a multi-press sequence (and the sequence has ended), i.e. there was no double press (or more),
-
a value of 2 when there were exactly two presses in a multi-press sequence (and the sequence has ended),
-
a value of 3 when there were exactly three presses in a multi-press sequence (and the sequence has ended),
-
a value of N when there were exactly N presses in a multi-press sequence (and the sequence has ended).
1.11.8.
1.12.7.
Sequence
of
generated
events
This section describes the sequence of events that will be generated by three types of momentary switches (distinguished by their feature flags). For each switch type, we will define the sequence of generated events for these three interactions:
-
Sequence for a switch which is pressed briefly.
-
Sequence for a switch pressed for a long time.
-
Sequence for a switch pressed for a very long time.
In
the
three
interactions
described
in
the
subsections
below,
if
the
NumberOfPositions
attribute
is
equal
to
2,
the
InitialPress
and
LongPress
events
have
the
NewPosition
field
set
to
1
and
the
ShortRelease
and
LongRelease
events
have
the
PreviousPosition
field
set
to
1.
For
larger
values
of
the
NumberOfPositions
attribute,
see
Section
1.11.10,
“NumberOfPositions
>
2”
Multi
Position
Details
.
1.11.8.1.
1.12.7.1.
Supports
InitialPress
+
LongPress
+
ShortRelease
+
LongRelease
This
switch
(with
feature
flags
MS
&
MSR
&
MSL
)
MSL)
SHALL
generate
either
a
sequence
of
two
or
three
(depending
on
how
long
the
switch
is
pressed)
events
for
one
interaction
cycle,
in
the
order
given
below
and
illustrated
in
the
figure
below.
-
short press:
InitialPress ,InitialPress, then ShortRelease -
long press (or very long press):
InitialPress ,InitialPress, thenLongPress ,LongPress, and finallyLongRelease .LongRelease. Please note that the LongPress event SHALL be generated exactly once for this case and SHALL not be repeated, irrespective how long the switch is pressed.
The image shows a time representation of the state of the switch (low=not pressed, high=pressed) with the colored dots indicating the various events generated at that moment in time.

1.11.8.2.
1.12.7.2.
Supports
InitialPress
+
ShortRelease
(but
not
LongPress,
LongRelease)
This
switch
(with
feature
flags
MS
&
MSR
&
!MSL
)
!MSL)
does
not
generate
events
for
the
"longpress"
case
and
therefore
it
SHALL
generate
a
sequence
of
two
events
for
one
interaction
cycle,
irrespective
of
how
long
the
switch
is
pressed,
in
the
order
given
and
illustrated
below.
-
any press length:
InitialPress ,InitialPress, then ShortRelease
Please
note
that
even
after
a
"long"
period
being
pressed,
the
release
event
is
ShortRelease
.
ShortRelease.
A
device
with
this
set
of
feature
flags
SHALL
NOT
generate
the
LongPress
and
LongRelease
events.

1.11.8.3.
1.12.7.3.
Supports
InitialPress
(but
not
LongPress,
ShortRelease
and
LongRelease)
This
switch
(with
feature
flags
MS
&
!MSR
!MSR
&
!MSL
)
!MSL)
SHALL
generate
a
single
InitialPress
event
for
one
interaction
cycle,
irrespective
of
how
long
the
switch
is
pressed,
as
illustrated
in
the
figure
below.
A
device
with
this
set
of
feature
flags
SHALL
NOT
generate
any
of
the
ShortRelease
,
ShortRelease,
LongPress
and
LongRelease
events.

1.11.9.
1.12.8.
Sequence
of
events
for
MultiPress
Multi-press
detection
is
a
feature
of
momentary
switches
(indicated
with
feature
flag
MSM
)
MSM)
that
they
can
count
and
report
sequences
of
press-release
cycles
within
a
certain
time
frame,
for
example
to
indicate
that
the
user
has
pressed
the
switch
once,
twice
or
three
(or
even
more)
times
in
succession.
The
definition
of
the
time
window
for
this
detection
is
manufacturer-specific
since
it
depends
on
the
switch
physics.
The
maximum
number
of
presses
which
can
be
detected
and
reported
SHALL
be
indicated
in
attribute
MultiPressMax
.
MultiPressMax.
The
minimum
value
and
default
value
for
MultiPressMax
are
both
2.
A
switch
supporting
MultiPress
SHALL
set
feature
flags
MS
&
MSR
&
MSM
,
MSM,
and
optionally
also
feature
flag
MSL
.
MSL.
It
SHALL
generate
the
MultiPressOngoing
and
MultiPressFinished
events
in
addition
to
the
other
events
defined
for
momentary
switches
(i.e.
InitialPress
,
ShortRelease
,
InitialPress,
ShortRelease,
and
in
case
of
MSL
,
MSL,
LongPress
and
LongRelease
).
LongRelease).
The MultiPressOngoing event is provided for parties interested in keeping track of the actual presses during the multi-press sequence. The MultiPressComplete event is provided for parties interested in the outcome of the whole sequence: after the multi-press sequence has ended, they will receive the MultiPressComplete event indicating how many times the switch was pressed.
In
the
figure
below,
three
sequences
of
user
interaction
are
indicated:
-
single press sequence: after the press and release moments, the InitialPress and ShortRelease events SHALL be generated. After some further time, when the switch has detected that there is no second press, it SHALL generate MultiPressComplete(1) since it has detected that the sequence consisted of one press. No MultiPressOngoing event SHALL be generated for this case.
-
double press sequence: after each of the press and release moments, the InitialPress and ShortRelease events SHALL be generated. Additionally, when the switch is pressed for the second time, the MultiPressOngoing(2) event SHALL be generated, as the switch has detected the second press. Note that this event coincides with the second InitialPress event; both SHALL be generated. After some further time, when the switch has detected that there is no third press, it SHALL generate MultiPressComplete(2) since it has detected that the sequence consisted of two presses.
-
third press sequence: after each press and release moments, the InitialPress and ShortRelease events SHALL be generated. Additionally, when the switch is pressed for the second time, the MultiPressOngoing(2) event SHALL be generated, as the switch has detected the second press. Note that this event coincides with the second InitialPress event; both SHALL be generated. Additionally, when the switch is pressed for the third time, the MultiPressOngoing(3) event SHALL be generated, as the switch has detected the third press. Note that this event coincides with the third InitialPress event; both SHALL be generated. After some further time, when the switch has detected that there is no fourth press, it SHALL generate MultiPressComplete(3) since it has detected that the sequence consisted of three presses.
For the above cases where multiple events need to be generated at the same time, the MultiPressOngoing event SHALL be generated directly after the InitialPress event.
|
Note
|
The numbers in parentheses in the bulleted text above and in the figure below indicate the value of the CurrentNumberOfPressesCounted resp. TotalNumberOfPressesCounted field in the event data. |
|
Note
|
As with the other figures, sufficient debounce time needs to be take into account for the detection of press and release events. This is included in the figure, and has been left out of the description above for readability, but SHALL be applied. |

1.11.10.
NumberOfPositions
>
2
1.12.9.
Multi
Position
Details
This section will discuss some archetypes of switch devices with more than 2 positions and how they SHALL set attribute values and generate events matching their characteristics.
For
the
SwitchLatched
,
InitialPress
,
SwitchLatched,
InitialPress,
LongPress
and
MultiPressOngoing
events,
the
field
NewPosition
SHALL
be
set
to
the
value
corresponding
to
the
new
position
to
which
the
switch
was
moved.
For
the
ShortRelease
,
ShortRelease,
LongRelease
and
MultiPressComplete
events,
the
field
PreviousPosition
SHALL
be
set
to
the
value
corresponding
to
the
position
of
the
switch
just
preceding
the
(latest)
release.
1.11.10.1.
1.12.9.1.
Latching
Switch
with
N
stable
positions
(N>2)
with
fixed
sequence
With
such
a
device,
the
user
can
move
the
switch
from
a
position
M
to
positions
M-1
and
M+1
(either
with
a
wraparound
between
the
end
positions,
or
fixed
stop
at
the
end
positions).
On
each
interaction
with
the
switch
device,
it
SHALL
generate
a
SwitchLatched
event
with
the
NewPosition
field
set
to
the
value
associated
with
the
new
position.
Due
to
the
physical
constraints,
such
an
event
will
have
a
NewPosition
field
which
is
equal
to
the
previous
NewPosition
field
plus
or
minus
1
(modulo
NumPositions
if
the
switch
does
not
have
end
stops).
In a first example, a switch has 3 positions, associated with values 0, 1 and 2. In this case, wraparound is not possible: from position 0 it can only be moved to position 1.

In another example, a switch has 8 positions, associated with values 0 through 7. In this case, the physics of the switch allow wraparound: from position 0 it can be moved to position 1 or to position 7.

1.11.10.2.
1.12.9.2.
Latching
Switch
with
N
stable
positions
(N>2)
with
random
sequence
(example:
radio
buttons)
With such a device, the user can press any of the available buttons, so this switch does not show the incrementing or decrementing behavior of NewPosition which we discussed for the latching switch with fixed sequence. In the example in the figure below, the 5 buttons are labelled "A" through "E" for the user and are associated with values 0 through 4. The user first presses the "A" button, and the switch device generates a SwitchLatched event with NewPosition set to 0. Then the user first presses the "D" button, and the switch device generates a SwitchLatched event with NewPosition set to 4.

1.11.10.3.
1.12.9.3.
Momentary
Switch
with
2
or
more
non-stable
positions
For a Momentary Switch with more than 1 stable position, it depends on the physics of the switch device which sequence of events will be generated.
|
Note
|
In this section we will mention only the InitialPress and ShortRelease events. The switch device could also generate the other events defined above for a momentary switch, depending on the capabilities of the switch device and the interaction with the switch device. |
The
first
variant
(figure
below,
example:
up/down
control
for
window
blinds)
shows
a
switch
in
neutral
position
(left
figure)
which
corresponds
to
CurrentPosition=0
.
CurrentPosition=0.
The
user
can
press
the
top
side
(position
value
1)
or
the
bottom
side
(position
value
2).
It
is
not
possible
to
go
directly
from
position
1
to
position
2
or
vice
versa
-
the
switch
will
always
need
to
go
through
the
neutral
position
0.
So when the user presses the top side of the switch, the InitialPress (NewPosition=1) event will be generated. When they release the top side, the ShortRelease (PreviousPosition=1) event will be generated. The user continues to press the bottom side, and the event InitialPress (NewPosition=2) is generated. Upon release of the bottom side, the event ShortRelease (PreviousPosition=2) is generated.

Another
variant
(figure
below,
example:
joystick)
has
a
control
handle
with
a
neutral
position
in
the
middle
(left
figure)
which
corresponds
to
CurrentPosition=0
.
CurrentPosition=0.
The
handle
can
be
moved
along
the
dotted
lines.
In the middle figure, the user moves the handle to the East position and then releases it (which makes it return to the neutral middle position). This generates this sequence of events:
InitialPress (NewPosition=3) // move to East ShortRelease (PreviousPosition=3) // back to middle (from East)
In the righthand figure, the user moves the handle to the SouthWest position, then to the South position and then releases it (which makes it return to the neutral middle position). This generates this sequence of events:
InitialPress (NewPosition=6) // move to SouthWest InitialPress (NewPosition=5) // move to South ShortRelease (PreviousPosition=5) // back to middle (from South)

Therefore, in the "joystick" variation, there could be a succession of InitialPress events without an intermediate ShortRelease events - unlike the "window blinds control" variation which will always have such an intermediate ShortRelease event.
1.13. Operational State Cluster
This cluster supports remotely monitoring and, where supported, changing the operational state of any device where a state machine is a part of the operation.
This cluster defines common states, scoped to this cluster (e.g. Stopped, Running, Paused, Error). A derived cluster specification may define more states scoped to the derivation. Manufacturer specific states are supported in this cluster and any derived clusters thereof. When defined in a derived instance, such states are scoped to the derivation.
Actual state transitions are dependent on both the implementation, and the requirements that may additionally be imposed by a derived cluster.
An implementation that supports remotely starting its operation can make use of this cluster’s Start command to do so. A device that supports remote pause or stop of its currently selected operation can similarly make use of this cluster’s Pause and Stop commands to do so. The ability to remotely pause or stop is independent of how the operation was started (for example, an operation started by using a manual button press can be stopped by using a Stop command if the device supports remotely stopping the operation).
Additionally, this cluster provides events for monitoring the operational state of the device.
1.13.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Rev | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial release |
1.13.4. Data Types
1.13.4.1. OperationalStateEnum Type
This type defines the set of known operational state values, and is derived from enum8. The following table defines the applicable ranges for values that are defined within this type. All values that are undefined SHALL be treated as reserved. As shown by the table, states that may be specific to a certain Device Type or other modality SHALL be defined in a derived cluster of this cluster.
| Value | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0x00 to 0x3F | GeneralStates | Generally applicable values for state, defined herein |
0x40 to 0x7F | DerivedClusterStates | Derived Cluster defined states |
0x80 to 0xBF | ManufacturerStates | Vendor specific states |
The derived cluster-specific state definitions SHALL NOT duplicate any general state definitions. That is, a derived cluster specification of this cluster cannot define states with the same semantics as the general states defined below.
A manufacturer-specific state definition SHALL NOT duplicate the general state definitions or derived cluster state definitions. That is, a manufacturer-defined state defined for this cluster or a derived cluster thereof cannot define a state with the same semantics as the general states defined below or states defined in a derived cluster.
The following table defines the generally applicable states.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | Stopped | The device is stopped | M |
0x01 | Running | The device is operating | M |
0x02 | Paused | The device is paused during an operation | M |
0x03 | Error | The device is in an error state | M |
1.13.4.2. OperationalStateStruct Type
The OperationalStateStruct is used to indicate a possible state of the device.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | OperationalStateID | all | 0 | M | ||
1 | OperationalStateLabel | string | max 64 | desc |
1.13.4.2.1. OperationalStateID Field
This SHALL be populated with a value from the OperationalStateEnum .
1.13.4.3. ErrorStateStruct Type
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | ErrorStateID | enum8 | all | 0 | M | |
1 | ErrorStateLabel | string | max 64 | empty | desc | |
2 | ErrorStateDetails | string | max 64 | empty | O |
1.13.4.3.1. ErrorStateID Field
The following table defines the enumeration ranges for the ErrorStateID field values.
| Value | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0x00 to 0x3F | GeneralErrors | Generally applicable values for error, defined herein |
0x40 to 0x7F | DerivedClusterErrors | Derived Cluster defined errors |
0x80 to 0xBF | ManufacturerError | Vendor specific errors |
The derived cluster-specific error definitions SHALL NOT duplicate the general error definitions. That is, a derived cluster specification of this cluster cannot define errors with the same semantics as the general errors defined below.
The manufacturer-specific error definitions SHALL NOT duplicate the general error definitions or derived cluster-specific error definitions. That is, a manufacturer-defined error defined for this cluster or a derived cluster thereof cannot define errors with the same semantics as the general errors defined below or errors defined in a derived cluster.
The set of ErrorStateID field values defined in each of the generic or derived Operational State cluster specifications is called ErrorState.
The following table defines the generally applicable ErrorState values.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | NoError | The device is not in an error state | M |
0x01 | UnableToStartOrResume | The device is unable to start or resume operation | M |
0x02 | UnableToCompleteOperation | The device was unable to complete the current operation | M |
0x03 | CommandInvalidInState | The device cannot process the command in its current state | M |
1.13.4.3.2. ErrorStateLabel Field
This field SHALL be present if the ErrorStateID is from the set reserved for Manufacturer Specific Errors, otherwise it SHALL NOT be present. If present, this SHALL contain a human-readable description of the ErrorStateID; e.g. for a manufacturer specific ErrorStateID of "0x80" the ErrorStateLabel MAY contain "My special error".
1.13.5. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x0000 | PhaseList | list[string] | max 32[max 64] | X | MS | R V | M |
0x0001 | CurrentPhase | uint8 | desc | X | MS | R V | M |
0x0002 | CountdownTime | elapsed-s | max 259200 | X C | null | R V | O |
0x0003 | OperationalStateList | list[ OperationalStateStruct ] | desc | MS | R V | M | |
0x0004 | OperationalState | all | R V | M | |||
0x0005 | OperationalError | desc | R V | M |
1.13.5.1. PhaseList Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate a list of names of different phases that the device can go through for the selected function or mode. The list may not be in sequence order. For example in a washing machine this could include items such as "pre-soak", "rinse", and "spin". These phases are manufacturer specific and may change when a different function or mode is selected.
A null value indicates that the device does not present phases during its operation. When this attribute’s value is null, the CurrentPhase attribute SHALL also be set to null.
1.13.5.2. CurrentPhase Attribute
This attribute represents the current phase of operation being performed by the server. This SHALL be the positional index representing the value from the set provided in the PhaseList Attribute, where the first item in that list is an index of 0. Thus, this attribute SHALL have a maximum value that is "length(PhaseList) - 1".
This attribute SHALL be null if the PhaseList attribute is null or if the PhaseList attribute is an empty list.
1.13.5.3. CountdownTime Attribute
This attribute SHALL represent the estimated time left before the operation is completed, in seconds. Changes to this value SHALL NOT be reported in a subscription (note the C Quality). A Client implementation MAY periodically poll this value to ensure alignment of any local rendering of the CountdownTime with the device provided value.
A value of 0 means that the operation has completed.
When this attribute is null, that represents that there is no time currently defined until operation completion. This MAY happen, for example, because no operation is in progress or because the completion time is unknown.
1.13.5.4. OperationalStateList Attribute
This attribute describes the set of possible operational states that the device exposes. An operational state is a fundamental device state such as Running or Error. Details of the phase of a device when, for example, in a state of Running are provided by the CurrentPhase attribute.
All devices SHALL, at a minimum, expose the set of states matching the commands that are also supported by the cluster instance, in addition to Error. The set of possible device states are defined in the OperationalStateEnum . A device type requiring implementation of this cluster SHALL define the set of states that are applicable to that specific device type.
1.13.5.5. OperationalState Attribute
This attribute specifies the current operational state of a device. This SHALL be populated with a valid OperationalStateID from the set of values in the OperationalStateList Attribute.
1.13.5.6. OperationalError Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify the details of any current error condition being experienced on the device when the OperationalState attribute is populated with Error. Please see ErrorStateStruct for general requirements on the population of this attribute.
When there is no error detected, this SHALL have an ErrorStateID of NoError.
1.13.6. Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | Pause | client ⇒ server | OperationalCommandResponse | O | Resume, O |
0x01 | Stop | client ⇒ server | OperationalCommandResponse | O | Start, O |
0x02 | Start | client ⇒ server | OperationalCommandResponse | O | O |
0x03 | Resume | client ⇒ server | OperationalCommandResponse | O | Pause, O |
0x04 | OperationalCommandResponse | client ⇐ server | N | O | Pause | Stop | Start | Resume |
Note that it is entirely possible due to regulatory or other reasons for an instance of this cluster to expose no possible commands. When that occurs, this cluster does not provide any ability to actuate the device, instead it provides readable (and by extension, can be subscribed to) information as to the state of the device only. The commands that are supported SHALL be exposed by the device in the AcceptedCommandList global attribute.
1.13.6.1. Pause Command
This command SHALL be supported if the device supports remotely pausing the operation. If this command is supported, the Resume command SHALL also be supported.
On receipt of this command, the device SHALL pause its operation if it is possible based on the current function of the server. For example, if it is at a point where it is safe to do so and/or permitted, but can be restarted from the point at which pause occurred.
If this command is received when already in the Paused state the device SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of NoError but take no further action.
A device that receives this command in any state other than Paused or Running SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of CommandInvalidInState but take no further action.
A device that is unable to honor the Pause command for whatever reason SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of CommandInvalidInState but take no further action.
Otherwise, on success:
The OperationalState attribute SHALL be set to Paused.
The device SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of NoError.
1.13.6.2. Stop Command
This command SHALL be supported if the device supports remotely stopping the operation.
On receipt of this command, the device SHALL stop its operation if it is at a position where it is safe to do so and/or permitted. Restart of the device following the receipt of the Stop command SHALL require attended operation unless remote start is allowed by the device type and any jurisdiction governing remote operation of the device.
If this command is received when already in the Stopped state the device SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of NoError but take no further action.
A device that is unable to honor the Stop command for whatever reason SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of CommandInvalidInState but take no further action.
Otherwise, on success:
The OperationalState attribute SHALL be set to Stopped.
The device SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of NoError.
1.13.6.3. Start Command
This command SHALL be supported if the device supports remotely starting the operation. If this command is supported, the 'Stop command SHALL also be supported.
On receipt of this command, the device SHALL start its operation if it is safe to do so and the device is in an operational state from which it can be started. There may be either regulatory or manufacturer-imposed safety and security requirements that first necessitate some specific action at the device before a Start command can be honored. In such instances, a device SHALL respond with a status code of CommandInvalidInState if a Start command is received prior to the required on-device action.
If this command is received when already in the Running state the device SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of NoError but take no further action.
A device that is unable to honor the Start command for whatever reason SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of UnableToStartOrResume but take no further action.
Otherwise, on success:
The OperationalState attribute SHALL be set to Running.
The device SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of NoError.
1.13.6.4. Resume Command
This command SHALL be supported if the device supports remotely resuming the operation. If this command is supported, the Pause command SHALL also be supported.
On receipt of this command, the device SHALL resume its operation from the point it was at when it received the Pause command, or from the point when it was paused by means outside of this cluster (for example by manual button press).
If this command is received when already in the Running state the device SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of NoError but take no further action.
A device that receives this command in any state other than Paused or Running SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of CommandInvalidInState but take no further action.
A device that is unable to honor the Resume command for any other reason SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of UnableToStartOrResume but take no further action.
Otherwise, on success:
The OperationalState attribute SHALL be set to Running.
The device SHALL respond with an OperationalCommandResponse command with an ErrorStateID of NoError.
1.13.6.5. OperationalCommandResponse Command
This command SHALL be supported by an implementation if any of the other commands defined by this cluster are supported (i.e. listed in the AcceptedCommandList global attribute). This command SHALL also be supported by an implementation of a derived cluster as a response to any commands that MAY be additionally defined therein.
This command SHALL be generated in response to any of the Start, Stop, Pause, or Resume commands. The data for this command SHALL be as follows:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | CommandResponseState | all | M |
1.13.6.5.1. CommandResponseState Field
This SHALL indicate the success or otherwise of the attempted command invocation. On a successful invocation of the attempted command, the ErrorStateID SHALL be populated with NoError. Please see the individual command sections for additional specific requirements on population.
1.13.7. Events
| ID | Name | Priority | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | OperationalError | CRITICAL | V | M |
0x01 | OperationCompletion | INFO | V | O |
1.13.7.1. OperationalError Event
This event is generated when a reportable error condition is detected. A device that generates this event SHALL also set the OperationalState attribute to Error, indicating an error condition.
This event SHALL contain the following fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | ErrorState | all | M |
1.13.7.2. OperationCompletion Event
This event is generated when the overall operation ends, successfully or otherwise. For example, the completion of a cleaning operation in a Robot Vacuum Cleaner, or the completion of a wash cycle in a Washing Machine.
This event SHALL contain the following fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | CompletionErrorCode | enum8 | all | M | ||
1 | TotalOperationalTime | elapsed-s | all | X | O | |
2 | PausedTime | elapsed-s | all | X | O |
1.13.7.2.1. CompletionErrorCode Field
This field provides an indication of the state at the end of the operation. This field SHALL have a value from the ErrorState set. A value of NoError indicates success, that is, no error has been detected.
1.13.7.2.2. TotalOperationalTime Field
The total operational time, in seconds, from when the operation was started via an initial Start command or manual action, until the operation completed. This includes any time spent while paused. There may be cases whereby the total operational time exceeds the maximum value that can be conveyed by this attribute, in such instances, this attribute SHALL be populated with null.
1.14. Alarm Base Cluster
This cluster is a base cluster from which clusters for particular alarms for a device type can be derived. Each derivation SHALL define the values for the AlarmMap data type used in this cluster. Each derivation SHALL define which alarms are latched.
1.14.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial revision |
1.14.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | RESET | Reset | Supports the ability to reset alarms |
1.14.5. Data Types
1.14.5.1. AlarmMap Type
This data type SHALL be a map32 with values defined by the derived cluster. The meaning of each bit position SHALL be consistent for all attributes in a derived cluster. That is, if bit 0 is defined for an alarm, the Latch, State, and Supported information for that alarm are also bit 0.
1.14.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x0000 | Mask | all | 0 | R V | M | ||
0x0001 | Latch | all | F | 0 | R V | RESET | |
0x0002 | State | all | 0 | R V | M | ||
0x0003 | Supported | all | F | 0 | R V | M |
1.14.6.1. Mask Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate a bitmap where each bit set in the Mask attribute corresponds to an alarm that SHALL be enabled.
1.14.6.2. Latch Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate a bitmap where each bit set in the Latch attribute SHALL indicate that the corresponding alarm will be latched when set, and will not reset to inactive when the underlying condition which caused the alarm is no longer present, and so requires an explicit reset using the Reset command.
1.14.6.3. State Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate a bitmap where each bit SHALL represent the state of an alarm. The value of true means the alarm is active, otherwise the alarm is inactive.
1.14.6.4. Supported Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate a bitmap where each bit SHALL represent whether or not an alarm is supported. The value of true means the alarm is supported, otherwise the alarm is not supported.
If an alarm is not supported, the corresponding bit in Mask, Latch, and State SHALL be false.
1.14.7. Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | Reset | client ⇒ server | Y | O | RESET |
0x01 | ModifyEnabledAlarms | client ⇒ server | Y | O | O |
1.14.7.1. Reset Command
This command resets active and latched alarms (if possible). Any generated Notify event SHALL contain fields that represent the state of the server after the command has been processed.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Alarms | all | 0 | M |
1.14.7.1.1. Alarms Field
This field SHALL indicate a bitmap where each bit set in this field corresponds to an alarm that SHALL be reset to inactive in the State attribute unless the alarm definition requires manual intervention. If the alarms indicated are successfully reset, the response status code SHALL be SUCCESS, otherwise, the response status code SHALL be FAILURE.
1.14.7.2. ModifyEnabledAlarms Command
This command allows a client to request that an alarm be enabled or suppressed at the server.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Mask | all | 0 | M |
1.14.7.2.1. Mask Field
This field SHALL indicate a bitmap where each bit set in the this field corresponds to an alarm that SHOULD be enabled or suppressed. A value of 1 SHALL indicate that the alarm SHOULD be enabled while a value of 0 SHALL indicate that the alarm SHOULD be suppressed.
A server that receives this command with a Mask that includes bits that are set for unknown alarms SHALL respond with a status code of INVALID_COMMAND.
A server that receives this command with a Mask that includes bits that are set for alarms which are not supported, as indicated in the Supported attribute, SHALL respond with a status code of INVALID_COMMAND.
A server that is unable to enable a currently suppressed alarm, or is unable to suppress a currently enabled alarm SHALL respond with a status code of FAILURE; otherwise the server SHALL respond with a status code of SUCCESS.
On a SUCCESS case, the server SHALL also change the value of the Mask attribute to the value of the Mask field from this command. After that the server SHALL also update the value of its State attribute to reflect the status of the new alarm set as indicated by the new value of the Mask attribute.
1.14.8. Events
| ID | Name | Priority | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | Notify | INFO | V | M |
1.14.8.1. Notify Event
This event SHALL be generated when one or more alarms change state, and SHALL have these fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Active | all | 0 | M | ||
1 | Inactive | all | 0 | M | ||
2 | State | all | 0 | M | ||
3 | Mask | all | 0 | M |
2. Measurement and Sensing
The Cluster Library is made of individual chapters such as this one. See Document Control in the Cluster Library for a list of all chapters and documents. References between chapters are made using a X.Y notation where X is the chapter and Y is the sub-section within that chapter. References to external documents are contained in Chapter 1 and are made using [ Rn ] notation.
2.1. General Description
2.1.1. Introduction
The clusters specified in this document are generic measurement and sensing interfaces that are sufficiently general to be of use across a wide range of application domains.
2.1.2. Cluster List
This section lists the measurement and sensing clusters as specified in this chapter.
| Cluster ID | Cluster Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0x0400 |
Attributes and commands for configuring the measurement of illuminance, and reporting illuminance measurements |
|
|
0x0402 |
Attributes and commands for configuring the measurement of temperature, and reporting temperature measurements |
|
|
0x0403 |
Attributes and commands for configuring the measurement of pressure, and reporting pressure measurements |
|
|
0x0404 |
Attributes and commands for configuring the measurement of flow, and reporting flow rates |
|
|
0x0405 |
Supports configuring the measurement of relative humidity, and reporting relative humidity measurements of water in the air |
|
|
0x0407 |
Supports configuring the measurement of relative humidity, and reporting relative humidity measurements of water on the leaves of plants |
|
|
0x0408 |
Supports configuring the measurement of relative humidity, and reporting relative humidity measurements of water in the soil |
|
|
0x0406 |
Attributes and commands for configuring occupancy sensing, and reporting occupancy status |
|
|
0x005C | An interface to smoke and CO alarms | |
various | Attributes and commands for reporting conditions of various resources | |
0x005B | Attributes for reporting air quality classification | |
various | Attributes and aliases for concentration measurements. |
2.1.3. Measured Value
This section provides requirements on the attributes MeasuredValue, MinMeasuredValue, MaxMeasuredValue, Tolerance as used in various clusters defined in this chapter.
2.1.3.1. Constraint
Where MinMeasuredValue or MaxMeasuredValue attributes are mandatory the null value MAY be used to indicate that a limit is unknown.
For any measurement cluster with MeasuredValue, MinMeasuredValue and MaxMeasuredValue attributes, the following SHALL be always be true:
-
If MinMeasuredValue and MaxMeasuredValue are both known, then MaxMeasuredValue SHALL be greater than MinMeasuredValue.
-
If MaxMeasuredValue is known, then MeasuredValue SHALL be less than or equal to MaxMeasuredValue.
-
If MinMeasuredValue is known, then MeasuredValue SHALL be greater than or equal to MinMeasuredValue.
2.1.3.2. Tolerance
For any measurement cluster with a MeasuredValue and Tolerance attribute, when Tolerance is implemented the following SHALL always be true:
-
The Tolerance attribute SHALL indicate the magnitude of the possible error that is associated with MeasuredValue attribute, using the same units and resolution. The true value SHALL be in the range (MeasuredValue – Tolerance) to (MeasuredValue + Tolerance).
-
If known, the true value SHALL never be outside the possible physical range. Some examples:
-
a temperature SHALL NOT be below absolute zero
-
a concentration SHALL NOT be negative
-
2.2. Illuminance Measurement Cluster
The Illuminance Measurement cluster provides an interface to illuminance measurement functionality, including configuration and provision of notifications of illuminance measurements.
2.2.2.
2.2.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
CCB 2167 |
|
3 |
|
2.2.3.
2.2.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
|
2.2.5.
Attributes
2.2.4.
Data
Types
2.2.4.1. LightSensorTypeEnum Type
The
Illuminance
Measurement
attributes
are
summarized
in
Illuminance
Measurement
Attributes
.
This
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Photodiode | Indicates photodiode sensor type | M |
1 | CMOS | Indicates CMOS sensor type | M |
64 to 254 | MS | Reserved for manufacturer specific light sensor types | O |
2.2.5. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
MeasuredValue |
uint16 |
0, MinMeasuredValue to MaxMeasuredValue |
PX |
0 |
R V |
M |
|
0x0001 |
MinMeasuredValue |
uint16 |
1 to MaxMeasuredValue-1 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0002 |
MaxMeasuredValue |
uint16 |
MinMeasuredValue+1 to 65534 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0003 |
Tolerance |
uint16 |
0 to 2048 |
R V |
O |
||
|
0x0004 |
LightSensorType |
|
all |
X |
null |
R V |
O |
2.2.5.1. MeasuredValue Attribute
The MeasuredValue attribute represents the illuminance in Lux (symbol lx) as follows:
-
MeasuredValue = 10,000 x log 10 (illuminance) + 1,
where
1
lx
≤
\$<=\$
illuminance
≤
\$<=\$
3.576
Mlx,
corresponding
to
a
MeasuredValue
in
the
range
1
to
0xfffe.
0xFFFE.
The MeasuredValue attribute can take the following values:
-
0 indicates a value of illuminance that is too low to be measured,
-
MinMeasuredValue
≤\$<=\$ MeasuredValue≤\$<=\$ MaxMeasuredValue under normal circumstances, -
null indicates that the illuminance measurement is invalid.
The MeasuredValue attribute is updated continuously as new measurements are made.
2.2.5.2. MinMeasuredValue Attribute
The MinMeasuredValue attribute indicates the minimum value of MeasuredValue that can be measured. A value of null indicates that this attribute is not defined. See Measured Value for more details.
2.2.5.3. MaxMeasuredValue Attribute
The MaxMeasuredValue attribute indicates the maximum value of MeasuredValue that can be measured. A value of null indicates that this attribute is not defined. See Measured Value for more details.
2.2.5.4. Tolerance Attribute
See Measured Value .
2.2.5.5. LightSensorType Attribute
The
LightSensorType
attribute
specifies
the
electronic
type
of
the
light
sensor.
This
attribute
shall
SHALL
be
set
to
one
of
the
non-reserved
values
listed
in
Values
of
the
LightSensorType
Attribute
.
Table
29.
Values
of
LightSensorTypeEnum
or
null
in
case
the
LightSensorType
Attribute
Value
Description
0
Photodiode
1
CMOS
0x40
to
0xfe
Reserved
for
manufacturer
specific
light
sensor
types
null
Unknown
type
is
unknown.
2.3. Temperature Measurement Cluster
This cluster provides an interface to temperature measurement functionality, including configuration and provision of notifications of temperature measurements.
2.3.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
CCB 2241 2370 |
|
3 |
CCB 2823 |
|
4 |
New data model format and notation |
2.3.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
TMP |
2.3.4. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
MeasuredValue |
|
MinMeasuredValue to MaxMeasuredValue |
XP |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0001 |
MinMeasuredValue |
|
-27315 to MaxMeasuredValue-1 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0002 |
MaxMeasuredValue |
|
MinMeasuredValue+1 to 32767 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0003 |
Tolerance |
uint16 |
0 to 2048 |
0 |
R V |
O |
2.3.4.1. MeasuredValue Attribute
Represents
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
temperature
in
degrees
Celsius
as
follows:
MeasuredValue
=
100
x
temperature
[°C]
Where
-273.15°C
≤
temperature
≤
327.67°C,
with
a
resolution
of
0.01°C.
measured
temperature.
The null value indicates that the temperature is unknown.
2.3.4.2. MinMeasuredValue Attribute
The
MinMeasuredValue
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
minimum
value
of
MeasuredValue
that
is
capable
of
being
measured.
See
Measured
Value
for
more
details.
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.3.4.3. MaxMeasuredValue Attribute
The
MaxMeasuredValue
This
attribute
indicates
the
maximum
value
of
MeasuredValue
that
is
capable
of
being
measured.
See
Measured
Value
for
more
details.
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.3.4.4. Tolerance Attribute
See Measured Value .
2.4. Pressure Measurement Cluster
This cluster provides an interface to pressure measurement functionality, including configuration and provision of notifications of pressure measurements.
2.4.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Mandatory global ClusterRevision attribute added |
|
2 |
CCB 2241 2370 |
|
3 |
New data model format and notation |
2.4.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
PRS |
2.4.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
EXT |
Extended |
|
|
2.4.5. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
MeasuredValue |
int16 |
MinMeasuredValue to MaxMeasuredValue |
XP |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0001 |
MinMeasuredValue |
int16 |
-32767 to MaxMeasuredValue-1 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0002 |
MaxMeasuredValue |
int16 |
MinMeasuredValue+1 to 32767 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0003 |
Tolerance |
uint16 |
0 to 2048 |
0 |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0010 |
ScaledValue |
int16 |
MinScaledValue to MaxScaledValue |
X |
0 |
R V |
EXT |
|
0x0011 |
MinScaledValue |
int16 |
-32767 to MaxScaledValue-1 |
X |
0 |
R V |
EXT |
|
0x0012 |
MaxScaledValue |
int16 |
MinScaledValue+1 to 32767 |
X |
0 |
R V |
EXT |
|
0x0013 |
ScaledTolerance |
uint16 |
0 to 2048 |
0 |
R V |
[EXT] |
|
|
0x0014 |
Scale |
int8 |
-127 to 127 |
0 |
R V |
EXT |
2.4.5.1. MeasuredValue Attribute
This
attribute
represents
SHALL
represent
the
pressure
in
kPa
as
follows:
MeasuredValue = 10 x Pressure [kPa]
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.4.5.2. MinMeasuredValue Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
minimum
value
of
MeasuredValue
that
can
be
measured.
See
Measured
Value
for
more
details.
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.4.5.3. MaxMeasuredValue Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
value
of
MeasuredValue
that
can
be
measured.
See
Measured
Value
for
more
details.
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.4.5.4. Tolerance Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
the
magnitude
of
the
possible
error
that
is
associated
with
ScaledValue.
See
Measured
Value
.
2.4.5.5. ScaledValue Attribute
ScaledValue
represents
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
pressure
in
Pascals
as
follows:
ScaledValue = 10 Scale x Pressure [Pa]
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.4.5.6. MinScaledValue Attribute
The
MinScaledValue
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
minimum
value
of
ScaledValue
that
can
be
measured.
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.4.5.7. MaxScaledValue Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
value
of
ScaledValue
that
can
be
measured.
MaxScaledValue
SHALL
be
greater
than
MinScaledValue.
The
null
value
indicates
that
the
value
is
not
available.
2.4.5.8. ScaledTolerance Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
magnitude
of
the
possible
error
that
is
associated
with
ScaledValue.
The
true
value
is
located
in
the
range
(ScaledValue – ScaledTolerance) to (ScaledValue + ScaledTolerance).
2.4.5.9. Scale Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
base
10
exponent
used
to
obtain
ScaledValue
(see
ScaledValue
Attribute
).
2.5. Flow Measurement Cluster
This cluster provides an interface to flow measurement functionality, including configuration and provision of notifications of flow measurements.
2.5.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Mandatory global ClusterRevision attribute added |
|
2 |
CCB 2241 2370 |
|
3 |
New data model format and notation |
2.5.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
FLW |
2.5.4. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
MeasuredValue |
uint16 |
MinMeasuredValue to MaxMeasuredValue |
XP |
null |
R V |
M |
|
0x0001 |
MinMeasuredValue |
uint16 |
0 to MaxMeasuredValue-1 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0002 |
MaxMeasuredValue |
uint16 |
MinMeasuredValue+1 to 65534 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0003 |
Tolerance |
uint16 |
0 to 2048 |
0 |
R V |
O |
2.5.4.1. MeasuredValue Attribute
MeasuredValue represents the flow in m 3 /h as follows:
MeasuredValue = 10 x Flow
The null value indicates that the flow measurement is unknown, otherwise the range SHALL be as described in Measured Value .
2.5.4.2. MinMeasuredValue Attribute
The MinMeasuredValue attribute indicates the minimum value of MeasuredValue that can be measured. See Measured Value for more details.
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.5.4.3. MaxMeasuredValue Attribute
The MaxMeasuredValue attribute indicates the maximum value of MeasuredValue that can be measured. See Measured Value for more details.
The null value indicates that the value is not available.
2.5.4.4. Tolerance Attribute
See Measured Value .
2.6. Water Content Measurement Clusters
This is a base cluster. The server cluster provides an interface to water content measurement functionality. The measurement is reportable and may be configured for reporting. Water content measurements include, but are not limited to, leaf wetness, relative humidity, and soil moisture.
2.6.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Mandatory global ClusterRevision attribute added |
|
2 |
CCB 2241 |
|
3 |
New data model format and notation |
2.6.3.
Cluster
Identifiers
IDs
The table below is a list of Cluster IDs that conform to this specification.
|
|
Name |
|
|---|---|---|
|
0x0405 |
Relative Humidity Measurement |
Percentage of water in the air |
|
0x0407 |
Leaf Wetness Measurement |
Percentage
of
water
|
|
0x0408 |
Soil Moisture Measurement |
Percentage of water in the soil |
2.6.4. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
MeasuredValue |
uint16 |
MinMeasuredValue to MaxMeasuredValue |
XP |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0001 |
MinMeasuredValue |
uint16 |
0 to MaxMeasuredValue-1 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0002 |
MaxMeasuredValue |
uint16 |
MinMeasuredValue+1 to 10000 |
X |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0003 |
Tolerance |
uint16 |
0 to 2048 |
R V |
O |
2.6.4.1. MeasuredValue Attribute
MeasuredValue represents the water content in % as follows:
MeasuredValue = 100 x water content
Where 0% < = water content < = 100%, corresponding to a MeasuredValue in the range 0 to 10000.
The maximum resolution this format allows is 0.01%.
MinMeasuredValue and MaxMeasuredValue define the range of the sensor.
The null value indicates that the measurement is unknown, otherwise the range SHALL be as described in Measured Value .
MeasuredValue is updated continuously as new measurements are made.
2.6.4.2. MinMeasuredValue Attribute
The MinMeasuredValue attribute indicates the minimum value of MeasuredValue that can be measured. The null value means this attribute is not defined. See Measured Value for more details.
2.6.4.3. MaxMeasuredValue Attribute
The MaxMeasuredValue attribute indicates the maximum value of MeasuredValue that can be measured. The null value means this attribute is not defined. See Measured Value for more details.
2.6.4.4. Tolerance Attribute
See Measured Value .
2.7. Occupancy Sensing Cluster
The server cluster provides an interface to occupancy sensing functionality, including configuration and provision of notifications of occupancy status.
2.7.2.
2.7.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
Physical Contact Occupancy feature with mandatory OccupancySensorTypeBitmap |
|
3 |
|
2.7.3.
2.7.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
|
2.7.5.
Occupancy
Sensor
Information
Attribute
Set
2.7.4.
Data
Types
2.7.4.1. OccupancyBitmap Type
For
convenience,
This
data
type
is
derived
from
map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Occupied |
Indicates
the
| M |
2.7.4.2. OccupancySensorTypeBitmap Type
The
occupancy
sensor
information
attribute
set
contains
the
attributes
summarized
in
Occupancy
Sensor
Information
Attribute
Set
.
This
data
type
is
derived
from
map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | PIR | Indicates a passive infrared sensor. | M |
1 | Ultrasonic | Indicates a ultrasonic sensor. | M |
2 | PhysicalContact | Indicates a physical contact sensor. | M |
2.7.4.3. OccupancySensorTypeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | PIR | Indicates a passive infrared sensor. | M |
1 | Ultrasonic | Indicates a ultrasonic sensor. | M |
2 | PIRAndUltrasonic | Indicates a passive infrared and ultrasonic sensor. | M |
3 | PhysicalContact | Indicates a physical contact sensor. | M |
2.7.5. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
Occupancy |
|
|
P |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0001 |
OccupancySensorType |
|
desc |
MS |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0002 |
OccupancySensorTypeBitmap |
|
R V |
M |
|||
|
0x0010 | PIROccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay | uint16 | all | 0 | RW VM | O | |
0x0011 | PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay | uint16 | all | 0 | RW VM | PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold, O | |
0x0012 | PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold | uint8 | 1 to 254 | 1 | RW VM | PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay, O | |
0x0020 | UltrasonicOccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay | uint16 | all | 0 | RW VM | O | |
0x0021 | UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay | uint16 | all | 0 | RW VM | UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold, O | |
0x0022 | UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold | uint8 | 1 to 254 | 1 | RW VM | UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay, O | |
0x0030 | PhysicalContactOccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay | uint16 | all | X | 0 | RW VM | O |
0x0031 | PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay | uint16 | all | X | 0 | RW VM | O |
0x0032 | PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold | uint8 | 1 to 254 | 1 | RW VM | PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay, O |
2.7.5.1. Occupancy Attribute
The
Occupancy
This
attribute
is
a
bitmap.
indicates
the
sensed
(processed)
status
of
occupancy.
2.7.5.2. OccupancySensorType Attribute
Bit
0
This
attribute
specifies
the
sensed
type
of
the
occupancy
sensor.
2.7.5.3. OccupancySensorTypeBitmap Attribute
This attribute specifies the types of the occupancy sensor. Each bit position, if set, indicates the corresponding sensing capability is implemented.
The
value
of
the
OccupancySensorType
SHALL
be
aligned
to
the
value
of
the
OccupancySensorTypeBitmap
attribute
as
follows:
1
=
occupied,
0
=
unoccupied.
defined
below.
| OccupancySensorTypeBitmap | OccupancySensorType |
|---|---|
PIR | PIR |
Ultrasonic | Ultrasonic |
PIR + Ultrasonic | PIRAndUltrasonic |
PhysicalContact | PhysicalContact |
PhysicalContact + PIR | PIR |
PhysicalContact + Ultrasonic | Ultrasonic |
PhysicalContact + PIR + Ultrasonic | PIRAndUltrasonic |
2.7.5.4. PIROccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay Attribute
All
other
bits
are
reserved.
This
attribute
specifies
the
time
delay,
in
seconds,
before
the
PIR
sensor
changes
to
its
unoccupied
state
after
the
last
detection
of
movement
in
the
sensed
area.
2.7.5.2.
OccupancySensorType
2.7.5.5.
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
Attribute
The
OccupancySensorType
This
attribute
specifies
the
type
time
delay,
in
seconds,
before
the
PIR
sensor
changes
to
its
occupied
state
after
the
detection
of
movement
in
the
occupancy
sensor.
sensed
area.
This
attribute
shall
be
set
is
mandatory
if
the
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
attribute
is
implemented.
2.7.5.6. PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
the
number
of
movement
detection
events
that
must
occur
in
the
period
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay,
before
the
PIR
sensor
changes
to
one
its
occupied
state.
This
attribute
is
mandatory
if
the
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
attribute
is
implemented.
2.7.5.7. UltrasonicOccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
the
time
delay,
in
seconds,
before
the
Ultrasonic
sensor
changes
to
its
unoccupied
state
after
the
last
detection
of
movement
in
the
non-reserved
values
listed
sensed
area.
2.7.5.8. UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
the
time
delay,
in
Values
seconds,
before
the
Ultrasonic
sensor
changes
to
its
occupied
state
after
the
detection
of
movement
in
the
OccupancySensorType
sensed
area.
This
attribute
is
mandatory
if
the
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
attribute
is
implemented.
2.7.5.9.
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
Attribute
.
This attribute specifies the number of movement detection events that must occur in the period UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay, before the Ultrasonic sensor changes to its occupied state. This attribute is mandatory if the UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay attribute is implemented.
2.7.5.10. PhysicalContactOccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay Attribute
This attribute specifies the time delay, in seconds, before the physical contact occupancy sensor changes to its unoccupied state after detecting the unoccupied event. The null value indicates that the sensor does not report occupied to unoccupied transition.
2.7.5.11. PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
the
time
delay,
in
seconds,
before
the
physical
contact
sensor
changes
to
its
occupied
state
after
the
detection
of
the
OccupancySensorType
occupied
event.
The null value indicates that the sensor does not report unoccupied to occupied transition.
2.7.5.12. PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold Attribute
This attribute specifies the number of movement detection events that must occur in the period PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay, before the PIR sensor changes to its occupied state. This attribute is mandatory if the PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay attribute is implemented.
2.8. Resource Monitoring Clusters
This generic cluster provides an interface to the current condition of a resource. A resource is a component of a device that is designed to be replaced, refilled, or emptied when exhausted or full. Examples of resources include filters, cartridges, and water tanks. While batteries fit this definition they are not intended to be used with this cluster. Use the power source cluster for batteries instead.
Note
| This cluster is not meant to be used for monitoring of the system resources, such as processing, memory utilization, networking properties, etc. |
This cluster SHALL be used via an alias to a specific resource type (see Cluster IDs ).
2.8.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 | Initial version of the Resource Monitoring cluster |
2.8.3. Cluster IDs
The table below is a list of aliased Cluster IDs which represent different resource types and conform to this cluster definition.
| ID | Name | Resource Type | PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
0x0071 | HEPA Filter Monitoring | HEPA Filter | HEPAFREMON |
0x0072 | Activated Carbon Filter Monitoring | Activated Carbon Filter | ACFREMON |
2.8.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
| Condition | O | Supports monitoring the condition of the resource in percentage |
|
1 |
| Warning | O | Supports warning indication |
|
2 |
|
|
| Supports specifying the list of replacement products |
2.8.5. Data Types
2.7.5.3.
OccupancySensorTypeBitmap
Attribute
2.8.5.1.
DegradationDirectionEnum
Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
Indicates the direction in which the condition of the resource changes over time.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Up |
The
| M |
1 | Down |
The
degradation
of
the
| M |
2.8.5.2. ChangeIndicationEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | OK |
Resource
is
in
| M |
1 | Warning | Resource will be exhausted soon, intervention will shortly be required | WRN |
2 | Critical | Resource is exhausted, immediate intervention is required | M |
2.8.5.3. ProductIdentifierTypeEnum Type
This
data
type
is
implemented.
derived
from
enum8.
Indicate the type of identifier used to describe the product. Devices SHOULD use globally-recognized IDs over OEM specific ones.
|
|
| Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
| 12-digit Universal Product Code | M |
|
1 |
| 8-digit Global Trade Item Number | M |
|
2 |
| 13-digit European Article Number | M |
3 | GTIN-14 | 14-digit Global Trade Item Number | M |
4 | OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer part number | M |
2.8.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x0000 | Condition | percent | R V | CON | |||
0x0001 | DegradationDirection | desc | F | R V | CON | ||
0x0002 | ChangeIndication | 0 | R V | M | |||
0x0003 | InPlaceIndicator | bool | R V | O | |||
0x0004 | LastChangedTime | epoch-s | all | X N | null | RW VO | O |
0x0005 | ReplacementProductList | list[ ReplacementProductStruct ] | max 5 | F | R V | REP |
2.8.6.1. Condition Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the current condition of the resource in percent.
2.8.6.2. DegradationDirection Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the direction of change for the condition of the resource over time, which helps to determine whether a higher or lower condition value is considered optimal.
2.8.6.3. ChangeIndication Attribute
This attribute SHALL be populated with a value from ChangeIndicationEnum that is indicative of the current requirement to change the resource.
2.8.6.4. InPlaceIndicator Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate whether a resource is currently installed. A value of true SHALL indicate that a resource is installed. A value of false SHALL indicate that a resource is not installed.
2.8.6.5. LastChangedTime Attribute
This
attribute
MAY
indicates
the
OccupancySensorTypeBitmap
time
at
which
the
resource
has
been
changed,
if
supported
by
the
server.
The
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
it
was
never
set
or
is
unknown.
2.8.6.6. ReplacementProductList Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the list of supported products that may be used as replacements for the current resource. Each item in this list represents a unique ReplacementProductStruct .
2.8.7. Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | ResetCondition | client ⇒ server | Y | O | O |
2.8.7.1. ResetCondition Command
Upon
receipt,
the
device
SHALL
reset
the
Condition
and
ChangeIndicator
attributes,
indicating
full
resource
availability
and
readiness
for
use,
as
initially
configured.
Invocation
of
this
command
MAY
cause
the
OccupancySensorType
LastChangedTime
to
be
updated
automatically
based
on
the
clock
of
the
server,
if
the
server
supports
setting
the
attribute.
2.9. Air Quality Cluster
This cluster provides an interface to air quality classification using distinct levels with human-readable labels.
2.9.1. Revision History
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
be
aligned
as
defined
the
highest
revision
number
in
the
table
below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 | Initial version of the Air Quality cluster |
2.9.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role | Scope | PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
AIRQUAL |
2.9.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | FAIR | Fair | O | Cluster supports the Fair air quality level |
|
1 |
| Moderate | O | Cluster supports the Moderate air quality level |
|
| VPOOR | VeryPoor | O | Cluster supports the Very poor air quality level |
3 | XPOOR | ExtremelyPoor | O | Cluster supports the Extremely poor air quality level |
2.9.5. Data Types
2.9.5.1. AirQualityEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
The
AirQualityEnum
provides
a
representation
of
the
quality
of
the
analyzed
air.
It
is
up
to
the
device
manufacturer
to
determine
the
mapping
between
the
measured
values
and
ultrasonic
their
corresponding
enumeration
values.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Unknown | The air quality is unknown. | M |
1 | Good | The air quality is good. | M |
|
2 |
| The air quality is fair. | FAIR |
|
|
|
| MOD |
|
|
|
| M |
|
|
|
| VPOOR |
6 | ExtremelyPoor | The air quality is extremely poor. | XPOOR |
2.7.6.
PIR
Configuration
2.9.6.
Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x0000 | AirQuality | desc | 0 | R V | M |
2.9.6.1.
AirQuality
Attribute
Set
This attribute SHALL indicate a value from AirQualityEnum that is indicative of the currently measured air quality.
2.10. Concentration Measurement Clusters
The server cluster provides an interface to concentration measurement functionality.
This cluster SHALL to be used via an alias to a specific substance (see Cluster IDs ).
2.10.1. Revision History
The
PIR
sensor
configuration
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
set
contains
value
SHALL
be
the
attributes
summarized
highest
revision
number
in
Attributes
the
table
below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Mandatory global ClusterRevision attribute added |
2 | CCB 2882 |
3 | Cluster redesigned to add support for Level Indication, Peak/Average Measurement, Medium/Unit of Measurement and Uncertainty. |
2.10.3. Cluster IDs
The table below is a list of Cluster IDs that conform to this specification.
| ID | Name | Substance Measured | PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
0x040C | Carbon Monoxide Concentration Measurement | Carbon Monoxide (CO) | CMOCONC |
0x040D | Carbon Dioxide Concentration Measurement | Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) | CDOCONC |
0x0413 | Nitrogen Dioxide Concentration Measurement | Nitrogen Dioxide (NO 2 ) | NDOCONC |
0x0415 | Ozone Concentration Measurement | Ozone (O 3 ) | OZCONC |
0x042A | PM2.5 Concentration Measurement | PM2.5 | PMICONC |
0x042B | Formaldehyde Concentration Measurement | Formaldehyde (CH2O) | FLDCONC |
0x042C | PM1 Concentration Measurement | PM1 | PMHCONC |
0x042D | PM10 Concentration Measurement | PM10 | PMKCONC |
0x042E | Total Volatile Organic Compounds Concentration Measurement | Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOC) | TVOCCONC |
0x042F | Radon Concentration Measurement | Radon (Rn) | RNCONC |
2.10.4. Features
This
cluster
SHALL
support
the
PIR
Configuration
Attribute
Set
.
FeatureMap
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | MEA | NumericMeasurement | O.a+ | Cluster supports numeric measurement of substance |
1 | LEV | LevelIndication | O.a+ |
Cluster
supports
basic
level
indication
for
substance
using
the
|
2 | MED | MediumLevel | [LEV] | Cluster supports the Medium Concentration Level |
3 | CRI | CriticalLevel | [LEV] | Cluster supports the Critical Concentration Level |
4 | PEA | PeakMeasurement | [MEA] | Cluster supports peak numeric measurement of substance |
5 | AVG | AverageMeasurement | [MEA] | Cluster supports average numeric measurement of substance |
2.10.5. Data Types
2.10.5.1. MeasurementUnitEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | PPM | Parts per Million (10 6 ) | MEA |
1 | PPB | Parts per Billion (10 9 ) | MEA |
2 | PPT | Parts per Trillion (10 12 ) | MEA |
3 | MGM3 | Milligram per m 3 | MEA |
4 | UGM3 | Microgram per m 3 | MEA |
5 | NGM3 | Nanogram per m 3 | MEA |
6 | PM3 | Particles per m 3 | MEA |
7 | BQM3 | Becquerel per m 3 | MEA |
Where mentioned, Billion refers to 10 9 , Trillion refers to 10 12 (short scale).
2.10.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
X P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| min MinMeasuredValue | X | null | R V | MEA |
0x0003 | PeakMeasuredValue | single | MinMeasuredValue to MaxMeasuredValue | X P | null | R V | PEA |
0x0004 | PeakMeasuredValueWindow | elapsed-s | max 604800 | P |
1 |
R V | PEA |
0x0005 | AverageMeasuredValue | single |
MinMeasuredValue
to
|
X P | null | R V | AVG |
0x0006 | AverageMeasuredValueWindow | elapsed-s | max 604800 | P |
1 |
|
|
0x0007 | Uncertainty | single | MS | MS | R V | [MEA] | |
0x0008 | MeasurementUnit | F | MS | R V | MEA | ||
0x0009 | MeasurementMedium | F | MS | R V | M | ||
0x000A | LevelValue | 0 | R V | LEV |
2.7.6.1.
PIROccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay
2.10.6.1.
MeasuredValue
Attribute
The
PIROccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
represent
the
time
delay,
in
seconds,
before
most
recent
measurement
as
a
single-precision
floating-point
number.
MeasuredValue’s
unit
is
represented
by
MeasurementUnit.
A
value
of
null
indicates
that
the
PIR
sensor
changes
to
its
unoccupied
state
after
measurement
is
unknown
or
outside
the
last
detection
valid
range.
MinMeasuredValue and MaxMeasuredValue define the valid range for MeasuredValue.
2.10.6.2. MinMeasuredValue Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
minimum
value
of
movement
in
MeasuredValue
that
is
capable
of
being
measured.
A
MinMeasuredValue
of
null
indicates
that
the
sensed
area.
MinMeasuredValue
is
not
defined.
2.7.6.2.
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
2.10.6.3.
MaxMeasuredValue
Attribute
The
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
represent
the
maximum
value
of
MeasuredValue
that
is
capable
of
being
measured.
A
MaxMeasuredValue
of
null
indicates
that
the
MaxMeasuredValue
is
not
defined.
2.10.6.4. PeakMeasuredValue Attribute
This attribute SHALL represent the maximum value of MeasuredValue that has been measured during the PeakMeasuredValueWindow . If this attribute is provided, the PeakMeasuredValueWindow attribute SHALL also be provided.
2.10.6.5. PeakMeasuredValueWindow Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
window
of
time
delay,
used
for
determining
the
PeakMeasuredValue.
The
value
is
in
seconds,
before
seconds.
2.10.6.6. AverageMeasuredValue Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
PIR
sensor
changes
to
its
occupied
state
after
average
value
of
MeasuredValue
that
has
been
measured
during
the
detection
AverageMeasuredValueWindow
.
If
this
attribute
is
provided,
the
AverageMeasuredValueWindow
attribute
SHALL
also
be
provided.
2.10.6.7. AverageMeasuredValueWindow Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
window
of
movement
in
time
used
for
determining
the
sensed
area.
AverageMeasuredValue.
The
value
is
in
seconds.
2.10.6.8. Uncertainty Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
range
of
error
or
deviation
that
can
be
found
in
MeasuredValue
and
PeakMeasuredValue.
This
is
mandatory
if
considered
a
+/-
value
and
should
be
considered
to
be
in
MeasurementUnit.
2.10.6.9. MeasurementUnit Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
unit
of
MeasuredValue.
See
MeasurementUnitEnum
.
2.10.6.10. MeasurementMedium Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
medium
in
which
MeasuredValue
is
implemented.
being
measured.
See
MeasurementMediumEnum
.
2.7.6.3.
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
2.10.6.11.
LevelValue
Attribute
This attribute SHALL represent the level of the substance detected. See LevelValueEnum .
2.11. Smoke CO Alarm Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for observing and managing the state of smoke and CO alarms.
2.11.1. Revision History
The
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
specifies
value
SHALL
be
the
highest
revision
number
of
movement
detection
events
that
must
occur
in
the
period
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay,
before
table
below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial Release |
2.11.4. Features
This
cluster
SHALL
support
the
PIR
sensor
changes
FeatureMap
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | SMOKE | SmokeAlarm | O.a+ | Supports Smoke alarm |
1 | CO | COAlarm | O.a+ | Supports CO alarm |
2.11.5. Data Types
2.11.5.1. AlarmStateEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Normal | Nominal state, the device is not alarming | M |
1 | Warning | Warning state | O |
2 | Critical | Critical state | M |
2.11.5.2. SensitivityEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | High | High sensitivity | O |
1 | Standard | Standard Sensitivity | M |
2 | Low | Low sensitivity | O |
2.11.5.3. ExpressedStateEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Normal | Nominal state, the device is not alarming | M |
1 | SmokeAlarm | Smoke Alarm state | SMOKE |
2 | COAlarm | CO Alarm state | CO |
3 | BatteryAlert | Battery Alert State | M |
4 | Testing | Test in Progress | M |
5 | HardwareFault | Hardware Fault Alert State | M |
6 | EndOfService | End of Service Alert State | M |
7 | InterconnectSmoke | Interconnected Smoke Alarm State | O |
8 | InterconnectCO | Interconnected CO Alarm State | O |
2.11.5.3.2. SmokeAlarm Value
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
this
alarm
is
currently
expressing
visual
indication
of
Smoke
Alarm.
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
the
alarm
is
currently
expressing
audible
indication
of
Smoke
Alarm
unless
the
DeviceMuted
attribute
is
mandatory
if
supported
and
set
to
Muted.
2.11.5.3.3. COAlarm Value
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
this
alarm
is
currently
expressing
visual
indication
of
CO
Alarm.
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
the
PIRUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
alarm
is
currently
expressing
audible
indication
of
CO
Alarm
unless
the
DeviceMuted
attribute
is
implemented.
supported
and
set
to
Muted.
2.11.5.3.4. BatteryAlert Value
This value SHALL indicate that this alarm is currently expressing visual indication of Critical Low Battery. This value SHALL indicate that the alarm is currently expressing audible indication of Critical Low Battery unless the DeviceMuted attribute is supported and set to Muted.
2.7.7.
Ultrasonic
Configuration
Attribute
Set
2.11.5.3.5.
Testing
Value
The
ultrasonic
sensor
configuration
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
this
alarm
is
currently
expressing
visual
and
audible
indication
of
SelfTest.
2.11.5.3.6. HardwareFault Value
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
this
alarm
is
currently
expressing
visual
indication
of
Hardware
Fault.
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
the
alarm
is
currently
expressing
audible
indication
of
Hardware
Fault
unless
the
DeviceMuted
attribute
is
supported
and
set
contains
to
Muted.
2.11.5.3.7. EndOfService Value
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
this
alarm
is
currently
expressing
visual
indication
of
End
Of
Service.
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
the
attributes
summarized
in
Attributes
alarm
is
currently
expressing
audible
indication
of
End
of
Service
unless
the
Ultrasonic
Configuration
Attribute
Set
.
DeviceMuted
attribute
is
supported
and
set
to
Muted.
2.11.5.3.8. InterconnectSmoke Value
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
this
alarm
is
currently
expressing
visual
indication
of
Smoke
Alarm
caused
by
Interconnect.
This
value
SHALL
indicate
that
the
Ultrasonic
Configuration
Attribute
Set
alarm
is
currently
expressing
audible
indication
of
Smoke
Alarm
caused
by
Interconnect
unless
the
DeviceMuted
attribute
is
supported
and
set
to
Muted.
2.11.5.3.9. InterconnectCO Value
This value SHALL indicate that this alarm is currently expressing visual indication of CO Alarm caused by Interconnect. This value SHALL indicate that the alarm is currently expressing audible indication of CO Alarm caused by Interconnect unless the DeviceMuted attribute is supported and set to Muted.
2.11.5.4. MuteStateEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | NotMuted | Not Muted | M |
1 | Muted | Muted | M |
2.11.5.5. EndOfServiceEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Normal | Device has not expired | M |
1 | Expired | Device has reached its end of service | M |
2.11.5.6. ContaminationStateEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Normal | Nominal state, the sensor is not contaminated | M |
1 | Low | Low contamination | O |
2 | Warning | Warning state | O |
3 | Critical | Critical state, will cause nuisance alarms | M |
2.11.5.6.1. Normal Value
This value SHALL indicate that the smoke sensor has nominal contamination levels, no customer action is required.
2.11.5.6.2. Low Value
This value SHALL indicate that the smoke sensor has detectable contamination levels, but the contamination is too low to cause a visible or audible alarm.
2.11.5.6.3. Warning Value
This value SHALL indicate that the smoke sensor has contamination levels in a warning state. At this level, the contamination may cause a visible or audible alarm. User intervention is suggested.
2.11.5.6.4. Critical Value
This value SHALL indicate that the smoke sensor has contamination levels in a critical state. At this level, the contamination should cause a visible or audible alarm. User intervention is required. Critical contamination of the sensor SHALL also be reflected as a HardwareFault.
2.11.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
all |
N |
|
| |
0x0001 | SmokeState | all | N | R V | SMOKE | ||
0x0002 | COState | all | N | R V | CO | ||
0x0003 | BatteryAlert | all | N | R V | M | ||
0x0004 | DeviceMuted | all | N | R V |
O |
||
|
|
|
|
all |
|
| ||
0x0006 | HardwareFaultAlert | bool | all | N | R V | M | |
0x0007 | EndOfServiceAlert | all | N | R V | M | ||
0x0008 | InterconnectSmokeAlarm | all | R V |
O |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
O | ||
0x000A | ContaminationState | all | R V | [SMOKE] | |||
0x000B | SmokeSensitivityLevel | all | RW VM |
[SMOKE] | |||
0x000C | ExpiryDate | epoch-s | all | F | R V | O |
2.7.7.1.
UltrasonicOccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay
2.11.6.1.
ExpressedState
Attribute
The
UltrasonicOccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
visibly-
and
specifies
audibly-expressed
state
of
the
time
delay,
alarm.
When
multiple
alarm
conditions
are
being
reflected
in
seconds,
before
the
Ultrasonic
sensor
changes
server,
this
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
condition
with
the
highest
priority.
Priority
order
of
conditions
is
determined
by
the
manufacturer
and
SHALL
be
supplied
as
a
part
of
certification
procedure.
If
the
value
of
ExpressedState
is
not
Normal,
the
attribute
corresponding
to
its
unoccupied
state
after
the
last
detection
value
SHALL
NOT
be
Normal.
For
example,
if
the
ExpressedState
is
set
to
SmokeAlarm,
the
value
of
movement
the
SmokeState
will
indicate
the
severity
of
the
alarm
(Warning
or
Critical).
Clients
SHOULD
also
read
the
other
attributes
to
be
aware
of
further
alarm
conditions
beyond
the
one
indicated
in
ExpressedState.
Visible
expression
is
typically
a
LED
light
pattern.
Audible
expression
is
a
horn
or
speaker
pattern.
Audible
expression
SHALL
BE
suppressed
if
the
sensed
area.
DeviceMuted
attribute
is
supported
and
set
to
Muted.
2.7.7.2.
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
2.11.6.2.
SmokeState
Attribute
The
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
This
attribute
and
specifies
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
time
delay,
in
seconds,
before
device’s
smoke
sensor
is
currently
triggering
a
smoke
alarm.
2.11.6.3. COState Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
Ultrasonic
device’s
CO
sensor
changes
is
currently
triggering
a
CO
alarm.
2.11.6.4. BatteryAlert Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
power
resource
fault
detection
mechanism
is
currently
triggered
at
the
device.
If
the
detection
mechanism
is
triggered,
this
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
its
occupied
Warning
or
Critical,
otherwise
it
SHALL
be
set
to
Normal.
The
battery
state
after
SHALL
also
be
reflected
in
the
detection
Power
Source
cluster
representing
the
device’s
battery
using
the
appropriate
supported
attributes
and
events.
2.11.6.5. DeviceMuted Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
whether
the
audible
expression
of
movement
in
the
sensed
area.
device
is
currently
muted.
Audible
expression
is
typically
a
horn
or
speaker
pattern.
2.11.6.6. TestInProgress Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
device
self-test
is
mandatory
if
currently
activated.
If
the
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
attribute
device
self-test
is
implemented.
activated,
this
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
True,
otherwise
it
SHALL
be
set
to
False.
2.7.7.3.
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
2.11.6.7.
HardwareFaultAlert
Attribute
The
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
number
of
movement
hardware
fault
detection
events
that
must
occur
in
mechanism
is
currently
triggered.
If
the
period
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay,
before
detection
mechanism
is
triggered,
this
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
True,
otherwise
it
SHALL
be
set
to
False.
2.11.6.8. EndOfServiceAlert Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
Ultrasonic
sensor
changes
end-of-service
has
been
triggered
at
the
device.
This
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
its
occupied
state.
Expired
when
the
device
reaches
the
end-of-service.
2.11.6.9. InterconnectSmokeAlarm Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
interconnected
smoke
alarm
is
mandatory
if
currently
triggering
by
branching
devices.
When
the
UltrasonicUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
attribute
interconnected
smoke
alarm
is
implemented.
being
triggered,
this
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
Warning
or
Critical,
otherwise
it
SHALL
be
set
to
Normal.
2.7.8.
Physical
Contact
Configuration
2.11.6.10.
InterconnectCOAlarm
Attribute
Set
The
physical
contact
configuration
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
interconnected
CO
alarm
is
currently
triggering
by
branching
devices.
When
the
interconnected
CO
alarm
is
being
triggered,
this
attribute
SHALL
be
set
contains
to
Warning
or
Critical,
otherwise
it
SHALL
be
set
to
Normal.
2.11.6.11. ContaminationState Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
attributes
summarized
below.
contamination
level
of
the
smoke
sensor.
2.11.6.12. SmokeSensitivityLevel Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
sensitivity
level
of
the
Physical
Contact
Configuration
smoke
sensor
configured
on
the
device.
2.11.6.13.
ExpiryDate
Attribute
Set
This attribute SHALL indicate the date when the device reaches its stated expiry date. After the ExpiryDate has been reached, the EndOfServiceAlert SHALL start to be triggered. To account for better customer experience across time zones, the EndOfServiceAlert MAY be delayed by up to 24 hours after the ExpiryDate. Similarly, clients MAY delay any actions based on the ExpiryDate by up to 24 hours to best align with the local time zone.
2.11.7. Commands
| ID | Name |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | SelfTestRequest | client ⇒ server | Y | O | O |
2.11.7.1. SelfTestRequest Command
This command SHALL initiate a device self-test. The return status SHALL indicate whether the test was successfully initiated. Only one SelfTestRequest may be processed at a time. When the value of the ExpressedState attribute is any of SmokeAlarm, COAlarm, Testing, InterconnectSmoke, InterconnectCO, the device SHALL NOT execute the self-test, and SHALL return status code BUSY.
Upon successful acceptance of SelfTestRequest, the TestInProgress attribute SHALL be set to True and ExpressedState attribute SHALL be set to Testing. Any faults identified during the test SHALL be reflected in the appropriate attributes and events. Upon completion of the self test procedure, the SelfTestComplete event SHALL be generated, the TestInProgress attribute SHALL be set to False and ExpressedState attribute SHALL be updated to reflect the current state of the server.
2.11.8. Events
| ID | Name | Priority | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| V | CO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| V | M |
|
|
|
|
|
M |
|
|
| INFO | V | M |
0x06 | AlarmMuted | INFO | V | O |
0x07 | MuteEnded | INFO | V |
O |
|
0x08 | InterconnectSmokeAlarm | CRITICAL | V | [SMOKE] |
0x09 | InterconnectCOAlarm | CRITICAL | V | [CO] |
0x0A | AllClear | INFO | V | M |
2.7.8.1.
PhysicalContactOccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay
Attribute
2.11.8.1.
SmokeAlarm
Event
The
PhysicalContactOccupiedToUnoccupiedDelay
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
SmokeState
attribute
specifies
the
time
delay,
in
seconds,
before
the
physical
contact
occupancy
sensor
changes
to
its
unoccupied
state
after
detecting
the
unoccupied
event.
either
Warning
or
Critical
state.
The
null
data
of
this
event
SHALL
contain
the
following
information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | AlarmSeverityLevel | all | M |
2.7.8.2.
PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
Attribute
2.11.8.2.
COAlarm
Event
The
PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
COState
attribute
specifies
the
time
delay,
in
seconds,
before
the
physical
contact
sensor
changes
to
its
occupied
state
after
either
Warning
or
Critical
state.
The
data
of
this
event
SHALL
contain
the
detection
following
information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | AlarmSeverityLevel | all | M |
2.11.8.3. LowBattery Event
This event SHALL be generated when BatteryAlert attribute changes to either Warning or Critical state.
The
null
data
of
this
event
SHALL
contain
the
following
information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | AlarmSeverityLevel | all | M |
2.11.8.4. HardwareFault Event
This event SHALL be generated when the device detects a hardware fault that leads to setting HardwareFaultAlert to True.
2.11.8.5. EndOfService Event
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
the
sensor
does
not
report
unoccupied
EndOfServiceAlert
is
set
to
occupied
transition.
Expired.
2.7.8.3.
PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
Attribute
2.11.8.6.
SelfTestComplete
Event
The
PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedThreshold
attribute
specifies
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
the
number
of
movement
detection
events
that
must
occur
in
SelfTest
completes,
and
the
period
PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay,
before
attribute
TestInProgress
changes
to
False.
2.11.8.7. AlarmMuted Event
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
the
PIR
sensor
DeviceMuted
attribute
changes
to
its
occupied
state.
Muted.
2.11.8.8. MuteEnded Event
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
DeviceMuted
attribute
is
mandatory
if
changes
to
NotMuted.
2.11.8.9. InterconnectSmokeAlarm Event
This
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
the
PhysicalContactUnoccupiedToOccupiedDelay
attribute
is
implemented.
device
hosting
the
server
receives
a
smoke
alarm
from
an
interconnected
sensor.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | AlarmSeverityLevel | all | M |
2.7.9.
Commands
2.11.8.10.
InterconnectCOAlarm
Event
This
cluster
has
no
cluster
specific
commands.
event
SHALL
be
generated
when
the
device
hosting
the
server
receives
a
CO
alarm
from
an
interconnected
sensor.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | AlarmSeverityLevel | AlarmStateEnum | all | M |
3. Lighting
The Cluster Library is made of individual chapters such as this one. See Document Control in the Cluster Library for a list of all chapters and documents. References between chapters are made using a X.Y notation where X is the chapter and Y is the sub-section within that chapter. References to external documents are contained in Chapter 1 and are made using [ Rn ] notation.
3.1. General Description
3.1.1. Introduction
The clusters specified in this document are for use typically in lighting applications, but MAY be used in any application domain.
3.1.2. Terms
Ballast Factor: A measure of the light output (lumens) of a ballast and lamp combination in comparison to an ANSI standard ballast operated with the same lamp. Multiply the ballast factor by the rated lumens of the lamp to get the light output of the lamp/ballast combination.
HSV: Hue, Saturation, Value. A color space, also known as HSB (Hue, Saturation, Brightness). This is a well-known transformation of the RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color space. For more information see e.g., http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HSV_color_space .
Illuminance: The density of incident luminous flux on a surface. Illuminance is the standard metric for lighting levels, and is measured in lux (lx).
3.1.3. Cluster List
This section lists the lighting specific clusters as specified in this chapter.
| Cluster ID | Cluster Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0x0300 |
Attributes and commands for controlling the color of a color-capable light. |
|
|
0x0301 |
Attributes and commands for configuring a lighting ballast |
3.2. Color Control Cluster
3.2.1. Introduction
This cluster provides an interface for changing the color of a light. Color is specified according to the Commission Internationale de l’Éclairage (CIE) specification CIE 1931 Color Space, [I1]. Color control is carried out in terms of x,y values, as defined by this specification.
Additionally, color MAY optionally be controlled in terms of color temperature, or as hue and saturation values based on optionally variable RGB and W color points. It is recommended that the hue and saturation are interpreted according to the HSV (aka HSB) color model.
Control over luminance is not included, as this is provided by means of the Level Control for Lighting cluster. It is recommended that the level provided by this cluster be interpreted as representing a proportion of the maximum intensity achievable at the current color.
3.2.2. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Rev | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
mandatory global ClusterRevision attribute added; CCB 2028 |
|
2 |
added Options attribute, CCB 2085 2104 2124 2230; ZLO 1.0 |
|
3 |
CCB 2501 2814 2839 2840 2843 2861 |
|
4 |
All Hubs changes |
|
5 |
new data model format and notation, FeatureMap support |
|
6 | Added clarifications to Scenes support for Matter |
3.2.3. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role | PICS Code | Primary Transaction |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
CC |
Type 1 (client to server) |
3.2.5. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
HS |
Hue/Saturation |
Supports color specification via hue/saturation. |
|
1 |
EHUE |
Enhanced Hue |
Enhanced hue is supported. |
|
2 |
CL |
Color loop |
Color loop is supported. |
|
3 |
XY |
XY |
Supports color specification via XY. |
|
4 |
CT |
Color temperature |
Supports specification of color temperature. |
Support for EHUE SHALL require support for HS.
Support for CL SHALL require support for EHUE.
3.2.6. Dependencies
3.2.6.1. Coupling color temperature to Level Control
If the Level Control for Lighting cluster identifier 0x0008 is supported on the same endpoint as the Color Control cluster and color temperature is supported, it is possible to couple changes in the current level to the color temperature.
The CoupleColorTempToLevel bit of the Options attribute of the Level Control cluster indicates whether the color temperature is to be linked with the CurrentLevel attribute in the Level Control cluster.
If the CoupleColorTempToLevel bit of the Options attribute of the Level Control cluster is equal to 1 and the ColorMode or EnhancedColorMode attribute is set to 2 (color temperature) then a change in the CurrentLevel attribute SHALL affect the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute. This relationship is manufacturer specific, with the qualification that the maximum value of the CurrentLevel attribute SHALL correspond to a ColorTemperatureMired attribute value equal to the CoupleColorTempToLevelMinMireds attribute. This relationship is one-way so a change to the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute SHALL NOT have any effect on the CurrentLevel attribute.
In order to simulate the behavior of an incandescent bulb, a low value of the CurrentLevel attribute SHALL be associated with a high value of the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (i.e., a low value of color temperature in kelvins).
If the CoupleColorTempToLevel bit of the Options attribute of the Level Control cluster is equal to 0, there SHALL be no link between color temperature and current level.
3.2.6.2. Independent transition in hue and saturation
Various commands in this cluster can be used to start transitions in hue and/or saturation.
When a transition in hue is in progress, and a command to change saturation (MoveSaturation (with MoveMode!=Stop), StepSaturation, MoveToSaturation) is received by the server, this latter command SHALL NOT interrupt the ongoing transition in hue.
When a transition in saturation is in progress, and a command to change hue (MoveHue (with MoveMode!=Stop), EnhancedMoveHue (with MoveMode!=Stop) StepHue, EnhancedStepHue, MoveToHue, EnhancedMoveToHue) is received by the server, this latter command SHALL NOT interrupt the ongoing transition in saturation.
3.2.7. Color Information Attribute Set
The attributes defined in this cluster specification are arranged into four sets of related attributes.
The Color Information attribute set contains the attributes summarized below.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
CurrentHue |
uint8 |
0 to 254 |
PN |
0 |
R V |
HS |
|
0x0001 |
CurrentSaturation |
uint8 |
0 to 254 |
PSN |
0 |
R V |
HS |
|
0x0002 |
RemainingTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
0 |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0003 |
CurrentX |
uint16 |
0
to
|
PSN |
|
R V |
XY |
|
0x0004 |
CurrentY |
uint16 |
0
to
|
PSN |
|
R V |
XY |
|
0x0005 |
DriftCompensation |
enum8 |
0 to 4 |
- |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0006 |
CompensationText |
string |
max 254 |
- |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0007 |
ColorTemperatureMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
PSN |
|
R V |
CT |
|
0x0008 |
ColorMode |
enum8 |
0 to 2 |
N |
1 |
R V |
M |
|
|
Options |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
RW VO |
M |
|
|
0x4000 |
EnhancedCurrentHue |
uint16 |
all |
SN |
0 |
R V |
EHUE |
|
0x4001 |
EnhancedColorMode |
enum8 |
0 to 3 |
|
1 |
R V |
M |
|
0x4002 |
ColorLoopActive |
uint8 |
all |
SN |
0 |
R V |
CL |
|
0x4003 |
ColorLoopDirection |
uint8 |
all |
SN |
0 |
R V |
CL |
|
0x4004 |
ColorLoopTime |
uint16 |
all |
SN |
0x0019 |
R V |
CL |
|
0x4005 |
ColorLoopStartEnhancedHue |
uint16 |
all |
0x2300 |
R V |
CL |
|
|
0x4006 |
ColorLoopStoredEnhancedHue |
uint16 |
all |
0 |
R V |
CL |
|
|
|
ColorCapabilities |
map16 |
0
to
|
0 |
R V |
M |
|
|
|
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
0 |
R V |
CT |
|
|
|
ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
|
R V |
CT |
|
|
|
CoupleColorTempToLevelMinMireds |
uint16 |
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds to ColorTemperatureMireds |
MS |
R V |
CT | ColorTemperatureMireds |
|
|
0x4010 |
StartUpColorTemperatureMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
|
MS |
RW VM |
CT | ColorTemperatureMireds |
Regarding attributes whose values persistent across an OTA restart (designated by ‘N’ in the Access column in the table above), only those attributes that are supported (due to the color capabilities of the device) need to be stored.
3.2.7.1. Scene Table Extensions
If
the
Scenes
server
cluster
is
implemented
on
the
same
endpoint,
the
following
extension
fields
attributes
SHALL
be
added
to
part
of
the
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
of
the
Scene
Table
Table.
If
an
attribute
is
not
implemented,
the
value
that
will
be
used
for
it
in
the
AttributeValuePairStruct
is
given
in
parentheses.
If
the
implicit
form
of
the
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
is
used,
the
order
of
the
attributes
in
the
AttributeValueList
is
in
the
given
order,
i.e.,
the
attribute
listed
as
1
is
added
first:
-
CurrentX (0)
-
CurrentY (0)
-
EnhancedCurrentHue (null)
-
CurrentSaturation (null)
-
ColorLoopActive (0)
-
ColorLoopDirection (0)
-
ColorLoopTime (0)
-
ColorTemperatureMireds (null)
EnhancedColorMode
Since there is a direct relation between ColorTemperatureMireds and XY, color temperature, if supported, is stored as XY in the scenes table.
Attributes in the scene table that are not supported by the device (according to the FeatureMap attribute) SHALL be present in the scene table but ignored.
If the Scenes cluster server is implemented on the same endpoint, and the cluster revision is 6 or above, then all extension fields in the list above, including up to EnhancedColorMode (item 9), SHALL be present in the extension fields set for a Scene to be considered valid. This disambiguates the color mode used within the Scene.
3.2.7.1.
3.2.7.2.
CurrentHue
Attribute
The CurrentHue attribute contains the current hue value of the light. It is updated as fast as practical during commands that change the hue.
The
hue
in
degrees
SHALL
be
related
to
the
CurrentHue
attribute
by
the
relationship:
Hue
=
CurrentHue
x
360
/
254
(CurrentHue
in
the
range
0
to
254
inclusive)
If this attribute is implemented then the CurrentSaturation and ColorMode attributes SHALL also be implemented.
3.2.7.2.
3.2.7.3.
CurrentSaturation
Attribute
The CurrentSaturation attribute holds the current saturation value of the light. It is updated as fast as practical during commands that change the saturation.
The
saturation
SHALL
be
related
to
the
CurrentSaturation
attribute
by
the
relationship:
Saturation
=
CurrentSaturation/254
(CurrentSaturation
in
the
range
0
to
254
inclusive)
If this attribute is implemented then the CurrentHue and ColorMode attributes SHALL also be implemented.
3.2.7.3.
3.2.7.4.
RemainingTime
Attribute
The RemainingTime attribute holds the time remaining, in 1/10ths of a second, until the currently active command will be complete.
3.2.7.4.
3.2.7.5.
CurrentX
Attribute
The CurrentX attribute contains the current value of the normalized chromaticity value x, as defined in the CIE xyY Color Space. It is updated as fast as practical during commands that change the color.
The value of x SHALL be related to the CurrentX attribute by the relationship
x = CurrentX / 65536 (CurrentX in the range 0 to 65279 inclusive)
3.2.7.5.
3.2.7.6.
CurrentY
Attribute
The CurrentY attribute contains the current value of the normalized chromaticity value y, as defined in the CIE xyY Color Space. It is updated as fast as practical during commands that change the color.
The value of y SHALL be related to the CurrentY attribute by the relationship
y = CurrentY / 65536 (CurrentY in the range 0 to 65279 inclusive)
3.2.7.6.
3.2.7.7.
DriftCompensation
Attribute
The DriftCompensation attribute indicates what mechanism, if any, is in use for compensation for color/intensity drift over time. It SHALL be one of the non-reserved values in Values of the DriftCompensation Attribute .
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
None |
|
1 |
Other / Unknown |
|
2 |
Temperature monitoring |
|
3 |
Optical luminance monitoring and feedback |
|
4 |
Optical color monitoring and feedback |
3.2.7.7.
3.2.7.8.
CompensationText
Attribute
The CompensationText attribute holds a textual indication of what mechanism, if any, is in use to compensate for color/intensity drift over time.
3.2.7.8.
3.2.7.9.
ColorTemperatureMireds
Attribute
The ColorTemperatureMireds attribute contains a scaled inverse of the current value of the color temperature. The unit of ColorTemperatureMireds is the mired (micro reciprocal degree), AKA mirek (micro reciprocal kelvin). It is updated as fast as practical during commands that change the color.
The color temperature value in kelvins SHALL be related to the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute in mireds by the relationship
Color temperature in kelvins = 1,000,000 / ColorTemperatureMireds, where ColorTemperatureMireds is in the range 1 to 65279 mireds inclusive, giving a color temperature range from 1,000,000 kelvins to 15.32 kelvins.
If this attribute is implemented then the ColorMode attribute SHALL also be implemented.
3.2.7.9.
3.2.7.10.
ColorMode
Attribute
The ColorMode attribute indicates which attributes are currently determining the color of the device.
The value of the ColorMode attribute cannot be written directly - it is set upon reception of any command in section Commands to the appropriate mode for that command.
| Value | Attributes that Determine the Color |
|---|---|
|
0 |
CurrentHue and CurrentSaturation |
|
1 |
CurrentX and CurrentY |
|
2 |
ColorTemperatureMireds |
3.2.7.10.
3.2.7.11.
Options
Attribute
The Options attribute is meant to be changed only during commissioning. The Options attribute is a bitmap that determines the default behavior of some cluster commands. Each command that is dependent on the Options attribute SHALL first construct a temporary Options bitmap that is in effect during the command processing. The temporary Options bitmap has the same format and meaning as the Options attribute, but includes any bits that may be overridden by command fields.
Below is the format and description of the Options attribute and temporary Options bitmap and the effect on dependent commands.
| Bit | Name | Values & Summary |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
ExecuteIfOff |
0
–
Do
not
execute
command
if
the
On/Off
cluster,
OnOff
attribute
is
FALSE.
|
ExecuteIfOff Options bit: Command execution SHALL NOT continue beyond the Options processing if all of these criteria are true:
-
The On/Off cluster exists on the same endpoint as this cluster.
-
The OnOff attribute of the On/Off cluster, on this endpoint, is FALSE.
-
The value of the ExecuteIfOff bit is 0.
3.2.7.11.
3.2.7.12.
EnhancedCurrentHue
Attribute
The EnhancedCurrentHue attribute represents non-equidistant steps along the CIE 1931 color triangle, and it provides 16-bits precision.
The upper 8 bits of this attribute SHALL be used as an index in the implementation specific XY lookup table to provide the non-equidistance steps. The lower 8 bits SHALL be used to interpolate between these steps in a linear way in order to provide color zoom for the user.
To provide compatibility with standard ZCL, the CurrentHue attribute SHALL contain a hue value in the range 0 to 254, calculated from the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute.
3.2.7.12.
3.2.7.13.
EnhancedColorMode
Attribute
The EnhancedColorMode attribute specifies which attributes are currently determining the color of the device, as detailed in Values of the EnhancedColorMode Attribute .
| Value | Attributes That Determine the Color |
|---|---|
|
0 |
CurrentHue and CurrentSaturation |
|
1 |
CurrentX and CurrentY |
|
2 |
ColorTemperatureMireds |
|
3 |
EnhancedCurrentHue and CurrentSaturation |
To provide compatibility with standard ZCL, the original ColorMode attribute SHALL indicate ‘CurrentHue and CurrentSaturation’ when the light uses the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute. If the ColorMode attribute is changed, e.g., due to one of the standard Color Control cluster commands defined in the ZCL, its new value SHALL be copied to the EnhancedColorMode attribute.
3.2.7.13.
3.2.7.14.
ColorLoopActive
Attribute
The ColorLoopActive attribute specifies the current active status of the color loop. If this attribute has the value 0, the color loop SHALL not be active. If this attribute has the value 1, the color loop SHALL be active. All other values (2 to 254) are reserved.
3.2.7.14.
3.2.7.15.
ColorLoopDirection
Attribute
The ColorLoopDirection attribute specifies the current direction of the color loop. If this attribute has the value 0, the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute SHALL be decremented. If this attribute has the value 1, the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute SHALL be incremented. All other values (2 to 254) are reserved.
3.2.7.15.
3.2.7.16.
ColorLoopTime
Attribute
The
ColorLoopTime
attribute
specifies
the
number
of
seconds
it
SHALL
take
to
perform
a
full
color
loop,
i.e.,
to
cycle
all
values
of
the
EnhancedCurrentHue
attribute
(between
0
and
0xfffe).
0xFFFE).
3.2.7.16.
3.2.7.17.
ColorLoopStartEnhancedHue
Attribute
The ColorLoopStartEnhancedHue attribute specifies the value of the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute from which the color loop SHALL be started.
3.2.7.17.
3.2.7.18.
ColorLoopStoredEnhancedHue
Attribute
The ColorLoopStoredEnhancedHue attribute specifies the value of the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute before the color loop was started. Once the color loop is complete, the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute SHALL be restored to this value.
3.2.7.18.
3.2.7.19.
ColorCapabilities
Attribute
Bits 0-4 of the ColorCapabilities attribute SHALL have the same values as the corresponding bits of the FeatureMap attribute. All other bits in ColorCapabilities SHALL be 0.
3.2.7.19.
3.2.7.20.
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds
Attribute
The
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds
attribute
indicates
the
minimum
mired
value
supported
by
the
hardware.
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds
corresponds
to
the
maximum
color
temperature
in
kelvins
supported
by
the
hardware.
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds
≤
\$<=\$
ColorTemperatureMireds.
3.2.7.20.
3.2.7.21.
ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds
Attribute
The
ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds
attribute
indicates
the
maximum
mired
value
supported
by
the
hardware.
ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds
corresponds
to
the
minimum
color
temperature
in
kelvins
supported
by
the
hardware.
ColorTemperatureMireds
≤
\$<=\$
ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds.
3.2.7.21.
3.2.7.22.
CoupleColorTempToLevelMinMireds
Attribute
The
CoupleColorTempToLevelMinMireds
attribute
specifies
a
lower
bound
on
the
value
of
the
ColorTemperatureMireds
attribute
for
the
purposes
of
coupling
the
ColorTemperatureMireds
attribute
to
the
CurrentLevel
attribute
when
the
CoupleColorTempToLevel
bit
of
the
Options
attribute
of
the
Level
Control
cluster
is
equal
to
1.
When
coupling
the
ColorTemperatureMireds
attribute
to
the
CurrentLevel
attribute,
this
value
SHALL
correspond
to
a
CurrentLevel
value
of
0xfe
0xFE
(100%).
This
attribute
SHALL
be
set
such
that
the
following
relationship
exists:
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds
≤
CoupleColorTempToLevelMinMireds
≤
ColorTemperatureMireds
Note that since this attribute is stored as a micro reciprocal degree (mired) value (i.e. color temperature in kelvins = 1,000,000 / CoupleColorTempToLevelMinMireds), the CoupleColorTempToLevelMinMireds attribute corresponds to an upper bound on the value of the color temperature in kelvins supported by the device.
3.2.7.22.
3.2.7.23.
StartUpColorTemperatureMireds
Attribute
The StartUpColorTemperatureMireds attribute SHALL define the desired startup color temperature value a lamp SHALL use when it is supplied with power and this value SHALL be reflected in the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute. In addition, the ColorMode and EnhancedColorMode attributes SHALL be set to 0x02 (color temperature). The values of the StartUpColorTemperatureMireds attribute are listed in the table below,
| Value | Action on power up |
|---|---|
|
0
to
|
Set the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute to this value. |
|
null |
Set the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute to its previous value. |
3.2.8. Defined Primaries Information Attribute Set
The Defined Primaries Information attribute set contains the attributes summarized in Defined Primaries Information Attribute Set .
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0010 |
NumberOfPrimaries |
uint8 |
0 to 6 |
FX |
- |
R V |
M |
|
0x0011 |
Primary1X |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 0 |
|
0x0012 |
Primary1Y |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 0 |
|
0x0013 |
Primary1Intensity |
uint8 |
all |
FX |
- |
R V |
M 0 |
|
0x0015 |
Primary2X |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 1 |
|
0x0016 |
Primary2Y |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 1 |
|
0x0017 |
Primary2Intensity |
uint8 |
all |
FX |
- |
R V |
M 1 |
|
0x0019 |
Primary3X |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 2 |
|
|
Primary3Y |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 2 |
|
|
Primary3Intensity |
uint8 |
all |
FX |
- |
R V |
M 2 |
M i = Mandatory if the value of the NumberOfPrimaries attribute is greater than i , otherwise optional.
3.2.8.1. NumberOfPrimaries Attribute
The NumberOfPrimaries attribute contains the number of color primaries implemented on this device. A value of null SHALL indicate that the number of primaries is unknown.
Where this attribute is implemented, the attributes below for indicating the “x” and “y” color values of the primaries SHALL also be implemented for each of the primaries from 1 to NumberOfPrimaries, without leaving gaps. Implementation of the Primary1Intensity attribute and subsequent intensity attributes is optional.
3.2.8.2. Primary1X Attribute
The Primary1X attribute contains the normalized chromaticity value x for this primary, as defined in the CIE xyY Color Space.
The value of x SHALL be related to the Primary1X attribute by the relationship
x = Primary1X / 65536 (Primary1X in the range 0 to 65279 inclusive)
3.2.8.3. Primary1Y Attribute
The Primary1Y attribute contains the normalized chromaticity value y for this primary, as defined in the CIE xyY Color Space.
The value of y SHALL be related to the Primary1Y attribute by the relationship
y = Primary1Y / 65536 (Primary1Y in the range 0 to 65279 inclusive)
3.2.8.4. Primary1Intensity Attribute
The
Primary1intensity
attribute
contains
a
representation
of
the
maximum
intensity
of
this
primary
as
defined
in
the
Dimming
Light
Curve
in
the
Ballast
Configuration
cluster
(see
Ballast
Configuration
Cluster
),
normalized
such
that
the
primary
with
the
highest
maximum
intensity
contains
the
value
0xfe.
0xFE.
A value of null SHALL indicate that this primary is not available.
3.2.9. Additional Defined Primaries Information Attribute Set
The Additional Defined Primaries Information attribute set contains the attributes summarized in Additional Defined Primaries Information Attribute Set .
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0020 |
Primary4X |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 3 |
|
0x0021 |
Primary4Y |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 3 |
|
0x0022 |
Primary4Intensity |
uint8 |
all |
FX |
- |
R V |
M 3 |
|
0x0024 |
Primary5X |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 4 |
|
0x0025 |
Primary5Y |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 4 |
|
0x0026 |
Primary5Intensity |
uint8 |
all |
FX |
- |
R V |
M 4 |
|
0x0028 |
Primary6X |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 5 |
|
0x0029 |
Primary6Y |
uint16 |
0
to
|
F |
- |
R V |
M 5 |
|
|
Primary6Intensity |
uint8 |
all |
FX |
- |
R V |
M 5 |
M i = Mandatory if the value of the NumberOfPrimaries attribute is greater than i , otherwise optional.
3.2.9.1. Remaining Attributes
The Primary4X, Primary4Y, Primary4Intensity, Primary5X, Primary5Y, Primary5Intensity, Primary6X, Primary6Y and Primary6Intensity attributes represent the capabilities of the 4 th , 5 th and 6 th primaries, where present, in the same way as the Primary1X, Primary1Y and Primary1Intensity attributes.
3.2.10. Defined Color Points Settings Attribute Set
The Defined Color Points Settings attribute set contains the attributes summarized in Defined Color Points Settings Attribute Set .
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0030 |
WhitePointX |
uint16 |
0
to
|
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
0x0031 |
WhitePointY |
uint16 |
0
to
|
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
0x0032 |
ColorPointRX |
uint16 |
0
to
|
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
0x0033 |
ColorPointRY |
uint16 |
0
to
|
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
0x0034 |
ColorPointRIntensity |
uint8 |
all |
X |
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0036 |
ColorPointGX |
uint16 |
0
to
|
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
0x0037 |
ColorPointGY |
uint16 |
0
to
|
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
0x0038 |
ColorPointGIntensity |
uint8 |
all |
X |
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
ColorPointBX |
uint16 |
0
to
|
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
|
ColorPointBY |
uint16 |
0
to
|
- |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
|
ColorPointBIntensity |
uint8 |
all |
X |
- |
RW VM |
O |
3.2.10.1. WhitePointX Attribute
The WhitePointX attribute contains the normalized chromaticity value x, as defined in the CIE xyY Color Space, of the current white point of the device.
The value of x SHALL be related to the WhitePointX attribute by the relationship
x = WhitePointX / 65536 (WhitePointX in the range 0 to 65279 inclusive)
3.2.10.2. WhitePointY Attribute
The WhitePointY attribute contains the normalized chromaticity value y, as defined in the CIE xyY Color Space, of the current white point of the device.
The value of y SHALL be related to the WhitePointY attribute by the relationship
y = WhitePointY / 65536 (WhitePointY in the range 0 to 65279 inclusive)
3.2.10.3. ColorPointRX Attribute
The ColorPointRX attribute contains the normalized chromaticity value x, as defined in the CIE xyY Color Space, of the red color point of the device.
The value of x SHALL be related to the ColorPointRX attribute by the relationship
x = ColorPointRX / 65536 (ColorPointRX in the range 0 to 65279 inclusive)
3.2.10.4. ColorPointRY Attribute
The ColorPointRY attribute contains the normalized chromaticity value y, as defined in the CIE xyY Color Space, of the red color point of the device.
The value of y SHALL be related to the ColorPointRY attribute by the relationship
y = ColorPointRY / 65536 (ColorPointRY in the range 0 to 65279 inclusive)
3.2.10.5. ColorPointRIntensity Attribute
The
ColorPointRIntensity
attribute
contains
a
representation
of
the
relative
intensity
of
the
red
color
point
as
defined
in
the
Dimming
Light
Curve
in
the
Ballast
Configuration
cluster
(see
Ballast
Configuration
Cluster
),
normalized
such
that
the
color
point
with
the
highest
relative
intensity
contains
the
value
0xfe.
0xFE.
A value of null SHALL indicate an invalid value.
3.2.10.6. Remaining Attributes
The ColorPointGX, ColorPointGY, ColorPointGIntensity, ColorPointBX, ColorPointBY and, ColorPointBIntensity attributes are used to represent the chromaticity values and intensities of the green and blue color points, in the same way as for the ColorPointRX, ColorPointRY and ColorPointRIntensity attributes.
If any one of these red, green or blue color point attributes is implemented then they SHALL all be implemented.
3.2.11. Commands
The command IDs for the Color Control cluster are listed in Command IDs for the Color Control Cluster .
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
MoveToHue |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
HS |
|
0x01 |
MoveHue |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
HS |
|
0x02 |
StepHue |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
HS |
|
0x03 |
MoveToSaturation |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
HS |
|
0x04 |
MoveSaturation |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
HS |
|
0x05 |
StepSaturation |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
HS |
|
0x06 |
MoveToHueAndSaturation |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
HS |
|
0x07 |
MoveToColor |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
XY |
|
0x08 |
MoveColor |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
XY |
|
0x09 |
StepColor |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
XY |
|
|
MoveToColorTemperature |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
CT |
|
0x40 |
EnhancedMoveToHue |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
EHUE |
|
0x41 |
EnhancedMoveHue |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
EHUE |
|
0x42 |
EnhancedStepHue |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
EHUE |
|
0x43 |
EnhancedMoveToHueAndSaturation |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
EHUE |
|
0x44 |
ColorLoopSet |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
CL |
|
0x47 |
StopMoveStep |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
HS | XY | CT |
|
|
MoveColorTemperature |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
CT |
|
|
StepColorTemperature |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
CT |
3.2.11.1. Generic Usage Notes
When asked to change color via one of these commands, the implementation SHALL select a color, within the limits of the hardware of the device, which is as close as possible to that requested. The determination as to the true representations of color is out of the scope of this specification. However, as long as the color data fields of the received command are within the permitted range of this specification and no error condition applies, the resulting status code SHALL be SUCCESS.
For example the MoveToColorTemperature command: if the target color temperature is not achievable by the hardware then the color temperature SHALL be clipped at the physical minimum or maximum achievable (depending on the direction of the color temperature transition) when the device reaches that color temperature (which MAY be before the requested transition time).
If a color loop is active (i.e., the ColorLoopActive attribute is equal to 1), it SHALL only be stopped by sending a specific ColorLoopSet command frame with a request to deactivate the color loop (i.e., the color loop SHALL not be stopped on receipt of another command which has a 'stop' semantic such as the EnhancedMoveToHue command with MoveMode==Stop, or the StopMoveStep command). In addition, while a color loop is active, a manufacturer MAY choose to ignore incoming color commands which affect a change in hue.
3.2.11.2. Note on Change of ColorMode
The first action taken when any one of these commands is received is to change the ColorMode attribute to the appropriate value for the command (see individual commands). Note that, when moving from one color mode to another (e.g., CurrentX/CurrentY to CurrentHue/CurrentSaturation), the starting color for the command is formed by calculating the values of the new attributes (in this case CurrentHue, CurrentSaturation) from those of the old attributes (in this case CurrentX and CurrentY).
When moving from a mode to another mode that has a more restricted color range (e.g., CurrentX/CurrentY to CurrentHue/CurrentSaturation, or CurrentHue/CurrentSaturation to ColorTemperatureMireds) it is possible for the current color value to have no equivalent in the new mode. The behavior in such cases is manufacturer dependent, and therefore it is recommended to avoid color mode changes of this kind during usage.
3.2.11.3. Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL both be present. Default values are provided to interpret missing fields from legacy devices. A temporary Options bitmap SHALL be created from the Options attribute, using the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields. Each bit of the temporary Options bitmap SHALL be determined as follows:
Each bit in the Options attribute SHALL determine the corresponding bit in the temporary Options bitmap, unless the OptionsMask field is present and has the corresponding bit set to 1, in which case the corresponding bit in the OptionsOverride field SHALL determine the corresponding bit in the temporary Options bitmap.
The resulting temporary Options bitmap SHALL then be processed as defined in section Options Attribute .
3.2.11.4. MoveToHue Command
The MoveToHue command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Hue |
uint8 |
0 to 254 |
M |
||
|
1 |
Direction |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.4.2. Direction Field
The Direction field SHALL be one of the non-reserved values in Values of the Direction Field .
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Shortest distance |
|
1 |
Longest distance |
|
2 |
Up |
|
3 |
Down |
3.2.11.4.3. TransitionTime Field
The TransitionTime field specifies, in 1/10ths of a second, the time that SHALL be taken to move to the new hue.
3.2.11.4.4. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.4.5. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL also set the ColorMode attribute to the value 0 and then SHALL move from its current hue to the value given in the Hue field.
The movement SHALL be continuous, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new hue SHALL be equal to the TransitionTime field.
As hue is effectively measured on a circle, the new hue MAY be moved to in either direction. The direction of hue change is given by the Direction field. If Direction is 'Shortest distance', the direction is taken that involves the shortest path round the circle. This case corresponds to expected normal usage. If Direction is 'Longest distance', the direction is taken that involves the longest path round the circle. This case can be used for 'rainbow effects'. In both cases, if both distances are the same, the Up direction SHALL be taken.
3.2.11.5. MoveHue Command
The MoveHue command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
MoveMode |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Rate |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.5.1. MoveMode Field
The MoveMode field SHALL be one of the non-reserved values in Values of the MoveMode Field . If the MoveMode field is equal to 0 (Stop), the Rate field SHALL be ignored.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Stop |
|
1 |
Up |
|
2 |
Reserved |
|
3 |
Down |
3.2.11.5.2. Rate Field
The Rate field specifies the rate of movement in steps per second. A step is a change in the device’s hue of one unit. If the MoveMode field is set to 1 (up) or 3 (down) and the Rate field has a value of zero, the command has no effect and a response command SHALL be sent in response, with the status code set to INVALID_COMMAND. If the MoveMode field is set to 0 (stop) the Rate field SHALL be ignored.
3.2.11.5.3. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride field
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.5.4. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to the value 0 and SHALL then move from its current hue in an up or down direction in a continuous fashion, as detailed in Actions on Receipt for MoveHue Command .
| MoveMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Stop |
If
moving,
stop,
else
ignore
the
command
(i.e.,
the
command
is
accepted
but
has
no
effect).
|
|
Up |
Increase the device’s hue at the rate given in the Rate field. If the hue reaches the maximum allowed for the device, then wraparound and proceed from its minimum allowed value. |
|
Down |
Decrease the device’s hue at the rate given in the Rate field. If the hue reaches the minimum allowed for the device, then wraparound and proceed from its maximum allowed value. |
3.2.11.6. StepHue Command
The StepHue command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
StepMode |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
StepSize |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.6.1. StepMode Field
The StepMode field SHALL be one of the non-reserved values in Values of the StepMode Field .
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Reserved |
|
1 |
Up |
|
2 |
Reserved |
|
3 |
Down |
3.2.11.6.2. StepSize Field
The change to be added to (or subtracted from) the current value of the device’s hue.
3.2.11.6.3. TransitionTime Field
The TransitionTime field specifies, in 1/10ths of a second, the time that SHALL be taken to perform the step. A step is a change in the device’s hue of ‘Step size’ units.
Note: Here the TransitionTime data field is of data type uint8, where uint16 is more common for TransitionTime data fields in other clusters / commands.
3.2.11.6.4. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.6.5. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to the value 0 and SHALL then move from its current hue in an up or down direction by one step, as detailed in Actions on Receipt for StepHue Command .
| StepMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Up |
Increase the device’s hue by one step, in a continuous fashion. If the hue value reaches the maximum value then wraparound and proceed from the minimum allowed value. |
|
Down |
Decrease the device’s hue by one step, in a continuous fashion. If the hue value reaches the minimum value then wraparound and proceed from the maximum allowed value. |
3.2.11.7. MoveToSaturation Command
The MoveToSaturation command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Saturation |
uint8 |
0 to 254 |
M |
||
|
1 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
2 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.7.1. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.7.2. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to the value 0 and SHALL then move from its current saturation to the value given in the Saturation field.
The movement SHALL be continuous, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new saturation SHALL be equal to the TransitionTime field, in 1/10ths of a second.
3.2.11.8. MoveSaturation Command
The MoveSaturation command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
MoveMode |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Rate |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.8.1. MoveMode Field
The MoveMode field SHALL be one of the non-reserved values in Values of the MoveMode Field . If the MoveMode field is equal to 0 (Stop), the Rate field SHALL be ignored.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Stop |
|
1 |
Up |
|
2 |
Reserved |
|
3 |
Down |
3.2.11.8.2. Rate Field
The Rate field specifies the rate of movement in steps per second. A step is a change in the device’s saturation of one unit. If the MoveMode field is set to 1 (up) or 3 (down) and the Rate field has a value of zero, the command has no effect and a response command SHALL be sent in response, with the status code set to INVALID_COMMAND. If the MoveMode field is set to 0 (stop) the Rate field SHALL be ignored.
3.2.11.8.3. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.8.4. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to the value 0 and SHALL then move from its current saturation in an up or down direction in a continuous fashion, as detailed in Actions on Receipt for MoveSaturation Command .
| MoveMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Stop |
If
moving,
stop,
else
ignore
the
command
(i.e.,
the
command
is
accepted
but
has
no
effect).
|
|
Up |
Increase the device’s saturation at the rate given in the Rate field. If the saturation reaches the maximum allowed for the device, stop. |
|
Down |
Decrease the device’s saturation at the rate given in the Rate field. If the saturation reaches the minimum allowed for the device, stop. |
3.2.11.9. StepSaturation Command
The StepSaturation command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
StepMode |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
StepSize |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.9.1. StepMode Field
The StepMode field SHALL be one of the non-reserved values in Values of the StepMode Field .
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
0 | Reserved |
1 |
Up |
|
2 |
Reserved |
|
3 |
Down |
3.2.11.9.2. StepSize Field
The change to be added to (or subtracted from) the current value of the device’s saturation.
3.2.11.9.3. TransitionTime Field
The TransitionTime field specifies, in 1/10ths of a second, the time that SHALL be taken to perform the step. A step is a change in the device’s saturation of ‘Step size’ units.
Note: Here the TransitionTime data field is of data type uint8, where uint16 is more common for TransitionTime data fields in other clusters / commands.
3.2.11.9.4. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.9.5. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to the value 0 and SHALL then move from its current saturation in an up or down direction by one step, as detailed in Actions on Receipt for StepSaturation Command .
| StepMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Up |
Increase the device’s saturation by one step, in a continuous fashion. However, if the saturation value is already the maximum value then do nothing. |
|
Down |
Decrease the device’s saturation by one step, in a continuous fashion. However, if the saturation value is already the minimum value then do nothing. |
3.2.11.10. MoveToHueAndSaturation Command
The MoveToHueAndSaturation command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Hue |
uint8 |
0 to 254 |
M |
||
|
1 |
Saturation |
uint8 |
0 to 254 |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.10.1. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.10.2. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to the value 0 and SHALL then move from its current hue and saturation to the values given in the Hue and Saturation fields.
The movement SHALL be continuous, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new color SHALL be equal to the TransitionTime field, in 1/10ths of a second.
The
path
through
color
space
taken
during
the
transition
is
not
specified,
but
it
is
recommended
that
the
shortest
path
is
taken
through
hue/saturation
color
space,
i.e.,
movement
is
‘in
'in
a
straight
line’
line'
across
the
hue/saturation
disk.
CIE
xyY
Color
Space.
3.2.11.11. MoveToColor Command
The MoveToColor command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
ColorX |
uint16 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
1 |
ColorY |
uint16 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.11.1. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.11.2. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the value of the ColorMode attribute, where implemented, to 1, and SHALL then move from its current color to the color given in the ColorX and ColorY fields.
The movement SHALL be continuous, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new color SHALL be equal to the TransitionTime field, in 1/10ths of a second.
The path through color space taken during the transition is not specified, but it is recommended that the shortest path is taken through color space, i.e., movement is 'in a straight line' across the CIE xyY Color Space.
3.2.11.12. MoveColor Command
The MoveColor command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
RateX |
int16 |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
RateY |
int16 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.12.1. RateX Field
The RateX field specifies the rate of movement in steps per second. A step is a change in the device’s CurrentX attribute of one unit.
3.2.11.12.2. RateY Field
The RateY field specifies the rate of movement in steps per second. A step is a change in the device’s CurrentY attribute of one unit.
3.2.11.12.3. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.12.4. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the value of the ColorMode attribute, where implemented, to 1, and SHALL then move from its current color in a continuous fashion according to the rates specified. This movement SHALL continue until the target color for the next step cannot be implemented on this device.
If both the RateX and RateY fields contain a value of zero, no movement SHALL be carried out, and the command execution SHALL have no effect other than stopping the operation of any previously received command of this cluster. This command can thus be used to stop the operation of any other command of this cluster.
3.2.11.13. StepColor Command
The StepColor command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
StepX |
int16 |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
StepY |
int16 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.13.1. StepX and StepY Fields
The StepX and StepY fields specify the change to be added to the device’s CurrentX attribute and CurrentY attribute respectively.
3.2.11.13.2. TransitionTime Field
The TransitionTime field specifies, in 1/10ths of a second, the time that SHALL be taken to perform the color change.
3.2.11.13.3. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.13.4. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the value of the ColorMode attribute, where implemented, to 1, and SHALL then move from its current color by the color step indicated.
The movement SHALL be continuous, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new color SHALL be equal to the TransitionTime field, in 1/10ths of a second.
The path through color space taken during the transition is not specified, but it is recommended that the shortest path is taken through color space, i.e., movement is 'in a straight line' across the CIE xyY Color Space.
Note also that if the required step is larger than can be represented by signed 16-bit integers then more than one step command SHOULD be issued.
3.2.11.14. MoveToColorTemperature Command
The MoveToColorTemperature command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
ColorTemperatureMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
1 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
2 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.14.1. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.14.2. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the value of the ColorMode attribute, where implemented, to 2, and SHALL then move from its current color to the color given by the ColorTemperatureMireds field.
The movement SHALL be continuous, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new color SHALL be equal to the TransitionTime field, in 1/10ths of a second.
By
definition
of
this
color
mode,
the
path
through
color
space
taken
during
the
transition
is
along
the
‘Black
'Black
Body
Line'.
3.2.11.15. EnhancedMoveToHue Command
The EnhancedMoveToHue command allows lamps to be moved in a smooth continuous transition from their current hue to a target hue.
The EnhancedMoveToHue command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
EnhancedHue |
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
Direction |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.15.1. EnhancedHue Field
The EnhancedHue field specifies the target extended hue for the lamp.
3.2.11.15.2. Direction Field
This field is identical to the Direction field of the MoveToHue command of the Color Control cluster (see sub-clause Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields ).
3.2.11.15.3. TransitionTime Field
This field is identical to the TransitionTime field of the MoveToHue command of the Color Control cluster (see sub-clause Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields ).
3.2.11.15.4. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.15.5. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to 0 and set the EnhancedColorMode attribute to the value 3. The device SHALL then move from its current enhanced hue to the value given in the EnhancedHue field.
The movement SHALL be continuous, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new enhanced hue SHALL be equal to the TransitionTime field.
3.2.11.16. EnhancedMoveHue Command
The EnhancedMoveHue command allows lamps to be moved in a continuous stepped transition from their current hue to a target hue.
The EnhancedMoveHue command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
MoveMode |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Rate |
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
3 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.16.1. MoveMode Field
This field is identical to the MoveMode field of the MoveHue command of the Color Control cluster (see sub-clause MoveHue Command ). If the MoveMode field is equal to 0 (Stop), the Rate field SHALL be ignored.
3.2.11.16.2. Rate field
The Rate field specifies the rate of movement in steps per second. A step is a change in the extended hue of a device by one unit. If the MoveMode field is set to 1 (up) or 3 (down) and the Rate field has a value of zero, the command has no effect and a response command SHALL be sent in response, with the status code set to INVALID_COMMAND. If the MoveMode field is set to 0 (stop) the Rate field SHALL be ignored.
3.2.11.16.3. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.16.4. Effect on receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to 0 and set the EnhancedColorMode attribute to the value 3. The device SHALL then move from its current enhanced hue in an up or down direction in a continuous fashion, as detailed in Actions on Receipt of the EnhancedMoveHueCommand .
| MoveMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Stop |
If
moving,
stop,
else
ignore
the
command
(i.e.,
the
command
is
accepted
but
has
no
effect).
|
|
Up |
Increase the device’s enhanced hue at the rate given in the Rate field. If the enhanced hue reaches the maximum allowed for the device, wraparound and proceed from its minimum allowed value. |
|
Down |
Decrease the device’s enhanced hue at the rate given in the Rate field. If the hue reaches the minimum allowed for the device, wraparound and proceed from its maximum allowed value. |
3.2.11.17. EnhancedStepHue Command
The EnhancedStepHue command allows lamps to be moved in a stepped transition from their current hue to a target hue, resulting in a linear transition through XY space.
The EnhancedStepHue command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
StepMode |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
StepSize |
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.17.1. StepMode Field
This field is identical to the StepMode field of the StepHue command of the Color Control cluster (see sub-clause StepHue Command ).
3.2.11.17.2. StepSize Field
The StepSize field specifies the change to be added to (or subtracted from) the current value of the device’s enhanced hue.
3.2.11.17.3. TransitionTime Field
The TransitionTime field specifies, in units of 1/10ths of a second, the time that SHALL be taken to perform the step. A step is a change to the device’s enhanced hue of a magnitude corresponding to the StepSize field.
Note: Here TransitionTime data field is of data type uint16, while the TransitionTime data field of the StepHue command is of data type uint8.
3.2.11.17.4. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.17.5. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to 0 and the EnhancedColorMode attribute to the value 3. The device SHALL then move from its current enhanced hue in an up or down direction by one step, as detailed in Actions on Receipt for the EnhancedStepHue Command .
| StepMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Up |
Increase the device’s enhanced hue by one step. If the enhanced hue reaches the maximum allowed for the device, wraparound and proceed from its minimum allowed value. |
|
Down |
Decrease the device’s enhanced hue by one step. If the hue reaches the minimum allowed for the device, wraparound and proceed from its maximum allowed value. |
3.2.11.18. EnhancedMoveToHueAndSaturation Command
The EnhancedMoveToHueAndSaturation command allows lamps to be moved in a smooth continuous transition from their current hue to a target hue and from their current saturation to a target saturation.
The EnhancedMoveToHueAndSaturation command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
EnhancedHue |
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
Saturation |
uint8 |
0 to 254 |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
3 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
4 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.18.1. EnhancedHue Field
The EnhancedHue field specifies the target extended hue for the lamp.
3.2.11.18.2. Saturation Field
This field is identical to the Saturation field of the MoveToHueAndSaturation command of the Color Control cluster (see sub-clause MoveToHueAndSaturation Command ).
3.2.11.18.3. TransitionTime Field
This field is identical to the TransitionTime field of the MoveToHue command of the Color Control cluster (see sub-clause MoveToHueAndSaturation Command ).
3.2.11.18.4. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.18.5. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set the ColorMode attribute to the value 0 and set the EnhancedColorMode attribute to the value 3. The device SHALL then move from its current enhanced hue and saturation to the values given in the EnhancedHue and Saturation fields.
The movement SHALL be continuous, i.e., not a step function, and the time taken to move to the new color SHALL be equal to the TransitionTime field, in 1/10ths of a second.
The
path
through
color
space
taken
during
the
transition
is
not
specified,
but
it
is
recommended
that
the
shortest
path
is
taken
through
hue/saturation
color
space,
i.e.,
movement
is
'in
a
straight
line'
across
the
hue/saturation
disk.
CIE
xyY
Color
Space.
3.2.11.19. ColorLoopSet Command
The Color Loop Set command allows a color loop to be activated such that the color lamp cycles through its range of hues.
The ColorLoopSet command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
UpdateFlags |
map8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Action |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
2 |
Direction |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
3 |
Time |
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
4 |
StartHue |
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
5 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
6 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.19.1. UpdateFlags Field
The UpdateFlags field specifies which color loop attributes to update before the color loop is started. This field SHALL be formatted as illustrated in Format of the UpdateFlags Field of the ColorLoopSet Command .
| Bit |
Name
|
|---|---|
|
0 |
UpdateAction |
|
1 |
UpdateDirection |
|
2 |
UpdateTime |
|
3 |
UpdateStartHue |
|
4-7 |
(Reserved) |
The UpdateAction sub-field is 1 bit in length and specifies whether the device SHALL adhere to the action field in order to process the command. If this sub-field is set to 1, the device SHALL adhere to the action field. If this sub-field is set to 0, the device SHALL ignore the Action field.
The UpdateDirection sub-field is 1 bit in length and specifies whether the device SHALL update the ColorLoopDirection attribute with the Direction field. If this sub-field is set to 1, the device SHALL update the value of the ColorLoopDirection attribute with the value of the Direction field. If this sub-field is set to 0, the device SHALL ignore the Direction field.
The UpdateTime sub-field is 1 bit in length and specifies whether the device SHALL update the ColorLoopTime attribute with the Time field. If this sub-field is set to 1, the device SHALL update the value of the ColorLoopTime attribute with the value of the Time field. If this sub-field is set to 0, the device SHALL ignore the Time field.
The UpdateStartHue sub-field is 1 bit in length and specifies whether the device SHALL update the ColorLoopStartEnhancedHue attribute with the StartHue field. If this sub-field is set to 1, the device SHALL update the value of the ColorLoopStartEnhancedHue attribute with the value of the StartHue field. If this sub-field is set to 0, the device SHALL ignore the StartHue field.
3.2.11.19.2. Action Field
The Action field specifies the action to take for the color loop if the UpdateAction sub-field of the UpdateFlags field is set to 1. This field SHALL be set to one of the non-reserved values listed in Values of the Action Field of the ColorLoopSet Command .
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
De-activate the color loop. |
|
1 |
Activate the color loop from the value in the ColorLoopStartEnhancedHue field. |
|
2 |
Activate the color loop from the value of the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute. |
3.2.11.19.3. Direction Field
The Direction field specifies the direction for the color loop if the Update Direction field of the UpdateFlags field is set to 1. This field SHALL be set to one of the non-reserved values listed in Values of the Direction Field of the ColorLoopSet Command .
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Decrement the hue in the color loop. |
|
1 |
Increment the hue in the color loop. |
3.2.11.19.4. Time Field
The Time field specifies the number of seconds over which to perform a full color loop if the UpdateTime sub-field of the UpdateFlags field is set to 1.
3.2.11.19.5. Start Hue Field
The StartHue field specifies the starting hue to use for the color loop if the Update StartHue field of the Update Flags field is set to 1.
3.2.11.19.6. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.19.7. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, the device SHALL first update its color loop attributes according to the value of the UpdateFlags field, as follows. If the UpdateDirection sub-field is set to 1, the device SHALL set the ColorLoopDirection attribute to the value of the Direction field. If the UpdateTime sub-field is set to 1, the device SHALL set the ColorLoopTime attribute to the value of the Time field. If the UpdateStartHue sub-field is set to 1, the device SHALL set the ColorLoopStartEnhancedHue attribute to the value of the StartHue field. If the color loop is active (and stays active), the device SHALL immediately react on updates of the ColorLoopDirection and ColorLoopTime attributes.
If the UpdateAction sub-field of the UpdateFlags field is set to 1, the device SHALL adhere to the action specified in the Action field, as follows. If the value of the Action field is set to 0 and the color loop is active, i.e. the ColorLoopActive attribute is set to 1, the device SHALL de-active the color loop, set the ColorLoopActive attribute to 0 and set the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute to the value of the ColorLoopStoredEnhancedHue attribute. If the value of the Action field is set to 0 and the color loop is inactive, i.e. the ColorLoopActive attribute is set to 0, the device SHALL ignore the action update component of the command. If the value of the action field is set to 1, the device SHALL set the ColorLoopStoredEnhancedHue attribute to the value of the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute, set the ColorLoopActive attribute to 1 and activate the color loop, starting from the value of the ColorLoopStartEnhancedHue attribute. If the value of the Action field is set to 2, the device SHALL set the ColorLoopStoredEnhancedHue attribute to the value of the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute, set the ColorLoopActive attribute to 1 and activate the color loop, starting from the value of the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute.
If the color loop is active, the device SHALL cycle over the complete range of values of the EnhancedCurrentHue attribute in the direction of the ColorLoopDirection attribute over the time specified in the ColorLoopTime attribute. The level of increments/decrements is application specific.
3.2.11.20. StopMoveStep Command
The StopMoveStep command is provided to allow MoveTo and Step commands to be stopped. (Note this automatically provides symmetry to the Level Control cluster.)
Note: the StopMoveStep command has no effect on an active color loop.
The StopMoveStep command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
1 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.20.1. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.20.2. Effect on Receipt
Upon receipt of this command, any MoveTo, Move or Step command currently in process SHALL be terminated. The values of the CurrentHue, EnhancedCurrentHue and CurrentSaturation attributes SHALL be left at their present value upon receipt of the StopMoveStep command, and the RemainingTime attribute SHALL be set to zero.
3.2.11.21. MoveColorTemperature Command
The MoveColorTemperature command allows the color temperature of a lamp to be moved at a specified rate.
The MoveColorTemperature command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
MoveMode |
map8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Rate |
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
3 |
ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
4 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
5 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.21.1. MoveMode Field
This field is identical to the MoveMode field of the MoveHue command of the Color Control cluster (see sub-clause MoveHue Command ). If the MoveMode field is equal to 0 (Stop), the Rate field SHALL be ignored.
3.2.11.21.2. Rate Field
The Rate field specifies the rate of movement in steps per second. A step is a change in the color temperature of a device by one unit. If the MoveMode field is set to 1 (up) or 3 (down) and the Rate field has a value of zero, the command has no effect and a response command SHALL be sent in response, with the status code set to INVALID_COMMAND. If the MoveMode field is set to 0 (stop) the Rate field SHALL be ignored.
3.2.11.21.3. ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds Field
The ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds field specifies a lower bound on the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (≡ an upper bound on the color temperature in kelvins) for the current move operation such that:
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds
≤
\$<=\$
ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds
field
≤
\$<=\$
ColorTemperatureMireds
As such if the move operation takes the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute towards the value of the ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds field it SHALL be clipped so that the above invariant is satisfied. If the ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds field is set to 0, ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds SHALL be used as the lower bound for the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute.
3.2.11.21.4. ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds Field
The ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds field specifies an upper bound on the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (≡ a lower bound on the color temperature in kelvins) for the current move operation such that:
ColorTemperatureMireds
≤
\$<=\$
ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds
field
≤
\$<=\$
ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds
As such if the move operation takes the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute towards the value of the ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds field it SHALL be clipped so that the above invariant is satisfied. If the ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds field is set to 0, ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds SHALL be used as the upper bound for the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute.
3.2.11.21.5. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.21.6. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set both the ColorMode and EnhancedColorMode attributes to 2. The device SHALL then move from its current color temperature in an up or down direction in a continuous fashion, as detailed in Actions on Receipt of the MoveColorTemperature Command .
| MoveMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Stop |
If moving, stop the operation, else ignore the command (i.e., the command is accepted but has no effect). |
|
Up |
Increase the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (≡ decrease the color temperature in kelvins) at the rate given in the Rate field. If the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute reaches the maximum allowed for the device (via either the ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds field or the ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds attribute), the move operation SHALL be stopped. |
|
Down |
Decrease the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (≡ increase the color temperature in kelvins) at the rate given in the Rate field. If the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute reaches the minimum allowed for the device (via either the ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds field or the ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds attribute), the move operation SHALL be stopped. |
3.2.11.22. StepColorTemperature Command
The StepColorTemperature command allows the color temperature of a lamp to be stepped with a specified step size.
The StepColorTemperature command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
StepMode |
map8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
StepSize |
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
TransitionTime |
uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
M |
||
|
3 |
ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
4 |
ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds |
uint16 |
0
to
|
M |
||
|
5 |
OptionsMask |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
|
|
6 |
OptionsOverride |
map8 |
desc |
0 |
M |
3.2.11.22.1. StepMode Field
This field is identical to the StepMode field of the StepHue command of the Color Control cluster (see sub-clause StepHue Command ).
3.2.11.22.2. StepSize Field
The StepSize field specifies the change to be added to (or subtracted from) the current value of the device’s color temperature.
3.2.11.22.3. TransitionTime Field
The TransitionTime field specifies, in units of 1/10ths of a second, the time that SHALL be taken to perform the step. A step is a change to the device’s color temperature of a magnitude corresponding to the StepSize field.
3.2.11.22.4. ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds Field
The ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds field specifies a lower bound on the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (≡ an upper bound on the color temperature in kelvins) for the current step operation such that:
ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds
≤
\$<=\$
ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds
field
≤
\$<=\$
ColorTemperatureMireds
As such if the step operation takes the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute towards the value of the Color Temperature Minimum Mireds field it SHALL be clipped so that the above invariant is satisfied. If the ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds field is set to 0, ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds SHALL be used as the lower bound for the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute.
3.2.11.22.5. ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds Field
The ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds field specifies an upper bound on the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (≡ a lower bound on the color temperature in kelvins) for the current step operation such that:
ColorTemperatureMireds ≤ ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds field ≤ ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds
As such if the step operation takes the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute towards the value of the ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds field it SHALL be clipped so that the above invariant is satisfied. If the ColorTemperatureMaximum Mireds field is set to 0, ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds SHALL be used as the upper bound for the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute.
3.2.11.22.6. OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields
The OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields SHALL be processed according to section Use of the OptionsMask and OptionsOverride fields .
3.2.11.22.7. Effect on Receipt
On receipt of this command, a device SHALL set both the ColorMode and EnhancedColorMode attributes to 2. The device SHALL then move from its current color temperature in an up or down direction by one step, as detailed in Actions on Receipt of the StepColorTemperature Command .
| StepMode | Action on Receipt |
|---|---|
|
Up |
Increase the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (≡ decrease the color temperature in kelvins) by one step. If the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute reaches the maximum allowed for the device (via either the ColorTemperatureMaximumMireds field or the ColorTempPhysicalMaxMireds attribute), the step operation SHALL be stopped. |
|
Down |
Decrease the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute (≡ increase the color temperature in kelvins) by one step. If the ColorTemperatureMireds attribute reaches the minimum allowed for the device (via either the ColorTemperatureMinimumMireds field or the ColorTempPhysicalMinMireds attribute), the step operation SHALL be stopped. |
3.3. Ballast Configuration Cluster
This cluster is used for configuring a lighting ballast.
|
Note
|
Support for Ballast Configuration cluster is provisional. |
3.3.2.
3.3.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
CCB 2104 2193 2230 2393 Deprecated some attributes |
|
3 |
CCB 2881 |
|
4 |
|
3.3.3.
3.3.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
|
3.3.5.
3.3.4.
Dependencies
If the Alarms server cluster is supported on the same endpoint then the Alarms functionality is enabled and the LampAlarmMode attribute SHALL be supported.
3.3.6.
Ballast
Configuration
Attribute
Set
3.3.5.
Data
Types
3.3.5.1. BallastStatusBitmap Type
The
attributes
defined
in
this
specification
are
arranged
into
sets
of
related
attributes.
This
data
type
is
derived
from
map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 | BallastNonOperational | Operational state of the ballast. |
1 | LampFailure | Operational state of the lamps. |
3.3.6.
Attributes
of
the
Ballast
Information
Attribute
Set
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
PhysicalMinLevel |
uint8 |
1 to 254 |
1 |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0001 |
PhysicalMaxLevel |
uint8 |
1 to 254 |
254 |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0002 |
BallastStatus |
|
|
0 |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0010 |
MinLevel | uint8 |
PhysicalMinLevel
|
|
PhysicalMinLevel | RW VM | M |
0x0011 | MaxLevel | uint8 |
MinLevel
to
PhysicalMaxLevel
|
PhysicalMaxLevel
|
RW VM |
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
0x0014 |
IntrinsicBallastFactor |
uint8 | all | X | RW VM | O |
|
|
|
|
uint8 |
|
X |
|
RW VM |
|
|
|
|
uint8 |
|
| M | ||
0x0030 | LampType | string | max 16 | empty string |
RW VM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RW VM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
all |
X |
|
RW VM |
|
|
|
|
|
all |
X |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
|
|
| 0 | RW VM | O | |
0x0035 | LampBurnHoursTripPoint | uint24 | all |
X |
null |
RW VM |
O |
3.3.7.1.
MinLevel
3.3.6.1.
PhysicalMinLevel
Attribute
The
This
attribute
SHALL
specify
the
minimum
light
output
the
ballast
can
achieve
according
to
the
dimming
light
curve
(see
Dimming
Curve
).
3.3.6.2. PhysicalMaxLevel Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify the maximum light output the ballast can achieve according to the dimming light curve (see Dimming Curve ).
3.3.6.3. BallastStatus Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify the status of various aspects of the ballast or the connected lights, see BallastStatusBitmap .
3.3.6.4. MinLevel Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
light
output
of
the
ballast
according
to
the
dimming
light
curve
(see
The
Dimming
Light
Curve
)
when
the
Level
Control
Cluster’s
Cluster’s
CurrentLevel
attribute
equals
to
1
(and
the
On/Off
Cluster’s
OnOff
attribute
equals
to
TRUE).
The
value
of
this
attribute
SHALL
be
both
greater
than
or
equal
to
PhysicalMinLevel
and
less
than
or
equal
to
MaxLevel.
If
an
attempt
is
made
to
set
this
attribute
to
a
level
where
these
conditions
are
not
met,
a
response
SHALL
be
returned
with
status
code
set
to
CONSTRAINT_ERROR,
and
the
level
SHALL
not
NOT
be
set.
3.3.7.2.
3.3.6.5.
MaxLevel
Attribute
The
MaxLevel
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
light
output
of
the
ballast
according
to
the
dimming
light
curve
(see
The
Dimming
Light
Curve
)
when
the
Level
Control
Cluster’s
Cluster’s
CurrentLevel
attribute
equals
to
254
(and
the
On/Off
Cluster’s
Cluster’s
OnOff
attribute
equals
to
TRUE).
The
value
of
this
attribute
SHALL
be
both
less
than
or
equal
to
PhysicalMaxLevel
and
greater
than
or
equal
to
MinLevel.
If
an
attempt
is
made
to
set
this
attribute
to
a
level
where
these
conditions
are
not
met,
a
response
SHALL
be
returned
with
status
code
set
to
CONSTRAINT_ERROR,
and
the
level
SHALL
not
NOT
be
set.
3.3.7.3.
3.3.6.6.
IntrinsicBallastFactor
Attribute
The
IntrinsicBallastFactor
This
attribute
specifies
as
a
percentage
SHALL
specify
the
ballast
factor
factor,
as
a
percentage,
of
the
ballast/lamp
combination,
prior
to
any
adjustment.
A value of null indicates in invalid value.
3.3.7.4.
3.3.6.7.
BallastFactorAdjustment
Attribute
The
BallastFactorAdjustment
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
multiplication
factor,
as
a
percentage,
to
be
applied
to
the
configured
light
output
of
the
lamps.
A
typical
usage
of
use
for
this
mechanism
attribute
is
to
compensate
for
reduction
in
efficiency
over
the
lifetime
of
a
lamp.
The light output is given by
actual light output = configured light output x BallastFactorAdjustment / 100%
The
range
for
this
attribute
is
manufacturer
dependent.
If
an
attempt
is
made
to
set
this
attribute
to
a
level
that
cannot
be
supported,
a
response
SHALL
be
returned
with
status
code
set
to
CONSTRAINT_ERROR,
and
the
level
SHALL
not
NOT
be
set.
changed.
The
value
of
null
indicates
that
ballast
factor
scaling
is
not
in
use.
3.3.8.1.
3.3.6.8.
LampQuantity
Attribute
The
LampQuantity
This
attribute
and
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
number
of
lamps
connected
to
this
ballast.
(
Note
1:
this
number
does
not
take
into
account
whether
lamps
are
actually
in
their
sockets
or
not).
3.3.9.1.
3.3.6.9.
LampType
Attribute
The
LampType
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
type
of
lamps
(including
their
wattage)
connected
to
the
ballast.
3.3.9.2.
3.3.6.10.
LampManufacturer
Attribute
The
LampManufacturer
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
name
of
the
manufacturer
of
the
currently
connected
lamps.
3.3.9.3.
3.3.6.11.
LampRatedHours
Attribute
The
LampRatedHours
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
number
of
hours
of
use
the
lamps
are
rated
for
by
the
manufacturer.
A value of null indicates an invalid or unknown time.
3.3.9.4.
3.3.6.12.
LampBurnHours
Attribute
The
LampBurnHours
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
length
of
time,
in
hours,
the
currently
connected
lamps
have
been
operated,
cumulative
since
the
last
re-lamping.
Burn
hours
SHALL
not
NOT
be
accumulated
if
the
lamps
are
off.
This
attribute
SHOULD
be
reset
to
zero
(e.g.,
remotely)
when
the
lamp(s)
lamps
are
changed.
If
partially
used
lamps
are
connected,
LampBurnHours
SHOULD
be
updated
to
reflect
the
burn
hours
of
the
lamps.
A value of null indicates an invalid or unknown time.
3.3.9.5.
3.3.6.13.
LampAlarmMode
Attribute
The
LampAlarmMode
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
which
attributes
MAY
cause
an
alarm
notification
to
be
generated,
as
listed
in
Values
of
the
LampAlarmMode
Attribute
.
generated.
A
‘1’
1
in
each
bit
position
causes
means
that
its
associated
attribute
to
be
is
able
to
generate
an
alarm.
(
Note:
All
alarms
are
also
logged
in
the
alarm
table
–
see
Alarms
cluster).
3.3.9.6.
3.3.6.14.
LampBurnHoursTripPoint
Attribute
The
LampBurnHoursTripPoint
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
specify
the
number
of
hours
the
LampBurnHours
attribute
MAY
reach
before
an
alarm
is
generated.
If the Alarms cluster is not present on the same device this attribute is not used and thus MAY be omitted (see Dependencies ).
The Alarm Code field included in the generated alarm SHALL be 0x01.
If
this
attribute
takes
has
the
value
of
null,
then
this
alarm
SHALL
not
NOT
be
generated.
3.3.11.
3.3.7.
The
Dimming
Light
Curve
The dimming curve is recommended to be logarithmic, as defined by the following equation:
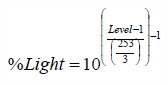
Where: %Light is the percent light output of the ballast and
-
Level is an 8-bit integer between 1 (0.1% light output) and 254 (100% output) that is adjusted for MinLevel and MaxLevel using the following equation:
Level = (MaxLevel – MinLevel) * CurrentLevel / 253 + (254 * MinLevel – MaxLevel) / 253.
Note 1: Value 255 is not used.
Note 2: The light output is determined by this curve together with the IntrinsicBallastFactor and BallastFactorAdjustment attributes.
The table below gives a couple of examples of the dimming light curve for different values of MinLevel, MaxLevel and CurrentLevel.
| MinLevel | MaxLevel | CurrentLevel | Level | %Light |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
254 |
1 |
1 |
0.10% |
|
1 |
254 |
10 |
10 |
0.13% |
|
1 |
254 |
100 |
100 |
1.49% |
|
1 |
254 |
254 |
254 |
100% |
|
170 |
254 |
1 |
170 |
10.1% |
|
170 |
254 |
10 |
173 |
11.0% |
|
170 |
254 |
100 |
203 |
24.8% |
|
170 |
254 |
254 |
254 |
100% |
|
170 |
230 |
1 |
170 |
10.1% |
|
170 |
230 |
10 |
172 |
10.7% |
|
170 |
230 |
100 |
193 |
19.2% |
|
170 |
230 |
254 |
230 |
51.9% |
4. HVAC
The Cluster Library is made of individual chapters such as this one. References between chapters are made using a X.Y notation where X is the chapter and Y is the sub-section within that chapter.
4.1. General Description
4.1.1. Introduction
The clusters specified in this document are for use typically in HVAC applications, but MAY be used in any application domain.
4.1.2. Terms
Precooling: Cooling a building in the early (cooler) part of the day, so that the thermal mass of the building decreases cooling needs in the later (hotter) part of the day.
4.1.3. Cluster List
This
section
lists
the
HVAC
specific
clusters
as
specified
in
this
document
and
gives
examples
of
typical
usage
for
the
purpose
of
clarification.
The
clusters
defined
in
this
document
are
listed
in
Clusters
Specified
in
the
HVAC
Functional
Domain
:
chapter.
| Cluster ID | Cluster Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0x0200 |
An interface for configuring and controlling pumps. |
|
|
0x0201 |
An interface for configuring and controlling the functionality of a thermostat |
|
|
0x0202 |
An interface for controlling a fan in a heating / cooling system |
|
|
0x0204 |
An interface for configuring the user interface of a thermostat (which MAY be remote from the thermostat) |


4.2. Pump Configuration and Control Cluster
The Pump Configuration and Control cluster provides an interface for the setup and control of pump devices, and the automatic reporting of pump status information. Note that control of pump speed is not included – speed is controlled by the On/Off and Level Control clusters.
4.2.2.
4.2.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
All Hubs changes |
|
3 |
New data model format and notation, added additional events |
|
4 | Added feature map |
4.2.3.
4.2.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
|
4.2.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | PRSCONST | ConstantPressure | O.a+ | Supports operating in constant pressure mode |
1 | PRSCOMP | CompensatedPressure | O.a+ | Supports operating in compensated pressure mode |
2 | FLW | ConstantFlow | O.a+ | Supports operating in constant flow mode |
3 | SPD | ConstantSpeed | O.a+ | Supports operating in constant speed mode |
4 | TEMP | ConstantTemperature | O.a+ | Supports operating in constant temperature mode |
5 | AUTO | Automatic | O | Supports operating in automatic mode |
6 | LOCAL | LocalOperation | O | Supports operating using local settings |
4.2.5. Dependencies
Where
external
pressure,
flow,
and
temperature
measurements
are
processed
by
this
cluster
(see
Values
of
the
ControlMode
Attribute
),
attribute),
these
are
provided
by
a
Pressure
Measurement
cluster,
a
Flow
Measurement
cluster,
and
a
Temperature
Measurement
client
cluster,
respectively.
These
3
client
clusters
are
used
for
connection
to
a
remote
sensor
device.
The
pump
is
able
to
use
the
sensor
measurement
provided
by
a
remote
sensor
for
regulation
of
the
pump
speed.
Note
that
control
of
the
pump
setpoint
is
not
included
in
this
cluster
–
the
On/Off
and
Level
Control
clusters
(see
Typical
Usage
of
Pump
Configuration
and
Control
Cluster
)
MAY
be
used
by
a
pump
device
to
turn
it
on
and
off
and
control
its
setpoint.
Note
that
the
Pump
Configuration
and
Control
cluster
MAY
override
on/off/setpoint
settings
for
specific
operation
modes
(See
section
OperationMode
Attribute
attribute
for
detailed
description
of
the
operation
and
control
of
the
pump.).
4.2.6.
Pump
Information
Attributes
Data
Types
4.2.6.1. PumpStatusBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map16.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 | DeviceFault | A fault related to the system or pump device is detected. |
1 | SupplyFault | A fault related to the supply to the pump is detected. |
2 | SpeedLow | Setpoint is too low to achieve. |
3 | SpeedHigh | Setpoint is too high to achieve. |
4 | LocalOverride | Device control is overridden by hardware, such as an external STOP button or via a local HMI. |
5 | Running |
Pump
|
6 | RemotePressure | A remote pressure sensor is used as the sensor for the regulation of the pump. |
7 | RemoteFlow | A remote flow sensor is used as the sensor for the regulation of the pump. |
8 | RemoteTemperature | A remote temperature sensor is used as the sensor for the regulation of the pump. |
4.2.6.1.1. DeviceFault Bit
If this bit is set, it MAY correspond to an event in the range 2-16, see Events .
4.2.6.1.2. SupplyFault Bit
If this bit is set, it MAY correspond to an event in the range 0-1 or 13, see Events .
4.2.6.1.3. LocalOverride Bit
While this bit is set, the EffectiveOperationMode is adjusted to Local. Any request changing OperationMode SHALL generate a FAILURE error status until LocalOverride is cleared on the physical device. When LocalOverride is cleared, the device SHALL return to the operation mode set in OperationMode.
4.2.6.1.4. RemotePressure Bit
If this bit is set, EffectiveControlMode is ConstantPressure and the setpoint for the pump is interpreted as a percentage of the range of the remote sensor ([MinMeasuredValue – MaxMeasuredValue]).
4.2.6.2. OperationModeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Normal | The pump is controlled by a setpoint, as defined by a connected remote sensor or by the ControlMode attribute. | M |
1 | Minimum | This value sets the pump to run at the minimum possible speed it can without being stopped. | SPD |
2 | Maximum | This value sets the pump to run at its maximum possible speed. | SPD |
3 | Local | This value sets the pump to run with the local settings of the pump, regardless of what these are. | LOCAL |
4.2.6.3. ControlModeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | ConstantSpeed | The pump is running at a constant speed. | SPD |
1 | ConstantPressure | The pump will regulate its speed to maintain a constant differential pressure over its flanges. | PRSCONST |
2 | ProportionalPressure | The pump will regulate its speed to maintain a constant differential pressure over its flanges. | PRSCOMP |
3 | ConstantFlow | The pump will regulate its speed to maintain a constant flow through the pump. | FLW |
5 | ConstantTemperature | The pump will regulate its speed to maintain a constant temperature. | TEMP |
7 | Automatic | The operation of the pump is automatically optimized to provide the most suitable performance with respect to comfort and energy savings. | AUTO |
4.2.6.3.1. ConstantSpeed Value
The setpoint is interpreted as a percentage of the range derived from the [MinConstSpeed – MaxConstSpeed] attributes.
4.2.6.3.2. ConstantPressure Value
The setpoint is interpreted as a percentage of the range of the sensor used for this control mode. In case of the internal pressure sensor, this will be the range derived from the [MinConstPressure – MaxConstPressure] attributes. In case of a remote pressure sensor, this will be the range derived from the [MinMeasuredValue – MaxMeasuredValue] attributes of the remote pressure sensor.
4.2.6.3.3. ProportionalPressure Value
The setpoint is interpreted as a percentage of the range derived of the [MinCompPressure – MaxCompPressure] attributes. The internal setpoint will be lowered (compensated) dependent on the flow in the pump (lower flow ⇒ lower internal setpoint).
4.2.6.3.4. ConstantFlow Value
The setpoint is interpreted as a percentage of the range of the sensor used for this control mode. In case of the internal flow sensor, this will be the range derived from the [MinConstFlow – MaxConstFlow] attributes. In case of a remote flow sensor, this will be the range derived from the [MinMeasuredValue – MaxMeasuredValue] attributes of the remote flow sensor.
4.2.6.3.5. ConstantTemperature Value
The setpoint is interpreted as a percentage of the range of the sensor used for this control mode. In case of the internal temperature sensor, this will be the range derived from the [MinConstTemp – MaxConstTemp] attributes. In case of a remote temperature sensor, this will be the range derived from the [MinMeasuredValue – MaxMeasuredValue] attributes of the remote temperature sensor.
4.2.7. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality |
|
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
MaxPressure |
int16 |
all |
|
|
|
M |
|
|
MaxSpeed |
uint16 |
all |
|
|
|
M |
|
|
MaxFlow |
uint16 |
all |
|
|
|
M |
|
|
MinConstPressure |
int16 |
all |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaxConstPressure |
int16 |
all |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MinCompPressure |
int16 |
all |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaxCompPressure |
int16 |
all |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MinConstSpeed |
uint16 |
all |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaxConstSpeed |
uint16 |
all |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MinConstFlow |
uint16 |
all |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaxConstFlow |
uint16 |
all |
| null |
R V |
FLW, [AUTO] |
0x000B | MinConstTemp | int16 | -27315 to max | X F | null |
| TEMP, [AUTO] |
|
|
|
int16 |
-27315 to max |
| null |
R V |
|
0x0010 | PumpStatus | desc | P | 0 | R V |
O |
|
|
|
| desc | N | desc | R V | M | |
0x0012 | EffectiveControlMode | desc | N | desc | R V | M | |
0x0013 | Capacity |
int16 |
|
| null |
R V |
M |
0x0014 | Speed | uint16 | all | X | null | R V | O |
0x0015 | LifetimeRunningHours | uint24 | all | X N | 0 | RW VM | O |
0x0016 | Power | uint24 | all | X | null |
R V | O |
0x0017 | LifetimeEnergyConsumed | uint32 | all | X N | 0 | RW VM | O |
0x0020 | OperationMode | desc | N | 0 | RW VM | M | |
0x0021 | ControlMode | desc | N | 0 | RW VM | O |
|
|
0x0022 | AlarmMask | map16 | desc | N | 0 | R V | D |
4.2.6.1.
4.2.7.1.
MaxPressure
Attribute
The
MaxPressure
This
attribute
specifies
the
maximum
pressure
the
pump
can
achieve.
It
is
a
physical
limit,
and
does
not
apply
to
any
specific
control
mode
or
operation
mode.
Valid
range
is
-3,276.7
kPa
to
3,276.7
kPa
(steps
of
0.1
kPa).
The
MaxPressure
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.2.
4.2.7.2.
MaxSpeed
Attribute
The
MaxSpeed
This
attribute
specifies
the
maximum
speed
the
pump
can
achieve.
It
is
a
physical
limit,
and
does
not
apply
to
any
specific
control
mode
or
operation
mode.
Valid
range
is
0
to
65,534
RPM
(steps
of
1
RPM).
The
MaxSpeed
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.3.
4.2.7.3.
MaxFlow
Attribute
The
MaxFlow
This
attribute
specifies
the
maximum
flow
the
pump
can
achieve.
It
is
a
physical
limit,
and
does
not
apply
to
any
specific
control
mode
or
operation
mode.
Valid
range
is
0
m
3
/h
to
6,553.4
m
3
/h
(steps
of
0.1
m
3
/h).
The
MaxFlow
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.4.
4.2.7.4.
MinConstPressure
Attribute
The
MinConstPressure
This
attribute
specifies
the
minimum
pressure
the
pump
can
achieve
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ConstantPressure.
Valid
range
is
–3,276.7
kPa
to
3,276.7
kPa
(steps
of
0.1
kPa).
The
MinConstPressure
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.5.
4.2.7.5.
MaxConstPressure
Attribute
The
MaxConstPressure
This
attribute
specifies
the
maximum
pressure
the
pump
can
achieve
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ConstantPressure.
Valid
range
is
–3,276.7
kPa
to
3,276.7
kPa
(steps
of
0.1
kPa).
The
MaxConstPressure
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.6.
4.2.7.6.
MinCompPressure
Attribute
The
MinCompPressure
This
attribute
specifies
the
minimum
compensated
pressure
the
pump
can
achieve
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ProportionalPressure.
Valid
range
is
–3,276.7
kPa
to
3,276.7
kPa
(steps
of
0.1
kPa).
The
MinCompPressure
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.7.
4.2.7.7.
MaxCompPressure
Attribute
The
MaxCompPressure
This
attribute
specifies
the
maximum
compensated
pressure
the
pump
can
achieve
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ProportionalPressure.
Valid
range
is
–3,276.7
kPa
to
3,276.7
kPa
(steps
of
0.1
kPa).
The
MaxCompPressure
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.8.
4.2.7.8.
MinConstSpeed
Attribute
The
MinConstSpeed
This
attribute
specifies
the
minimum
speed
the
pump
can
achieve
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ConstantSpeed.
Valid
range
is
0
to
65,534
RPM
(steps
of
1
RPM).
The
MinConstSpeed
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.9.
4.2.7.9.
MaxConstSpeed
Attribute
The
MaxConstSpeed
This
attribute
specifies
the
maximum
speed
the
pump
can
achieve
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ConstantSpeed.
Valid
range
is
0
to
65,534
RPM
(steps
of
1
RPM).
The
MaxConstSpeed
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.10.
4.2.7.10.
MinConstFlow
Attribute
The
MinConstFlow
This
attribute
specifies
the
minimum
flow
the
pump
can
achieve
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ConstantFlow.
Valid
range
is
0
m
3
/h
to
6,553.4
m
3
/h
(steps
of
0.1
m
3
/h).
The
MinConstFlow
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.11.
4.2.7.11.
MaxConstFlow
Attribute
The
MaxConstFlow
This
attribute
specifies
the
maximum
flow
the
pump
can
achieve
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ConstantFlow.
Valid
range
is
0
m
3
/h
to
6,553.4
m
3
/h
(steps
of
0.1
m
3
/h).
The
MaxConstFlow
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.12.
4.2.7.12.
MinConstTemp
Attribute
The
MinConstTemp
This
attribute
specifies
the
minimum
temperature
the
pump
can
maintain
in
the
system
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ConstantTemperature.
Valid
range
is
–273.15
°C
to
327.67
°C
(steps
of
0.01
°C).
The
MinConstTemp
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.6.13.
4.2.7.13.
MaxConstTemp
Attribute
The
MaxConstTemp
This
attribute
specifies
the
maximum
temperature
the
pump
can
maintain
in
the
system
when
it
is
working
with
the
ControlMode
attribute
set
to
ConstantTemperature.
MaxConstTemp
SHALL
be
greater
than
or
equal
to
_MinConstTemp_
MinConstTemp
Valid
range
is
–273.15
°C
to
327.67
°C
(steps
of
0.01
°C).
The
MaxConstTemp
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
invalid.
4.2.7.1.
4.2.7.14.
PumpStatus
Attribute
The
PumpStatus
This
attribute
specifies
the
activity
status
of
the
pump
functions
as
listed
in
Values
of
the
PumpStatus
Attribute
PumpStatusBitmap
.
Where
a
pump
controller
function
is
active,
the
corresponding
bit
SHALL
be
set
to
1.
Where
a
pump
controller
function
is
not
active,
the
corresponding
bit
SHALL
be
set
to
0.
4.2.7.2.
4.2.7.15.
EffectiveOperationMode
Attribute
The
EffectiveOperationMode
This
attribute
specifies
current
effective
operation
mode
of
the
pump.
pump
as
defined
in
OperationModeEnum
.
The
value
of
the
EffectiveOperationMode
attribute
is
the
same
as
the
OperationMode
attribute,
but
if
unless
one
of
the
following
points
are
true:
The pump is physically set to run with the local settings
or the-
The LocalOverride bit in the PumpStatus attribute is set,
the value MAY be different from the OperationMode attribute.
See
section
OperationMode
Attribute
and
ControlMode
attributes
for
a
detailed
description
of
the
operation
and
control
of
the
pump.
4.2.7.3.
4.2.7.16.
EffectiveControlMode
Attribute
The
EffectiveControlMode
This
attribute
specifies
the
current
effective
control
mode
of
the
pump.
pump
as
defined
in
ControlModeEnum
.
The
EffectiveControlMode
This
attribute
contains
the
control
mode
that
currently
applies
to
the
pump.
It
will
have
the
value
of
the
ControlMode
attribute,
unless
a
one
of
the
following
points
are
true:
The ControlMode attribute is set to Automatic. In this case, the value of the EffectiveControlMode SHALL match the behavior of the pump.
A remote sensor is used as the sensor for regulation of the pump. In this case, EffectiveControlMode will display ConstantPressure, ConstantFlow or ConstantTemperature if the remote sensor is a pressure sensor, a flow sensor or a temperature sensor respectively, regardless of the value of the ControlMode attribute.
In case the ControlMode attribute is not included on the device and no remote sensors are connected, the value of the EffectiveControlMode SHALL match the vendor-specific behavior of the pump.
See
section
OperationMode
Attribute
and
ControlMode
attributes
for
detailed
a
description
of
the
operation
and
control
of
the
pump.
4.2.7.4.
4.2.7.17.
Capacity
Attribute
The
Capacity
This
attribute
specifies
the
actual
capacity
of
the
pump
as
a
percentage
of
the
effective
maximum
setpoint
value.
It
is
updated
dynamically
as
the
speed
of
the
pump
changes.
If the value is not available (the measurement or estimation of the speed is done in the pump), this attribute will indicate the null value.
Valid
range
is
0
%
to
163.835%
(0.005
%
granularity).
Although
the
Capacity
this
attribute
is
a
signed
value,
values
of
capacity
less
than
zero
have
no
physical
meaning.
4.2.7.5.
4.2.7.18.
Speed
Attribute
The
Speed
This
attribute
specifies
the
actual
speed
of
the
pump
measured
in
RPM.
It
is
updated
dynamically
as
the
speed
of
the
pump
changes.
If the value is not available (the measurement or estimation of the speed is done in the pump), this attribute will indicate the null value.
Valid
range
is
0
to
65.534
RPM.
4.2.7.6.
4.2.7.19.
LifetimeRunningHours
Attribute
The
LifetimeRunningHours
This
attribute
specifies
the
accumulated
number
of
hours
that
the
pump
has
been
powered
and
the
motor
has
been
running.
It
is
updated
dynamically
as
it
increases.
It
is
preserved
over
power
cycles
of
the
pump.
If
LifeTimeRunningHours
rises
above
maximum
value
it
“rolls
over”
and
starts
at
0
(zero).
This attribute is writeable, in order to allow setting to an appropriate value after maintenance. If the value is not available, this attribute will indicate the null value.
Valid
range
is
0
to
16,777,214
hrs.
4.2.7.7.
4.2.7.20.
Power
Attribute
The
Power
This
attribute
specifies
the
actual
power
consumption
of
the
pump
in
Watts.
The
value
of
the
Power
this
attribute
is
updated
dynamically
as
the
power
consumption
of
the
pump
changes.
This attribute is read only. If the value is not available (the measurement of power consumption is not done in the pump), this attribute will indicate the null value.
Valid
range
is
0
to
16,777,214
Watts.
4.2.7.8.
4.2.7.21.
LifetimeEnergyConsumed
Attribute
The
LifetimeEnergyConsumed
This
attribute
specifies
the
accumulated
energy
consumption
of
the
pump
through
the
entire
lifetime
of
the
pump
in
kWh.
The
value
of
the
LifetimeEnergyConsumed
attribute
is
updated
dynamically
as
the
energy
consumption
of
the
pump
increases.
If
LifetimeEnergyConsumed
rises
above
maximum
value
it
“rolls
over”
and
starts
at
0
(zero).
This attribute is writeable, in order to allow setting to an appropriate value after maintenance.
Valid
range
is
0
kWh
to
4,294,967,294
kWh.
This
attribute
SHALL
be
null
if
the
value
is
unknown.
4.2.8.1.
4.2.7.22.
OperationMode
Attribute
The
OperationMode
This
attribute
specifies
the
operation
mode
of
the
pump.
This
attribute
SHALL
have
one
of
the
values
listed
pump
as
defined
in
Values
of
the
OperationMode
Attribute
OperationModeEnum
.
The
actual
operating
mode
of
the
pump
is
a
result
of
the
setting
of
the
attributes
OperationMode
,
OperationMode,
ControlMode
and
the
optional
connection
of
a
remote
sensor.
The
operation
and
control
is
prioritized
as
shown
in
the
scheme
in
Priority
Scheme
of
Pump
Operation
and
Control
:
below:
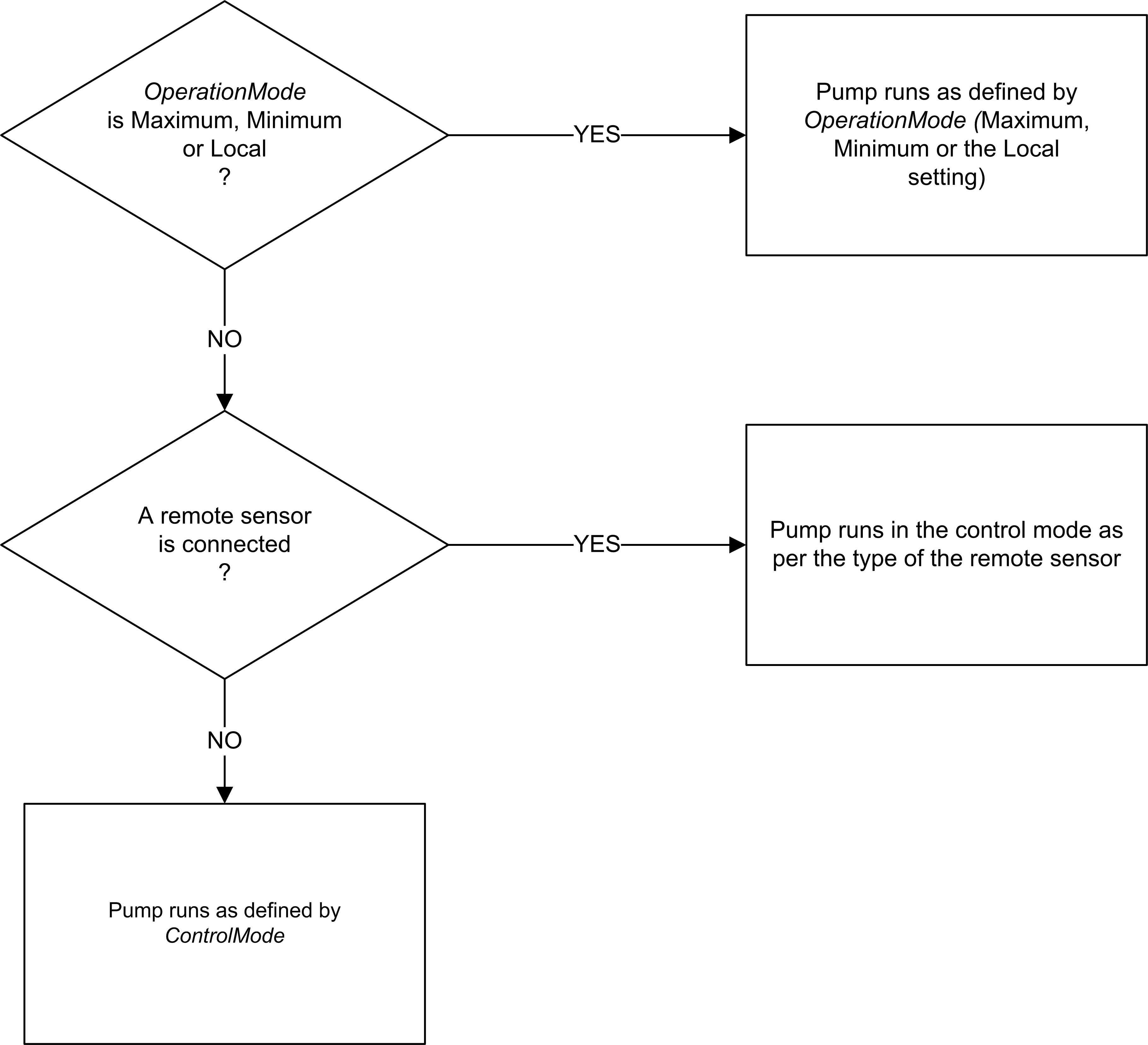
If
the
OperationMode
this
attribute
is
Maximum,
Minimum
or
Local,
the
OperationMode
attribute
decides
how
the
pump
is
operated.
If
the
OperationMode
this
attribute
is
Normal
and
a
remote
sensor
is
connected
to
the
pump,
the
type
of
the
remote
sensor
decides
the
control
mode
of
the
pump.
A
connected
remote
pressure
sensor
will
make
the
pump
run
in
control
mode
Constant
pressure
and
vice
versa
for
flow
and
temperature
type
sensors.
This
is
regardless
of
the
setting
of
the
ControlMode
attribute.
If
the
OperationMode
this
attribute
is
Normal
and
no
remote
sensor
is
connected,
the
control
mode
of
the
pump
is
decided
by
the
ControlMode
attribute.
OperationMode
MAY
be
changed
at
any
time,
even
when
the
pump
is
running.
The
behavior
of
the
pump
at
the
point
of
changing
the
value
of
the
OperationMode
this
attribute
is
vendor-specific.
In
the
OperationMode
Attribute
Value
Name
Description
0
Normal
The
pump
is
controlled
by
case
a
setpoint,
as
defined
by
device
does
not
support
a
connected
remote
sensor
or
by
specific
operation
mode,
the
ControlMode
attribute.
(N.B.
The
setpoint
is
write
interaction
to
this
attribute
with
an
internal
variable
which
MAY
unsupported
operation
mode
value
SHALL
be
controlled
between
0%
ignored
and
100%,
e.g.,
by
means
of
the
Level
Control
cluster)
1
Minimum
This
value
sets
the
pump
to
run
at
the
minimum
possible
speed
it
can
without
being
stopped
2
Maximum
This
value
sets
the
pump
to
run
at
its
maximum
possible
speed
3
Local
This
value
sets
the
pump
to
run
with
the
local
settings
of
a
response
containing
the
pump,
regardless
status
of
what
these
are
CONSTRAINT_ERROR
SHALL
be
returned.
4.2.8.2.
4.2.7.23.
ControlMode
Attribute
The
ControlMode
This
attribute
specifies
the
control
mode
of
the
pump.
This
attribute
SHALL
have
one
of
the
values
listed
pump
as
defined
in
Values
of
the
ControlMode
Attribute
ControlModeEnum
.
See
section
the
OperationMode
Attribute
attribute
for
a
detailed
description
of
the
operation
and
control
of
the
pump.
In
the
case
a
device
does
not
support
or
implement
a
specific
control
mode,
a
write
interaction
to
the
ControlMode
attribute
with
an
unsupported
control
mode
value
SHALL
be
ignored
and
a
response
containing
the
status
of
CONSTRAINT_ERROR
SHALL
be
returned.
ControlMode
MAY
be
changed
at
any
time,
even
when
the
pump
is
running.
The
behavior
of
the
pump
at
the
point
of
changing
is
vendor-specific.
In
case
of
the
internal
pressure
sensor,
this
will
be
the
range
derived
from
the
[
MinConstPressure
–
MaxConstPressure
]
attributes.
In
case
of
a
remote
pressure
sensor,
this
will
be
the
range
derived
from
the
[
MinMeasuredValue
–
MaxMeasuredValue
]
attributes
of
the
remote
pressure
sensor.
2
ProportionalPressure
The
pump
will
regulate
its
speed
to
maintain
a
constant
differential
pressure
over
its
flanges.
The
setpoint
is
interpreted
as
a
percentage
of
the
range
derived
of
the
[
MinCompPressure
–
MaxCompPressure
]
attributes.
The
internal
setpoint
will
be
lowered
(compensated)
dependent
on
the
flow
in
the
pump
(lower
flow
⇒
lower
internal
setpoint)
3
ConstantFlow
The
pump
will
regulate
its
speed
to
maintain
a
constant
flow
through
the
pump.
The
setpoint
is
interpreted
as
device
does
not
support
a
percentage
of
the
range
of
the
sensor
used
for
this
specific
control
mode.
In
case
of
the
internal
flow
sensor,
this
will
be
the
range
derived
from
the
[
MinConstFlow
–
MaxConstFlow
]
attributes.
In
case
of
a
remote
flow
sensor,
this
will
be
the
range
derived
from
the
[
MinMeasuredValue
–
MaxMeasuredValue
]
attributes
of
mode,
the
remote
flow
sensor.
5
ConstantTemperature
The
pump
will
regulate
its
speed
write
interaction
to
maintain
a
constant
temperature.
The
setpoint
is
interpreted
as
a
percentage
of
the
range
of
the
sensor
used
for
this
attribute
with
an
unsupported
control
mode.
In
case
of
the
internal
temperature
sensor,
this
will
mode
value
SHALL
be
the
range
derived
from
the
[
MinConstTemp
–
MaxConstTemp
]
attributes.
In
case
of
ignored
and
a
remote
temperature
sensor,
this
will
be
the
range
derived
from
the
[
MinMeasuredValue
–
MaxMeasuredValue
]
attributes
of
response
containing
the
remote
temperature
sensor.
7
Automatic
The
operation
status
of
the
pump
is
automatically
optimized
to
provide
the
most
suitable
performance
with
respect
to
comfort
and
energy
savings.
This
behavior
is
manufacturer
defined.
The
pump
can
CONSTRAINT_ERROR
SHALL
be
stopped
by
setting
the
setpoint
of
the
level
control
cluster
to
0,
or
by
using
the
On/Off
cluster.
If
the
pump
is
started
(at
any
setpoint),
the
speed
of
the
pump
is
entirely
determined
by
the
pump.
returned.
4.2.9.
4.2.8.
Events
| ID | Name | Priority | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
SupplyVoltageLow |
|
V |
O |
|
|
SupplyVoltageHigh |
|
V |
O |
|
|
PowerMissingPhase |
|
V |
O |
|
|
SystemPressureLow |
|
V |
O |
|
|
SystemPressureHigh |
|
V |
O |
|
|
DryRunning |
|
V |
O |
|
|
MotorTemperatureHigh |
|
V |
O |
|
|
PumpMotorFatalFailure |
|
V |
O |
|
|
ElectronicTemperatureHigh |
|
V |
O |
|
|
PumpBlocked |
|
V |
O |
|
|
SensorFailure |
|
V |
O |
|
|
ElectronicNonFatalFailure |
|
V |
O |
|
|
ElectronicFatalFailure |
|
V |
O |
|
|
GeneralFault |
|
V |
O |
|
|
Leakage |
|
V |
O |
|
|
AirDetection |
|
V |
O |
|
|
TurbineOperation |
|
V |
O |
4.3. Thermostat Cluster
This cluster provides an interface to the functionality of a thermostat.
4.3.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
CCB 1981 2186 2249 2250 2251; NFR Thermostat Setback |
|
3 |
CCB 2477 2560 2773 2777 2815 2816 3029 |
|
4 |
All Hubs changes |
|
5 |
New data model format and notation, added FeatureMap, collapsed attribute sets, clarified edge cases around limits, default value of xxxSetpointLimit now respects AbsxxxSetpointLimit |
|
6 | Introduced the LTNE feature and adapted text (spec issue #5778) |
4.3.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
TSTAT |
4.3.3.1.
4.3.4.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Description | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
HEAT |
Heating |
Thermostat is capable of managing a heating device |
|
|
1 |
COOL |
Cooling |
Thermostat is capable of managing a cooling device |
|
|
2 |
OCC |
Occupancy |
Supports Occupied and Unoccupied setpoints |
O |
|
3 |
SCH |
Schedule Configuration |
Supports remote configuration of a weekly schedule of setpoint transitions |
O |
|
4 |
SB |
Setback |
Supports configurable setback (or span) |
O |
|
5 |
AUTO |
Auto Mode |
Supports a System Mode of Auto |
O |
|
6 | LTNE | Local Temperature Not Exposed | Thermostat does not expose the LocalTemperature Value in the LocalTemperature attribute | O |
4.3.4.1. Local Temperature Not Exposed (LTNE) feature
This feature indicates that the Calculated Local Temperature used internally is unavailable to report externally, for example due to the temperature control being done by a separate subsystem which does not offer a view into the currently measured temperature, but allows setpoints to be provided.
4.3.4.
4.3.5.
Units
of
Temperature
Temperatures within this cluster are represented by types using units of degree Celsius.
The temperature data type used throughout this cluster is defined in the Derived Data Types section of the Data Model.
The following temperature-related data types are also defined in and used throughout this cluster:
While temperature values MUST be transferred over the air using these types, this does not limit how Thermostats may display or store temperature values. Thermostats which display temperature values SHOULD follow the recommendations in Conversion of Temperature Values for Display .
|
Caution
|
Calculations
with
temperature
attributes
Where calculations or comparisons are performed, attribute values must be converted to a common type. In many cases, it is not sufficient to simply use the integer representation as the scaling from °C to integer value differs. |
4.3.5.
4.3.6.
Setpoint
Limits
There are a number of attributes which impose limits on setpoint values. This imposes constraints which MUST be maintained by any mechanism which modifies a limit or setpoint. Individual attribute descriptions detail the actions to be taken should a conflict arise while modifying the value.
User configurable limits must be within device limits:
-
AbsMinHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$ MinHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$ MaxHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$ AbsMaxHeatSetpointLimit
-
AbsMinCoolSetpointLimit \$<=\$ MinCoolSetpointLimit \$<=\$ MaxCoolSetpointLimit \$<=\$ AbsMaxCoolSetpointLimit
Setpoints must be within user configurable limits:
-
MinHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$ OccupiedHeatingSetpoint \$<=\$ MaxHeatSetpointLimit
-
MinCoolSetpointLimit \$<=\$ OccupiedCoolingSetpoint \$<=\$ MaxCoolSetpointLimit
-
MinHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$ UnoccupiedHeatingSetpoint \$<=\$ MaxHeatSetpointLimit
-
MinCoolSetpointLimit \$<=\$ UnoccupiedCoolingSetpoint \$<=\$ MaxCoolSetpointLimit
and if, and only if, the AUTO feature is supported, a deadband must be maintained between Heating and Cooling setpoints and limits:
-
AbsMinHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$
(AbsMinCoolSetpointLimit( AbsMinCoolSetpointLimit -MinSetpointDeadBand)MinSetpointDeadBand ) -
AbsMaxHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$
(AbsMaxCoolSetpointLimit( AbsMaxCoolSetpointLimit -MinSetpointDeadBand)MinSetpointDeadBand ) -
MinHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$
(MinCoolSetpointLimit( MinCoolSetpointLimit -MinSetpointDeadBand)MinSetpointDeadBand ) -
MaxHeatSetpointLimit \$<=\$
(MaxCoolSetpointLimit( MaxCoolSetpointLimit -MinSetpointDeadBand)MinSetpointDeadBand ) -
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint \$<=\$
(OccupiedCoolingSetpoint( OccupiedCoolingSetpoint -MinSetpointDeadBand)MinSetpointDeadBand ) -
UnoccupiedHeatingSetpoint \$<=\$
(UnoccupiedCoolingSetpoint( UnoccupiedCoolingSetpoint -MinSetpointDeadBand)MinSetpointDeadBand )
4.3.6.
4.3.7.
Dependencies
If the Alarms server cluster is supported on the same endpoint then the Alarms functionality is enabled and the AlarmMask attribute SHALL be supported. For remote temperature sensing, the Temperature Measurement client cluster MAY be included on the same endpoint. For occupancy sensing, the Occupancy Sensing client cluster MAY be included on the same endpoint.
4.3.7.
4.3.8.
Data
Types
4.3.8.1. TemperatureDifference Type
This data type is derived from int16 and represents a temperature difference with a resolution of 0.01°C.
value = ( temperature in °C ) x 100
-4°C ⇒ -400
123.45°C ⇒ 12345
The full (non-null) range of -327.67°C to 327.67°C may be used.
4.3.8.2. SignedTemperature Type
This data type is derived from int8 and represents a temperature from -12.7°C to 12.7°C with a resolution of 0.1°C.
value = ( temperature in °C ) x 10
-4°C ⇒ -40
12.3°C ⇒ 123
This type is employed where compactness of representation is important and where the resolution and range are still satisfactory.
4.3.8.3. UnsignedTemperature Type
This data type is derived from uint8 and represents a temperature from 0°C to 25.5°C with a resolution of 0.1°C.
value = ( temperature in °C ) x 10
4°C ⇒ 40
12.3°C ⇒ 123
This type is employed where compactness of representation is important and where the resolution and range are still satisfactory.
4.3.8.4. ACErrorCodeBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map32.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 | CompressorFail | Compressor Failure or Refrigerant Leakage |
1 | RoomSensorFail | Room Temperature Sensor Failure |
2 | OutdoorSensorFail | Outdoor Temperature Sensor Failure |
3 | CoilSensorFail | Indoor Coil Temperature Sensor Failure |
4 | FanFail | Fan Failure |
4.3.8.5. AlarmCodeBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 | Initialization | Initialization failure. The device failed to complete initialization at power-up. |
1 | Hardware | Hardware failure |
2 | SelfCalibration | Self-calibration failure |
4.3.8.6. HVACSystemTypeBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0..1 | CoolingStage | Stage of cooling the HVAC system is using. |
2..3 | HeatingStage | Stage of heating the HVAC system is using. |
4 | HeatingType | Type of heating used by the HVAC system. |
5 | HeatingFuel | Type of fuel used by the HVAC system. |
4.3.8.6.1. CoolingStage Bits
These bits SHALL indicate what stage of cooling the HVAC system is using.
00 = Cool Stage 1
01 = Cool Stage 2
10 = Cool Stage 3
11 = Reserved
4.3.8.6.2. HeatingStage Bits
These bits SHALL indicate what stage of heating the HVAC system is using.
00 = Heat Stage 1
01 = Heat Stage 2
10 = Heat Stage 3
11 = Reserved
4.3.8.7. ProgrammingOperationModeBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 | ScheduleActive | Schedule programming mode. This enables any programmed weekly schedule configurations. |
1 | AutoRecovery | Auto/recovery mode |
2 | Economy | Economy/EnergyStar mode |
4.3.8.8. RelayStateBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map16.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 | Heat | Heat State On |
1 | Cool | Cool State On |
2 | Fan | Fan State On |
3 | HeatStage2 | Heat 2 nd State On |
4 | CoolStage2 | Cool 2 nd State On |
5 | FanStage2 | Fan 2 nd State On |
6 | FanStage3 | Fan 3 rd Stage On |
4.3.8.9. RemoteSensingBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | LocalTemperature | Calculated Local Temperature is derived from a remote node | M |
1 | OutdoorTemperature | OutdoorTemperature is derived from a remote node | |
2 | Occupancy | Occupancy is derived from a remote node | OCC |
4.3.8.10. DayOfWeek Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 | Sunday | Sunday |
1 | Monday | Monday |
2 | Tuesday | Tuesday |
3 | Wednesday | Wednesday |
4 | Thursday | Thursday |
5 | Friday | Friday |
6 | Saturday | Saturday |
7 | Away | Away or Vacation |
4.3.8.11. ModeForSequence Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 | HeatSetpointPresent | Adjust Heat Setpoint |
1 | CoolSetpointPresent | Adjust Cool Setpoint |
4.3.8.12. SetpointAdjustMode Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Heat | Adjust Heat Setpoint | HEAT |
1 | Cool | Adjust Cool Setpoint | COOL |
2 | Both | Adjust Heat Setpoint and Cool Setpoint | HEAT | COOL |
4.3.8.13. ACCapacityFormatEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | BTUh | British Thermal Unit per Hour | O |
4.3.8.14. ACCompressorTypeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Unknown | Unknown compressor type | O |
1 | T1 | Max working ambient 43 °C | O |
2 | T2 | Max working ambient 35 °C | O |
3 | T3 | Max working ambient 52 °C | O |
4.3.8.15. ACLouverPositionEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Closed | Fully Closed | O |
2 | Open | Fully Open | O |
3 | Quarter | Quarter Open | O |
4 | Half | Half Open | O |
5 | ThreeQuarters | Three Quarters Open | O |
4.3.8.16. ACRefrigerantTypeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Unknown | Unknown Refrigerant Type | O |
1 | R22 | R22 Refrigerant | O |
2 | R410a | R410a Refrigerant | O |
3 | R407c | R407c Refrigerant | O |
4.3.8.17. ACTypeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Unknown | Unknown AC Type | O |
1 | CoolingFixed | Cooling and Fixed Speed | O |
2 | HeatPumpFixed | Heat Pump and Fixed Speed | O |
3 | CoolingInverter | Cooling and Inverter | O |
4 | HeatPumpInverter | Heat Pump and Inverter | O |
4.3.8.18. ThermostatControlSequence Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | CoolingOnly | Heat and Emergency are not possible | [COOL] |
1 | CoolingWithReheat | Heat and Emergency are not possible | [COOL] |
2 | HeatingOnly | Cool and precooling (see Terms ) are not possible | [HEAT] |
3 | HeatingWithReheat | Cool and precooling are not possible | [HEAT] |
4 | CoolingAndHeating | All modes are possible | [HEAT & COOL] |
5 | CoolingAndHeatingWithReheat | All modes are possible | [HEAT & COOL] |
Note
|
CoolingAndHeating
A thermostat indicating it supports CoolingAndHeating (or CoolingAndHeatingWithReheat) SHOULD be able to request heating or cooling on demand and will usually support the Auto SystemMode. Systems which support cooling or heating, requiring external intervention to change modes or where the whole building must be in the same mode, SHOULD report CoolingOnly or HeatingOnly based on the current capability. |
4.3.8.19. SetpointChangeSourceEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Manual | Manual, user-initiated setpoint change via the thermostat | O |
1 | Schedule | Schedule/internal programming-initiated setpoint change | [SCH] |
2 | External | Externally-initiated setpoint change (e.g., DRLC cluster command, attribute write) | O |
4.3.8.20. StartOfWeek Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Sunday | M | |
1 | Monday | M | |
2 | Tuesday | M | |
3 | Wednesday | M | |
4 | Thursday | M | |
5 | Friday | M | |
6 | Saturday | M |
4.3.8.21. ThermostatSystemMode Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Off | The Thermostat does not generate demand for Cooling or Heating | O |
1 | Auto | Demand is generated for either Cooling or Heating, as required | AUTO |
3 | Cool | Demand is only generated for Cooling | [COOL] |
4 | Heat | Demand is only generated for Heating | [HEAT] |
5 | EmergencyHeat | 2 nd stage heating is in use to achieve desired temperature | [HEAT] |
6 | Precooling | (see Terms ) | [COOL] |
7 | Fan only | O | |
8 | Dry | O | |
9 | Sleep | O |
| Attribute Values | Temperature Below Heat Setpoint | Temperature Between Heat Setpoint and Cool Setpoint | Temperature Above Cool Setpoint |
|---|---|---|---|
Heat | Temperature below target | Temperature on target | Temperature on target |
Cool | Temperature on target | Temperature on target | Temperature above target |
Auto | Temperature below target | Temperature on target | Temperature above target |
4.3.8.22. TemperatureSetpointHold Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | SetpointHoldOff | Follow scheduling program | M |
1 | SetpointHoldOn | Maintain current setpoint, regardless of schedule transitions | M |
4.3.8.23. ThermostatScheduleTransition Type
This represents a single transition in a Thermostat schedule
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Access | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | TransitionTime | uint16 | 0 to 1439 | RW | M | ||
1 | HeatSetpoint | temperature | all | RW | M | ||
2 | CoolSetpoint | temperature | all | RW | M |
4.3.8.23.1. TransitionTime Field
This field SHALL represent the start time of the schedule transition during the associated day. The time will be represented by a 16 bits unsigned integer to designate the minutes since midnight. For example, 6am will be represented by 360 minutes since midnight and 11:30pm will be represented by 1410 minutes since midnight.
4.3.9. Attributes
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
LocalTemperature |
temperature |
all |
XP |
null |
R V |
M |
|
0x0001 |
OutdoorTemperature |
temperature |
all |
X |
null |
R V |
O |
|
0x0002 |
Occupancy |
|
desc |
1 |
R V |
OCC |
|
|
0x0003 |
AbsMinHeatSetpointLimit |
temperature |
desc |
F |
7°C |
R V |
[HEAT] |
|
0x0004 |
AbsMaxHeatSetpointLimit |
temperature |
desc |
F |
30°C |
R V |
[HEAT] |
|
0x0005 |
AbsMinCoolSetpointLimit |
temperature |
desc |
F |
16°C |
R V |
[COOL] |
|
0x0006 |
AbsMaxCoolSetpointLimit |
temperature |
desc |
F |
32°C |
R V |
[COOL] |
|
0x0007 |
PICoolingDemand |
uint8 |
0% to 100% |
P |
- |
R V |
[COOL] |
|
0x0008 |
PIHeatingDemand |
uint8 |
0% to 100% |
P |
- |
R V |
[HEAT] |
|
0x0009 |
HVACSystemTypeConfiguration |
|
desc |
N |
0 |
R[W] VM |
D |
|
0x0010 |
LocalTemperatureCalibration |
|
-2.5°C to 2.5°C |
N |
0°C |
RW VM |
|
|
0x0011 |
OccupiedCoolingSetpoint |
temperature |
desc |
NS |
26°C |
RW VO |
COOL |
|
0x0012 |
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint |
temperature |
desc |
NS |
20°C |
RW VO |
HEAT |
|
0x0013 |
UnoccupiedCoolingSetpoint |
temperature |
desc |
N |
26°C |
RW VO |
COOL & OCC |
|
0x0014 |
UnoccupiedHeatingSetpoint |
temperature |
desc |
N |
20°C |
RW VO |
HEAT & OCC |
|
0x0015 |
MinHeatSetpointLimit |
temperature |
desc |
N |
AbsMinHeatSetpointLimit |
RW VM |
[HEAT] |
|
0x0016 |
MaxHeatSetpointLimit |
temperature |
desc |
N |
AbsMaxHeatSetpointLimit |
RW VM |
[HEAT] |
|
0x0017 |
MinCoolSetpointLimit |
temperature |
desc |
N |
AbsMinCoolSetpointLimit |
RW VM |
[COOL] |
|
0x0018 |
MaxCoolSetpointLimit |
temperature |
desc |
N |
AbsMaxCoolSetpointLimit |
RW VM |
[COOL] |
|
0x0019 |
MinSetpointDeadBand |
|
0°C to 2.5°C |
N |
2.5°C |
R[W] VM |
AUTO |
|
|
RemoteSensing |
|
00000xxx |
N |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
ControlSequenceOfOperation |
desc |
N |
4 |
RW VM |
M |
|
|
|
SystemMode |
|
desc |
NS |
1 |
RW VM |
M |
|
|
AlarmMask |
|
desc |
0 |
R V |
O |
|
|
|
ThermostatRunningMode |
|
desc |
0 |
R V |
[AUTO] |
|
|
0x0020 |
StartOfWeek |
|
desc |
F |
– |
R V |
SCH |
|
0x0021 |
NumberOfWeeklyTransitions |
uint8 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
SCH |
|
0x0022 |
NumberOfDailyTransitions |
uint8 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
SCH |
|
0x0023 |
TemperatureSetpointHold |
|
desc |
N |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0024 |
TemperatureSetpointHoldDuration |
uint16 |
0 to 1440 |
NX |
null |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0025 |
ThermostatProgrammingOperationMode |
desc |
P |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
0x0029 |
ThermostatRunningState |
|
desc |
- |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0030 |
SetpointChangeSource |
|
desc |
0 |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0031 |
SetpointChangeAmount |
|
all |
X |
null |
R V |
O |
|
0x0032 |
SetpointChangeSourceTimestamp |
utc |
all |
0 |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0034 |
OccupiedSetback |
|
OccupiedSetbackMin to OccupiedSetbackMax |
XN |
null |
RW VM |
SB |
|
0x0035 |
OccupiedSetbackMin |
|
0 to OccupiedSetbackMax |
XF |
null |
R V |
SB |
|
0x0036 |
OccupiedSetbackMax |
|
OccupiedSetbackMin to 25.4°C |
XF |
null |
R V |
SB |
|
0x0037 |
UnoccupiedSetback |
|
UnoccupiedSetbackMin to UnoccupiedSetbackMax |
XN |
null |
RW VM |
SB & OCC |
|
0x0038 |
UnoccupiedSetbackMin |
|
0 to UnoccupiedSetbackMax |
XF |
null |
R V |
SB & OCC |
|
0x0039 |
UnoccupiedSetbackMax |
|
UnoccupiedSetbackMin to 25.4°C |
XF |
null |
R V |
SB & OCC |
|
|
EmergencyHeatDelta |
|
all |
N |
25.5°C |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0040 |
ACType |
|
desc |
N |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0041 |
ACCapacity |
uint16 |
all |
N |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0042 |
ACRefrigerantType |
|
desc |
N |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0043 |
ACCompressorType |
|
desc |
N |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0044 |
ACErrorCode |
|
all |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
0x0045 |
ACLouverPosition |
|
desc |
N |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
0x0046 |
ACCoilTemperature |
temperature |
all |
X |
null |
R V |
O |
|
0x0047 |
ACCapacityFormat |
|
desc |
N |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
4.3.7.1.
LocalTemperature
Attribute
4.3.9.1.
Scene
Table
Extensions
This
attribute
represents
If
the
temperature,
Scenes
server
cluster
is
implemented
on
the
same
endpoint,
the
following
attributes
SHALL
be
part
of
the
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
of
the
Scene
Table.
If
the
implicit
form
of
the
ExtensionFieldSetStruct
is
used,
the
order
of
the
attributes
in
the
AttributeValueList
is
in
the
given
order,
i.e.,
the
attribute
listed
as
measured
locally
or
remotely
(over
1
is
added
first:
4.3.9.2. Calculated Local Temperature
The
local
temperature
SHALL
be
calculated
from
the
network),
measured
temperature
,
including
any
adjustments
applied
by
LocalTemperatureCalibration
attribute
(if
any)
as
follows:
LocalTemperature
Calculated
Local
Temperature
=
(
measured
temperature
)
+
LocalTemperatureCalibration
.
The
null
measured
temperature
value
indicates
that
may
be
local,
or
remote,
depending
on
the
temperature
measurement
is
invalid.
value
of
the
RemoteSensing
attribute
when
supported.
All
setpoint
attributes
in
the
Thermostat
cluster
SHALL
be
triggered
based
off
the
LocalTemperature
attribute
this
calculated
value
(i.e.,
measured
temperature
and
any
calibration
offset).
If the Local Temperature Not Exposed (LTNE) feature is present, the behavior of the thermostat SHALL be that the equipment’s temperature control uses the calculated local temperature even if that value is not reported in the LocalTemperature attribute.
4.3.7.2.
4.3.9.3.
LocalTemperature
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the current Calculated Local Temperature , when available.
If the LTNE feature is not supported:
If the LocalTemperatureCalibration is invalid or currently unavailable, the attribute SHALL report null.
If the LocalTemperatureCalibration is valid, the attribute SHALL report that value.
Otherwise, if the LTNE feature is supported, there is no feedback externally available for the LocalTemperatureCalibration . In that case, the LocalTemperature attribute SHALL always report null.
4.3.9.4. OutdoorTemperature Attribute
This
attribute
represents
SHALL
indicate
the
outdoor
temperature,
as
measured
locally
or
remotely
(over
the
network).
4.3.7.3.
4.3.9.5.
Occupancy
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
whether
the
heated/cooled
space
is
occupied
or
not,
as
measured
locally
or
remotely
(over
the
network).
If
bit
0
=
1,
the
space
is
occupied,
else
it
is
unoccupied.
All
other
bits
are
reserved.
4.3.7.4.
4.3.9.6.
AbsMinHeatSetpointLimit
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
absolute
minimum
level
that
the
heating
setpoint
MAY
be
set
to.
This
is
a
limitation
imposed
by
the
manufacturer.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints
4.3.7.5.
4.3.9.7.
AbsMaxHeatSetpointLimit
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
absolute
maximum
level
that
the
heating
setpoint
MAY
be
set
to.
This
is
a
limitation
imposed
by
the
manufacturer.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints
4.3.7.6.
4.3.9.8.
AbsMinCoolSetpointLimit
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
absolute
minimum
level
that
the
cooling
setpoint
MAY
be
set
to.
This
is
a
limitation
imposed
by
the
manufacturer.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints
4.3.7.7.
4.3.9.9.
AbsMaxCoolSetpointLimit
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
absolute
maximum
level
that
the
cooling
setpoint
MAY
be
set
to.
This
is
a
limitation
imposed
by
the
manufacturer.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints
4.3.7.8.
4.3.9.10.
PICoolingDemand
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
level
of
cooling
demanded
by
the
PI
(proportional
integral)
control
loop
in
use
by
the
thermostat
(if
any),
in
percent.
This
value
is
0
when
the
thermostat
is
in
“off”
or
“heating”
mode.
This attribute is reported regularly and MAY be used to control a cooling device.
4.3.7.9.
4.3.9.11.
PIHeatingDemand
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
level
of
heating
demanded
by
the
PI
loop
in
percent.
This
value
is
0
when
the
thermostat
is
in
“off”
or
“cooling”
mode.
This attribute is reported regularly and MAY be used to control a heating device.
4.3.7.10.
4.3.9.12.
HVACSystemTypeConfiguration
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
HVAC
system
type
controlled
by
the
thermostat.
If
the
thermostat
uses
physical
DIP
switches
to
set
these
parameters,
this
information
SHALL
be
available
read-only
from
the
DIP
switches.
If
these
parameters
are
set
via
software,
there
SHALL
be
read/write
access
in
order
to
provide
remote
programming
capability.
The
meanings
of
individual
bits
are
detailed
below.
Each
bit
represents
a
type
of
system
configuration.
4.3.7.11.
4.3.9.13.
LocalTemperatureCalibration
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
offset
the
Thermostat
server
SHALL
make
to
the
measured
temperature
(locally
or
remotely)
before
calculating,
displaying,
or
communicating
to
adjust
the
LocalTemperature
attribute.
Calculated
Local
Temperature
prior
to
using,
displaying
or
reporting
it.
The
purpose
of
this
attribute
is
to
adjust
the
calibration
of
the
Thermostat
server
per
the
user’s
user’s
preferences
(e.g.,
to
match
if
there
are
multiple
servers
displaying
different
values
for
the
same
HVAC
area)
or
compensate
for
variability
amongst
temperature
sensors.
If
a
Thermostat
client
attempts
to
write
LocalTemperatureCalibration
attribute
to
an
unsupported
value
(e.g.,
out
of
the
range
supported
by
the
Thermostat
server),
the
Thermostat
server
SHALL
respond
with
a
Write
Attribute
Response
Command
with
a
status
of
SUCCESS
and
set
the
value
of
LocalTemperatureCalibration
to
the
upper
or
lower
limit
reached.
4.3.7.12.
4.3.9.14.
OccupiedCoolingSetpoint
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
cooling
mode
setpoint
when
the
room
is
occupied.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute such that these constraints are violated, a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
If the occupancy status of the room is unknown, this attribute SHALL be used as the cooling mode setpoint.
4.3.7.13.
4.3.9.15.
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
heating
mode
setpoint
when
the
room
is
occupied.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute such that these constraints are violated, a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
If the occupancy status of the room is unknown, this attribute SHALL be used as the heating mode setpoint.
4.3.7.14.
4.3.9.16.
UnoccupiedCoolingSetpoint
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
cooling
mode
setpoint
when
the
room
is
unoccupied.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute such that these constraints are violated, a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
If the occupancy status of the room is unknown, this attribute SHALL not be used.
4.3.7.15.
4.3.9.17.
UnoccupiedHeatingSetpoint
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
heating
mode
setpoint
when
the
room
is
unoccupied.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute such that these constraints are violated, a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
If the occupancy status of the room is unknown, this attribute SHALL not be used.
4.3.7.16.
4.3.9.18.
MinHeatSetpointLimit
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
minimum
level
that
the
heating
setpoint
MAY
be
set
to.
This attribute, and the following three attributes, allow the user to define setpoint limits more constrictive than the manufacturer imposed ones. Limiting users (e.g., in a commercial building) to such setpoint limits can help conserve power.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which conflicts with setpoint values then those setpoints SHALL be adjusted by the minimum amount to permit this attribute to be set to the desired value. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which is not consistent with the constraints and cannot be resolved by modifying setpoints then a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
4.3.7.17.
4.3.9.19.
MaxHeatSetpointLimit
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
level
that
the
heating
setpoint
MAY
be
set
to.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which conflicts with setpoint values then those setpoints SHALL be adjusted by the minimum amount to permit this attribute to be set to the desired value. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which is not consistent with the constraints and cannot be resolved by modifying setpoints then a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
4.3.7.18.
4.3.9.20.
MinCoolSetpointLimit
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
minimum
level
that
the
cooling
setpoint
MAY
be
set
to.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which conflicts with setpoint values then those setpoints SHALL be adjusted by the minimum amount to permit this attribute to be set to the desired value. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which is not consistent with the constraints and cannot be resolved by modifying setpoints then a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
4.3.7.19.
4.3.9.21.
MaxCoolSetpointLimit
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
level
that
the
cooling
setpoint
MAY
be
set
to.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which conflicts with setpoint values then those setpoints SHALL be adjusted by the minimum amount to permit this attribute to be set to the desired value. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which is not consistent with the constraints and cannot be resolved by modifying setpoints then a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
4.3.7.20.
4.3.9.22.
MinSetpointDeadBand
Attribute
On
devices
which
support
the
AUTO
feature,
this
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
minimum
difference
between
the
Heat
Setpoint
and
the
Cool
Setpoint.
Refer to Setpoint Limits for constraints. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which conflicts with setpoint values then those setpoints SHALL be adjusted by the minimum amount to permit this attribute to be set to the desired value. If an attempt is made to set this attribute to a value which is not consistent with the constraints and cannot be resolved by modifying setpoints then a response with the status code CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
4.3.7.21.
4.3.9.23.
RemoteSensing
Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
when
the
local
temperature,
outdoor
temperature
and
occupancy
are
being
sensed
by
remote
networked
sensors,
rather
than
internal
sensors.
A
If
the
LTNE
feature
is
present
in
the
server,
the
LocalTemperature
RemoteSensing
bit
set
to
1
indicates
remote
sensing
value
SHALL
always
report
a
value
of
the
relevant
value.
0.
If
the
LocalTemperature
RemoteSensing
bit
is
derived
from
written
with
a
remote
node
M
value
of
1
OutdoorTemperature
When
set,
OutdoorTemperature
is
derived
from
a
remote
node
OutdoorTemperature
2
Occupancy
When
set,
Occupancy
when
the
LTNE
feature
is
derived
from
present,
the
write
SHALL
fail
and
the
server
SHALL
report
a
remote
node
OCC
CONSTRAINT_ERROR.
4.3.7.22.
4.3.9.24.
ControlSequenceOfOperation
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
overall
operating
environment
of
the
thermostat,
and
thus
the
possible
system
modes
that
the
thermostat
can
operate
in.
It
SHALL
be
set
to
one
of
the
following
values.
Table
82.
ControlSequenceOfOperation
Values
Value
Name
Conformance
Description
0
CoolingOnly
[COOL]
Heat
and
Emergency
are
not
possible
1
CoolingWithReheat
[COOL]
Heat
and
Emergency
are
not
possible
2
HeatingOnly
[HEAT]
Cool
and
precooling
(see
Terms
)
are
not
possible
3
HeatingWithReheat
[HEAT]
Cool
and
precooling
are
not
possible
4
CoolingAndHeating
[HEAT
&
COOL]
All
modes
are
possible
5
CoolingAndHeatingWithReheat
[HEAT
&
COOL]
All
modes
are
possible
Note
CoolingAndHeating
A
thermostat
indicating
it
supports
CoolingAndHeating
(or
CoolingAndHeatingWithReheat)
SHOULD
be
able
to
request
heating
or
cooling
on
demand
and
will
usually
support
the
Auto
SystemMode.
Systems
which
support
cooling
or
heating,
requiring
external
intervention
to
change
modes
or
where
the
whole
building
must
be
in
the
same
mode,
SHOULD
report
CoolingOnly
or
HeatingOnly
based
on
the
current
capability.
4.3.7.23.
4.3.9.25.
SystemMode
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
current
operating
mode
of
the
thermostat,
It
thermostat.
Its
value
SHALL
be
set
to
one
of
the
following
values,
as
limited
by
the
ControlSequenceOfOperation
Attribute
.
Note
It
is
not
mandatory
to
support
all
values.
Table
83.
SystemMode
Values
Value
Name
Conformance
Description
0
Off
O
The
Thermostat
does
not
generate
demand
for
Cooling
or
Heating
1
Auto
AUTO
Demand
is
generated
for
either
Cooling
or
Heating,
as
required
3
Cool
[COOL]
Demand
is
only
generated
for
Cooling
4
Heat
[HEAT]
Demand
is
only
generated
for
Heating
5
EmergencyHeat
[HEAT]
2
nd
stage
heating
is
in
use
to
achieve
desired
temperature
6
Precooling
[COOL]
(see
Terms
)
7
Fan
only
O
8
Dry
O
9
Sleep
O
Table
84.
Interpretation
of
Heat,
Cool
and
Auto
SystemMode
Values
Attribute
Values
Temperature
Below
Heat
Setpoint
Temperature
Between
Heat
Setpoint
and
Cool
Setpoint
Temperature
Above
Cool
Setpoint
Heat
Temperature
below
target
Temperature
on
target
Temperature
on
target
Cool
Temperature
on
target
Temperature
on
target
Temperature
above
target
Auto
Temperature
below
target
Temperature
on
target
Temperature
above
target
attribute.
4.3.7.24.
4.3.9.26.
AlarmMask
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
whether
each
of
the
alarms
listed
below
in
AlarmCodeBitmap
is
enabled.
When
the
bit
number
corresponding
to
the
alarm
code
is
set
to
1,
the
alarm
is
enabled,
else
it
is
disabled.
Bits
not
corresponding
to
a
code
in
the
table
are
reserved.
When
the
Alarms
cluster
is
implemented
on
a
device,
and
one
of
the
alarm
conditions
included
in
this
table
AlarmCodeBitmap
occurs,
an
alarm
notification
is
generated,
with
the
alarm
code
field
set
as
listed
in
the
table.
AlarmCodeBitmap
.
4.3.7.25.
Thermostat
Running
Mode
4.3.9.27.
ThermostatRunningMode
Attribute
This
attribute
represents
SHALL
indicate
the
running
mode
of
the
thermostat.
This
attribute
uses
the
SystemMode
Values
ThermostatSystemMode
but
can
only
be
Off,
Cool
or
Heat.
This
attribute
is
intended
to
provide
additional
information
when
the
thermostat’s
thermostat’s
system
mode
is
in
auto
mode.
4.3.7.26.
4.3.9.28.
StartOfWeek
Attribute
This
attribute
represents
SHALL
indicate
the
day
of
the
week
that
this
thermostat
considers
to
be
the
start
of
week
for
weekly
set
point
scheduling.
This attribute MAY be able to be used as the base to determine if the device supports weekly scheduling by reading the attribute. Successful response means that the weekly scheduling is supported.
4.3.7.27.
4.3.9.29.
NumberOfWeeklyTransitions
Attribute
This
attribute
determines
SHALL
indicate
how
many
weekly
schedule
transitions
the
thermostat
is
capable
of
handling.
4.3.7.28.
4.3.9.30.
NumberOfDailyTransitions
Attribute
This
attribute
determines
SHALL
indicate
how
many
daily
schedule
transitions
the
thermostat
is
capable
of
handling.
4.3.7.29.
4.3.9.31.
TemperatureSetpointHold
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
temperature
hold
status
on
the
thermostat.
If
hold
status
is
on,
the
thermostat
SHOULD
maintain
the
temperature
set
point
for
the
current
mode
until
a
system
mode
change.
If
hold
status
is
off,
the
thermostat
SHOULD
follow
the
setpoint
transitions
specified
by
its
internal
scheduling
program.
If
the
thermostat
supports
setpoint
hold
for
a
specific
duration,
it
SHOULD
also
implement
the
TemperatureSetpointHoldDuration
attribute.
4.3.7.30.
4.3.9.32.
TemperatureSetpointHoldDuration
Attribute
This
attribute
sets
SHALL
indicate
the
period
in
minutes
for
which
a
setpoint
hold
is
active.
Thermostats
that
support
hold
for
a
specified
duration
SHOULD
implement
this
attribute.
The
null
value
indicates
the
field
is
unused.
All
other
values
are
reserved.
4.3.7.31.
4.3.9.33.
ThermostatProgrammingOperationMode
Attribute
This
attribute
determines
SHALL
indicate
the
operational
state
of
the
thermostat’s
thermostat’s
programming.
The
thermostat
SHALL
modify
its
programming
operation
when
this
attribute
is
modified
by
a
client
and
update
this
attribute
when
its
programming
operation
is
modified
locally
by
a
user.
The
thermostat
MAY
support
more
than
one
active
ThermostatProgrammingOperationMode
.
ProgrammingOperationModeBitmap
.
For
example,
the
thermostat
MAY
operate
simultaneously
in
Schedule
Programming
Mode
and
Recovery
Mode.
Thermostats which contain a schedule MAY use this attribute to control how that schedule is used, even if they do not support the Schedule Configuration feature.
When ScheduleActive is not set, the setpoint is altered only by manual up/down changes at the thermostat or remotely, not by internal schedule programming.
|
Note
|
Modifying the ScheduleActive bit does not clear or delete previous weekly schedule programming configurations. |
4.3.7.32.
4.3.9.34.
ThermostatRunningState
Attribute
This
attribute
represents
SHALL
indicate
the
current
relay
state
of
the
heat,
cool,
and
fan
relays.
Unimplemented outputs SHALL be treated as if they were Off.
4.3.7.33.
4.3.9.35.
SetpointChangeSource
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
source
of
the
current
active
OccupiedCoolingSetpoint
or
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
(i.e.,
who
or
what
determined
the
current
setpoint).
This attribute enables service providers to determine whether changes to setpoints were initiated due to occupant comfort, scheduled programming or some other source (e.g., electric utility or other service provider). Because automation services MAY initiate frequent setpoint changes, this attribute clearly differentiates the source of setpoint changes made at the thermostat.
4.3.7.34.
4.3.9.36.
SetpointChangeAmount
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
delta
between
the
current
active
OccupiedCoolingSetpoint
or
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
and
the
previous
active
setpoint.
This
attribute
is
meant
to
accompany
the
SetpointChangeSource
attribute;
devices
implementing
SetpointChangeAmount
SHOULD
also
implement
SetpointChangeSource
.
.
The null value indicates that the previous setpoint was unknown.
4.3.7.35.
4.3.9.37.
SetpointChangeSourceTimestamp
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
time
in
UTC
at
which
the
SetpointChangeSourceAmount
SetpointChangeAmount
attribute
change
was
recorded.
4.3.7.36.
4.3.9.38.
OccupiedSetback
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
amount
that
the
Thermostat
server
will
allow
the
LocalTemperature
attribute
Calculated
Local
Temperature
to
float
above
the
OccupiedCooling
setpoint
OccupiedCoolingSetpoint
(i.e.,
OccupiedCooling
OccupiedCoolingSetpoint
+
OccupiedSetback
)
or
below
the
OccupiedHeating
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
setpoint
(i.e.,
OccupiedHeating
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
–
OccupiedSetback
)
before
initiating
a
state
change
to
bring
the
temperature
back
to
the
user’s
user’s
desired
setpoint.
This
attribute
is
sometimes
also
referred
to
as
the
“span.”
The purpose of this attribute is to allow remote configuration of the span between the desired setpoint and the measured temperature to help prevent over-cycling and reduce energy bills, though this may result in lower comfort on the part of some users.
The null value indicates the attribute is unused.
If
the
Thermostat
client
attempts
to
write
OccupiedSetback
to
a
value
greater
than
OccupiedSetbackMax
,
,
the
Thermostat
server
SHALL
set
its
OccupiedSetback
value
to
OccupiedSetbackMax
and
SHALL
send
a
Write
Attribute
Response
command
with
a
Status
Code
field
enumeration
of
SUCCESS
response.
If
the
Thermostat
client
attempts
to
write
OccupiedSetback
to
a
value
less
than
OccupiedSetbackMin
,
,
the
Thermostat
server
SHALL
set
its
OccupiedSetback
value
to
OccupiedSetbackMin
and
SHALL
send
a
Write
Attribute
Response
command
with
a
Status
Code
field
enumeration
of
SUCCESS
response.
4.3.7.37.
4.3.9.39.
OccupiedSetbackMin
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
minimum
value
that
the
Thermostat
server
will
allow
the
OccupiedSetback
attribute
to
be
configured
by
a
user.
The null value indicates the attribute is unused.
4.3.7.38.
4.3.9.40.
OccupiedSetbackMax
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
value
that
the
Thermostat
server
will
allow
the
OccupiedSetback
attribute
to
be
configured
by
a
user.
The null value indicates the attribute is unused.
4.3.7.39.
4.3.9.41.
UnoccupiedSetback
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
amount
that
the
Thermostat
server
will
allow
the
LocalTemperature
attribute
Calculated
Local
Temperature
to
float
above
the
UnoccupiedCooling
setpoint
UnoccupiedCoolingSetpoint
(i.e.,
UnoccupiedCooling
UnoccupiedCoolingSetpoint
+
UnoccupiedSetback)
UnoccupiedSetback
)
or
below
the
UnoccupiedHeating
UnoccupiedHeatingSetpoint
setpoint
(i.e.,
UnoccupiedHeating
UnoccupiedHeatingSetpoint
-
UnoccupiedSetback)
UnoccupiedSetback
)
before
initiating
a
state
change
to
bring
the
temperature
back
to
the
user’s
user’s
desired
setpoint.
This
attribute
is
sometimes
also
referred
to
as
the
“span.”
The purpose of this attribute is to allow remote configuration of the span between the desired setpoint and the measured temperature to help prevent over-cycling and reduce energy bills, though this may result in lower comfort on the part of some users.
The null value indicates the attribute is unused.
If
the
Thermostat
client
attempts
to
write
UnoccupiedSetback
to
a
value
greater
than
UnoccupiedSetbackMax,
UnoccupiedSetbackMax
,
the
Thermostat
server
SHALL
set
its
UnoccupiedSetback
value
to
UnoccupiedSetbackMax
and
SHALL
send
a
Write
Attribute
Response
command
with
a
Status
Code
field
enumeration
of
SUCCESS
response.
If
the
Thermostat
client
attempts
to
write
UnoccupiedSetback
to
a
value
less
than
UnoccupiedSetbackMin,
UnoccupiedSetbackMin
,
the
Thermostat
server
SHALL
set
its
UnoccupiedSetback
value
to
UnoccupiedSetbackMin
and
SHALL
send
a
Write
Attribute
Response
command
with
a
Status
Code
field
enumeration
of
SUCCESS
response.
4.3.7.40.
4.3.9.42.
UnoccupiedSetbackMin
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
minimum
value
that
the
Thermostat
server
will
allow
the
UnoccupiedSetback
attribute
to
be
configured
by
a
user.
The null value indicates the attribute is unused.
4.3.7.41.
4.3.9.43.
UnoccupiedSetbackMax
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
value
that
the
Thermostat
server
will
allow
the
UnoccupiedSetback
attribute
to
be
configured
by
a
user.
The null value indicates the attribute is unused.
4.3.7.42.
4.3.9.44.
EmergencyHeatDelta
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
delta
between
LocalTemperature
the
Calculated
Local
Temperature
and
the
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
or
UnoccupiedHeatingSetpoint
attributes
at
which
the
Thermostat
server
will
operate
in
emergency
heat
mode.
If
the
difference
between
LocalTemperature
the
Calculated
Local
Temperature
and
Un/OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
OccupiedCoolingSetpoint
or
UnoccupiedCoolingSetpoint
is
greater
than
or
equal
to
the
EmergencyHeatDelta
and
the
Thermostat
server’s
server’s
SystemMode
attribute
is
in
a
heating-related
mode,
then
the
Thermostat
server
SHALL
immediately
switch
to
the
SystemMode
attribute
value
that
provides
the
highest
stage
of
heating
(e.g.,
emergency
heat)
and
continue
operating
in
that
running
state
until
the
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
value
is
reached.
For
example:
-
LocalTemperatureCalculated Local Temperature = 10.0°C -
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint = 16.0°C
-
EmergencyHeatDelta = 2.0°C
⇒
OccupiedHeatingSetpoint
-
LocalTemperature
Calculated
Local
Temperature
≥?
EmergencyHeatDelta
-
⇒ 16°C - 10°C ≥? 2°C
⇒ TRUE >>> Thermostat server changes its SystemMode to operate in 2 nd stage or emergency heat mode
The purpose of this attribute is to provide Thermostat clients the ability to configure rapid heating when a setpoint is of a specified amount greater than the measured temperature. This allows the heated space to be quickly heated to the desired level set by the user.
4.3.7.43.
4.3.9.45.
ACType
Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
type
of
Mini
Split
ACType
ACTypeEnum
of
Mini
Split
AC
is
defined
depending
on
how
Cooling
and
Heating
condition
is
achieved
by
Mini
Split
AC.
4.3.7.44.
4.3.9.46.
ACCapacity
Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
capacity
of
Mini
Split
AC
in
terms
of
the
format
defined
by
the
ACCapacityFormat
attribute
4.3.7.45.
4.3.9.47.
ACRefrigerantType
Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
type
of
refrigerant
used
within
the
Mini
Split
AC.
4.3.7.46.
4.3.9.48.
ACCompressorType
Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
type
of
Compressor
compressor
used
within
the
Mini
Split
AC.
4.3.7.47.
4.3.9.49.
ACErrorCode
Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
type
of
errors
encountered
within
the
Mini
Split
AC.
Error
values
are
reported
with
four
bytes
values.
Each
bit
within
the
four
bytes
indicates
the
unique
error.
4.3.7.48.
4.3.9.50.
ACLouverPosition
Attribute
This
attribute
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
position
of
Louver
on
the
AC.
4.3.7.49.
4.3.9.51.
ACCoilTemperature
Attribute
This
attribute
represents
SHALL
indicate
the
temperature
of
the
AC
coil,
as
measured
locally
or
remotely
(over
the
network).
4.3.7.50.
4.3.9.52.
ACCapacityFormat
Attribute
This
attribute
specifies
SHALL
indicate
the
format
for
the
ACCapacity
attribute.
4.3.8.
4.3.10.
Commands
|
|
Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
SetpointRaiseLower |
|
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
SetWeeklySchedule |
|
Y |
M |
SCH |
|
0x02 |
GetWeeklySchedule |
|
GetWeeklyScheduleResponse |
O |
SCH |
|
0x03 |
ClearWeeklySchedule |
|
N |
M |
SCH |
|
0x04 |
GetRelayStatusLog |
|
GetRelayStatusLogResponse |
O |
O |
|
0x00 |
GetWeeklyScheduleResponse |
|
N |
SCH |
|
|
0x01 |
GetRelayStatusLogResponse |
|
N |
|
4.3.8.1.
Setpoint
Raise/Lower
4.3.10.1.
SetpointRaiseLower
Command
Upon
receipt,
the
attributes
for
the
indicated
setpoint(s)
SHALL
have
the
amount
specified
in
the
Amount
field
added
to
them.
If
the
resulting
value
is
outside
the
limits
imposed
by
MinCoolSetpointLimit,
MaxCoolSetpointLimit,
MinCoolSetpointLimit
,
MaxCoolSetpointLimit
,
MinHeatSetpointLimit
and
MaxHeatSetpointLimit,
MaxHeatSetpointLimit
,
the
value
is
clamped
to
those
limits.
This
is
not
considered
an
error
condition.
|
|
Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Mode |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Amount |
int8 |
all |
M |
4.3.8.2.
4.3.10.2.
Mode
Field
The
mode
field
SHALL
be
set
to
one
of
the
values
below.
It
specifies
specify
which
setpoints
are
to
be
adjusted.
4.3.8.2.1.
4.3.10.2.1.
Heat
Bit
If the server does not support the HEAT feature then it SHALL respond with INVALID_ARGUMENT. If the server supports the AUTO feature and the resulting setpoint would be invalid solely due to MinSetpointDeadBand then the Cooling setpoint SHALL be increased sufficiently to maintain the deadband.
4.3.8.2.2.
4.3.10.2.2.
Cool
Bit
If the server does not support the COOL feature then it SHALL respond with INVALID_ARGUMENT. If the server supports the AUTO feature and the resulting setpoint would be invalid solely due to MinSetpointDeadBand then the Heating setpoint SHALL be decreased sufficiently to maintain the deadband.
4.3.8.3.
4.3.10.3.
Amount
Field
This
field
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
amount
(possibly
negative)
that
should
be
added
to
the
setpoint(s),
in
steps
of
0.1°C.
4.3.8.4.
Set
Weekly
Schedule
4.3.10.4.
SetWeeklySchedule
Command
Upon receipt, the weekly schedule for updating set points SHALL be stored in the thermostat and SHOULD begin at the time of receipt. A status code SHALL be sent in response.
When a command is received that requires a total number of transitions greater than the device supports, the status of the response SHALL be INSUFFICIENT_SPACE.
When any of the set points sent in the sequence is out of range (AbsMin/MaxSetPointLimit), or when the Mode for Sequence field includes a mode not supported by the device, the status of the response SHALL be CONSTRAINT_ERROR and no set points from the entire sequence SHOULD be used.
When an overlapping transition is detected, the status of the response SHALL be FAILURE.
When a device which does not support multiple days in a command receives a command with more than one bit set in the DayOfWeekforSequence field, or when a device which does not support multiple modes in a command receives a command with more than one bit set in the ModeForSequence field, or when the contents of the Transitions field does not agree with NumberOfTransitionsForSequence, DayOfWeekforSequence or ModeForSequence, the status of the response SHALL be INVALID_COMMAND.
When the transitions could be added successfully, the status of the response SHALL be SUCCESS.
|
|
Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NumberOfTransitionsForSequence |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
DayOfWeekforSequence |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
2 |
ModeForSequence |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
3 |
Transitions |
list[ ThermostatScheduleTransition ] |
max 10 |
M |
The set weekly schedule command is used to update the thermostat weekly set point schedule from a management system. If the thermostat already has a weekly set point schedule programmed, then it SHOULD replace each daily set point set as it receives the updates from the management system. For example, if the thermostat has 4 set points for every day of the week and is sent a Set Weekly Schedule command with one set point for Saturday then the thermostat SHOULD remove all 4 set points for Saturday and replace those with the updated set point but leave all other days unchanged. If the schedule is larger than what fits in one frame or contains more than 10 transitions, the schedule SHALL then be sent using multiple Set Weekly Schedule Commands.
Each Set Weekly Schedule Command has 3 header bytes – Number of Transitions for Sequence, Day of Week for Sequence, and Mode for Sequence. The application SHALL decode the payload according to what has specified in the 3 header bytes.
4.3.8.5.
Number
of
Transitions
for
Sequence
4.3.10.5.
NumberOfTransitionsForSequence
Field
The
Number
of
Transitions
for
Sequence
This
field
indicates
SHALL
indicate
how
many
individual
transitions
to
expect
for
this
sequence
of
commands.
If
a
device
supports
more
than
10
transitions
in
its
schedule
they
can
send
this
by
sending
more
than
1
“Set
Weekly
Schedule”
command,
each
containing
the
separate
information
that
the
device
needs
to
set.
4.3.8.6.
Day
of
Week
for
Sequence
4.3.10.6.
DayOfWeekforSequence
Field
This
field
represents
SHALL
represent
the
day
of
the
week
at
which
all
the
transitions
within
the
payload
of
the
command
SHOULD
be
associated
to.
This
field
is
a
bitmap
and
therefore
the
associated
set
point
could
overlap
onto
multiple
days
(you
could
set
one
transition
time
for
all
“week
days”
or
whatever
combination
of
days
the
implementation
requests).
Each set point transition will begin with the day of week for this transition. There can be up to 10 transitions for each command.
4.3.8.7.
Mode
for
Sequence
4.3.10.7.
ModeForSequence
Field
This
field
determines
SHALL
indicate
how
the
application
SHALL
decode
decodes
the
Set
Point
Fields
setpoint
fields
of
each
transition
in
the
Transitions
list.
If the HeatSetpointPresent bit is On, the HeatSetpoint field SHALL be included in every entry of the Transitions list.
If the HeatSetpointPresent bit is Off, the HeatSetpoint field SHALL NOT be included in any entry of the Transitions list.
If the CoolSetpointPresent bit is On, the CoolSetpoint field SHALL be included in every entry of the Transitions list.
If the CoolSetpointPresent bit is Off, the CoolSetpoint field SHALL NOT be included in any entry of the Transitions list.
At least one of the bits in the Mode For Sequence byte SHALL be on.
Both bits must be respected, even if the HEAT or COOL feature is not supported, to ensure the command is decoded and handled correctly.
4.3.8.8.
4.3.10.8.
Transitions
Field
This
field
contains
SHALL
contain
the
list
of
setpoint
transitions
used
to
update
the
specified
daily
schedules
4.3.8.9.
Get
Weekly
Schedule
4.3.10.9.
GetWeeklySchedule
Command
Upon receipt, the unit SHOULD send in return the Get Weekly Schedule Response command. The Days to Return and Mode to Return fields are defined as bitmask for the flexibility to support multiple days and multiple modes within one command. If thermostat cannot handle incoming command with multiple days and/or multiple modes within one command, it SHALL send default response of INVALID_COMMAND in return.
|
|
Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
DaysToReturn |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
ModeToReturn |
|
desc |
M |
4.3.8.9.1.
Days
To
Return
4.3.10.9.1.
DaysToReturn
Field
This
field
indicates
SHALL
indicate
the
number
of
days
the
client
would
like
to
return
the
set
point
values
for
and
could
be
any
combination
of
single
days
or
the
entire
week.
This
field
has
the
same
format
as
Day
Of
Week
for
Sequence
Values
.
4.3.8.10.
Clear
Weekly
Schedule
4.3.10.10.
ClearWeeklySchedule
Command
The
Clear
Weekly
Schedule
This
command
is
used
to
clear
the
weekly
schedule.
The
Clear
weekly
schedule
has
no
payload.
Upon receipt, all transitions currently stored SHALL be cleared and a default response of SUCCESS SHALL be sent in response. There are no error responses to this command.
4.3.8.11.
Get
Relay
Status
Log
4.3.10.11.
GetRelayStatusLog
Command
The
Get
Relay
Status
Log
This
command
is
used
to
query
the
thermostat
internal
relay
status
log.
This
command
has
no
payload.
Upon receipt, the unit SHALL respond with Relay Status Log command if the relay status log feature is supported on the unit.
The log storing order is First in First Out (FIFO) when the log is generated and stored into the Queue.
The
first
record
in
the
log
(i.e.,
the
oldest)
one,
is
the
first
to
be
replaced
when
there
is
a
new
record
and
there
is
no
more
space
in
the
log.
Thus,
Thus,
the
newest
record
will
overwrite
the
oldest
one
if
there
is
no
space
left.
The log storing order is Last In First Out (LIFO) when the log is being retrieved from the Queue by a client device.
Once the "Get Relay Status Log Response" frame is sent by the Server, the "Unread Entries" attribute SHOULD be decremented to indicate the number of unread records that remain in the queue.
If
the
"Unread
Entries" attribute
Entries"
attribute
reaches
zero
and
the
Client
sends
a
new
"Get
Relay
Status
Log
Request",
the
Server
MAY
send
one
of
the
following
items
as
a
response:
-
resendResend the last Get Relay Status Log Responseor
-
generateGenerate new log record at the time of request and send Get Relay Status Log Response with the new data
For both cases, the "Unread Entries" attribute will remain zero.
4.3.8.12.
Get
Weekly
Schedule
Response
4.3.10.12.
GetWeeklyScheduleResponse
Command
This
command
has
the
same
payload
format
as
the
Set
Weekly
Schedule.
Please
refer
to
the
payload
detail
in
Set
Weekly
Schedule
Command
SetWeeklySchedule
.
4.3.8.13.
Get
Relay
Status
Log
Response
4.3.10.13.
GetRelayStatusLogResponse
Command
This command is sent from the thermostat cluster server in response to the Get Relay Status Log. After the Relay Status Entry is sent over the air to the requesting client, the specific entry will be cleared from the thermostat internal log.
|
|
Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
TimeOfDay |
uint16 |
0 to 1439 |
M |
||
|
1 |
RelayStatus |
|
desc |
M |
||
|
2 |
LocalTemperature |
temperature |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
3 |
HumidityInPercentage |
uint8 |
0% to 100% |
X |
M |
|
|
4 |
SetPoint |
temperature |
all |
M |
||
|
5 |
UnreadEntries |
uint16 |
all |
M |
4.3.8.13.1.
Time
of
Day
4.3.10.13.1.
TimeOfDay
Field
Represents
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
sample
time
of
the
day,
in
minutes
since
midnight,
when
the
relay
status
was
captured
for
this
associated
log
entry.
For
example,
6am
will
be
represented
by
360
minutes
since
midnight
and
11:30pm
will
be
represented
by
1410
minutes
since
midnight.
4.3.8.13.2.
Relay
Status
4.3.10.13.2.
RelayStatus
Field
Presents
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
relay
status
for
thermostat
when
the
log
is
captured.
Each
bit
represents
one
relay
used
by
the
thermostat.
If
the
bit
is
on,
the
associated
relay
is
on
and
active.
Each
thermostat
manufacturer
can
create
its
own
mapping
between
the
bitmask
bitmap
and
the
associated
relay.
4.3.8.13.3.
Local
Temperature
4.3.10.13.3.
LocalTemperature
Field
Presents
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
local
temperature
LocalTemperature
when
the
log
is
captured.
The
null
value
indicates
that
LocalTemperature
was
invalid.
invalid
or
unavailable.
4.3.8.13.4.
4.3.10.13.4.
Humidity
Field
This
field
presents
SHALL
indicate
the
humidity
as
a
percentage
when
the
log
was
captured.
The
null
value
indicates
that
the
humidity
value
was
invalid
or
unknown.
4.3.9.1.
Temperature
(
temperature
type)
4.4.
Fan
Control
Cluster
This
type,
derived
from
int16,
represents
a
temperature
on
cluster
specifies
an
interface
to
control
the
Celsius
scale
with
a
resolution
speed
of
0.01°C.
value
=
(
temperature
in
°C
)
x
100
-4°C
⇒
-400
123.45°C
⇒
12345
a
fan.
|
Note
|
Support
for
Fan
Control
cluster
is
|
4.3.9.2.
Temperature
Difference
(
temp-diff
type)
4.4.1.
Revision
History
This
type,
derived
from
int16,
represents
a
temperature
difference
with
a
resolution
of
0.01°C.
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
=
(
temperature
SHALL
be
the
highest
revision
number
in
°C
)
x
100
-4°C
⇒
-400
123.45°C
⇒
12345
the
table
below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Global mandatory ClusterRevision attribute added |
|
2 |
New data model format and notation; Percent, speed and motion settings; General cleanup |
|
3 |
Addition
of
|
|
4 | Change conformance for FanModeSequenceEnum |
4.3.9.4.
Unsigned
Temperature
(°C
x
10)
(
temp-u8
type)
This
type,
derived
from
uint8,
represents
a
temperature
from
0°C
to
25.5°C
with
a
resolution
of
0.1°C.
4.4.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role | Scope | PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
FAN |
4.3.9.5.
ThermostatScheduleTransition
4.4.4.
Features
This
represents
a
single
transition
in
a
Thermostat
schedule
cluster
SHALL
support
the
FeatureMap
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Auto |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
Wind |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
Airflow Direction |
|
4.3.9.5.1.
TransitionTime
4.4.4.1.
MultiSpeed
Feature
This
field
represents
Legacy
Fan
Control
cluster
revision
0-1
defined
3
speeds
(low,
medium
and
high)
plus
automatic
speed
control
but
left
it
up
to
the
start
time
implementer
to
decide
what
was
supported.
Therefore,
it
is
assumed
that
legacy
client
implementations
are
capable
of
determining,
from
the
schedule
transition
during
server,
the
associated
day.
number
of
speeds
supported
between
1,
2,
or
3,
and
whether
automatic
speed
control
is
supported.
The
time
will
be
represented
by
MultiSpeed
feature
includes
new
attributes
that
support
a
16
bits
unsigned
integer
running
fan
speed
value
from
1
to
designate
the
minutes
since
midnight.
For
example,
6am
will
be
represented
by
360
minutes
since
midnight
and
11:30pm
will
be
represented
by
1410
minutes
since
midnight.
a
maximum
of
100.
See
Speed
Rules
for
more
details.
4.4.5. Data Types
4.3.9.6.
HeatSetpoint
4.4.5.1.
RockBitmap
Type
| Bit | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | RockLeftRight |
Indicate
rock
left
to
|
M |
1 | RockUpDown | Indicate rock up and down | M |
2 | RockRound | Indicate rock around | M |
4.3.9.7.
CoolSetpoint
4.4.5.2.
WindBitmap
Type
| Bit | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
SleepWind
|
Indicate sleep wind | M |
|
1 |
NaturalWind | Indicate natural wind | M |
4.4.5.3. StepDirectionEnum Type
|
|
| Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| Step moves in increasing direction | M |
|
|
| Step moves in decreasing direction | M |
4.4.3.
Classification
4.4.5.4.
AirflowDirectionEnum
Type
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
Reverse | Airflow is in the reverse direction | M |
4.4.4.
Cluster
Identifiers
4.4.5.5.
FanModeEnum
Type
|
|
Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| Off |
Fan
| M |
1 | Low | Fan using low speed | desc |
2 | Medium | Fan using medium speed | desc |
3 | High | Fan using high speed | M |
4 | On | D | |
5 | Auto | Fan is using auto mode | AUT |
6 | Smart | Fan is using smart mode | D |
4.4.5.6. FanModeSequenceEnum Type
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
Off/High/Auto |
Fan
|
[AUT].a |
5 | Off/High |
Fan
is
capable
of
|
[!AUT].a |
4.4.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
FanMode |
|
0 to 6 |
N |
0 |
RW VO |
M |
|
0x0001 |
FanModeSequence |
|
0 to 5 |
N |
MS |
R[W] VO |
Zigbee |
0x0001 | FanModeSequence | 0 to 5 | F | MS | R V | M |
|
|
0x0002 |
PercentSetting |
|
0 to 100 |
X |
0 |
RW VO |
M |
|
0x0003 |
PercentCurrent |
|
0 to 100 |
desc |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0004 |
SpeedMax |
uint8 |
1 to 100 |
F |
MS |
R V |
SPD |
|
0x0005 |
SpeedSetting |
uint8 |
0 to SpeedMax |
X |
0 |
RW VO |
SPD |
|
0x0006 |
SpeedCurrent |
uint8 |
0 to SpeedMax |
P |
desc |
R V |
SPD |
|
0x0007 |
RockSupport |
|
desc |
F |
0 |
R V |
RCK |
|
0x0008 |
RockSetting |
|
desc |
P |
0 |
RW VO |
RCK |
|
0x0009 |
WindSupport |
|
desc |
F |
0 |
R V |
WND |
|
|
WindSetting |
|
desc |
P |
0 |
RW VO |
WND |
|
|
|
|
desc |
|
|
|
|
4.4.6.1.1.
Off
4.4.6.1.
FanMode
Attribute
Setting
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
current
speed
mode
of
the
fan.
This
attribute
value
MAY
be
written
by
the
client
to
Off
indicate
a
new
speed
mode
of
the
fan.
This
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
one
of
the
values
of
these
attributes
to
0
(zero):
in
FanModeEnum
.
When
the
FanMode
attribute
is
written
to,
the
PercentSetting
PercentCurrent
and
SpeedSetting
(if
present)
attributes
SHALL
be
set
to
appropriate
values,
as
defined
by
the
Percent
Rules
and
Speed
Rules
respectively,
unless
otherwise
specified
below.
When the FanMode attribute is set to any given mode, the PercentCurrent and SpeedCurrent (if present) SHALL indicate the actual currently operating fan speed, unless otherwise specified below.
4.4.6.1.2.
Low,
Medium,
High
or
Unsupported
4.4.6.1.1.
Off
Value
If
the
fan
only
supports
1
speed
then:
only
Setting
the
High
attribute
value
SHALL
be
supported
SpeedMax
attribute,
if
present,
SHALL
be
1
If
the
fan
only
supports
2
speeds
then
only
the
Low
and
High
attribute
values
SHALL
be
supported.
If
a
client
attempts
to
write
an
unsupported
value
(such
as
On),
the
FanMode
attribute
Off
SHALL
be
set
to
High.
If
the
value
is
High,
Medium,
or
Low
the
server
SHALL
set
values
of
these
percent
speed
attributes
to
a
single
value
in
the
corresponding
range
as
defined
in
the
percent
rules
:
0
(zero):
-
SpeedSetting (if present)
-
SpeedCurrent (if present)
4.4.6.1.3.
4.4.6.1.2.
Auto
Value
Setting the attribute value to Auto SHALL set the values of these attributes to null:
-
SpeedSetting (if present)
These attributes SHALL continue to indicate the current state of the fan while this attribute value is Auto:
-
SpeedCurrent (if present)
4.4.6.2. FanModeSequence Attribute
This attribute indicates the fan speed ranges that SHALL be supported.
4.4.6.3. PercentSetting Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the speed setting for the fan. This attribute MAY be written by the client to indicate a new fan speed. If the client writes null to this attribute, the attribute value SHALL NOT change. If this is set to 0, the server SHALL set the FanMode attribute value to Off.
4.4.6.3.1. Percent Rules
It is up to the server implementation to map between ranges of the PercentSetting attribute and FanMode attribute enumerated values. Percent values are split into ranges, each range corresponding to a supported FanMode attribute value. Percent ranges SHALL NOT overlap. All percent values in the High speed range SHALL be higher than all percent values in the Medium and Low speed ranges, if supported. All percent values in the Medium speed range SHALL be higher than all percent values in the Low speed range. If the client sets the FanMode attribute to Low, Medium or High, the server SHALL set the PercentSetting attribute to a value within the corresponding range. If the client sets the PercentSetting attribute, the server SHALL set the FanMode attribute to Low, Medium or High, based on the percent value being in the corresponding range.
If
the
Section
4.4.5.1
MultiSpeed
feature
is
supported,
the
calculation
of
SpeedSetting
or
SpeedCurrent
(speed)
from
a
percent
value
change
for
PercentSetting
or
PercentCurrent
respectively
(percent)
SHALL
hold
true:
-
speed = ceil( SpeedMax * (percent * 0.01) )
4.4.6.4. PercentCurrent Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
actual
currently
operating
fan
speed,
or
zero
to
indicate
that
the
fan
is
off.
See
Section
4.4.6.3.1
Percent
Rules
for
more
details.
4.4.6.5. SpeedMax Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate that the fan has one speed (value of 1) or the maximum speed, if the fan is capable of multiple speeds.
4.4.6.6. SpeedSetting Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
speed
setting
for
the
fan.
This
attribute
MAY
be
written
by
the
client
to
indicate
a
new
fan
speed.
If
the
client
writes
null
to
this
attribute,
the
attribute
value
SHALL
NOT
change.
If
this
is
set
to
0,
the
server
SHALL
set
the
FanMode
attribute
value
to
Off.
Please
see
the
Section
4.4.6.6.1
Speed
Rules
for
details
on
other
values.
4.4.6.6.1. Speed Rules
It is up to the server implementation to map between ranges of the SpeedSetting attribute and FanMode attribute enumerated values. Speed values are split into ranges, each range corresponding to a FanMode attribute value. Speed ranges SHALL NOT overlap. All speed values in the High speed range SHALL be higher than all speed values in the Medium and Low speed ranges, if supported. All speed values in the Medium speed range SHALL be higher than all speed values in the Low speed range. If the client sets the FanMode attribute to Low, Medium or High, the server SHALL set the SpeedSetting attribute to a value within the corresponding range. If the client sets the SpeedSetting attribute, the server SHALL set the FanMode attribute to Low, Medium or High, based on the speed value being in the corresponding range.
This calculation for the value of PercentSetting or PercentCurrent (percent) from a speed value change for SpeedSetting or SpeedCurrent respectively (speed) SHALL hold true:
-
percent = floor( speed/SpeedMax * 100 )
4.4.6.7. SpeedCurrent Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the actual currently operating fan speed, or zero to indicate that the fan is off.
4.4.6.8. RockSupport Attribute
This
attribute
is
a
bitmap
that
indicates
what
rocking
motions
the
server
supports.
The
bitmap
is
shown
in
the
table
below.
4.4.6.9. RockSetting Attribute
This attribute is a bitmap that indicates the current active fan rocking motion settings. Each bit SHALL only be set to 1, if the corresponding bit in the RockSupport attribute is set to 1, otherwise a status code of CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
If a combination of supported bits is set by the client, and the server does not support the combination, the lowest supported single bit in the combination SHALL be set and active, and all other bits SHALL indicate zero.
4.4.6.10. WindSupport Attribute
This
attribute
is
a
bitmap
that
indicates
what
wind
modes
the
server
supports.
At
least
one
wind
mode
bit
SHALL
be
set.
The
bitmap
is
shown
in
the
table
below.
Bit
Name
0
Sleep
Wind
1
Natural
Wind
4.4.6.10.1.
Sleep
Wind
The
fan
speed,
based
on
current
settings,
SHALL
gradually
slow
down
to
a
final
minimum
speed.
For
this
process,
the
sequence,
speeds
and
duration
are
MS.
4.4.6.10.2.
Natural
Wind
The
fan
speed
SHALL
vary
to
emulate
natural
wind.
For
this
setting,
the
sequence,
speeds
and
duration
are
MS.
4.4.6.11. WindSetting Attribute
This attribute is a bitmap that indicates the current active fan wind feature settings. Each bit SHALL only be set to 1, if the corresponding bit in the WindSupport attribute is set to 1, otherwise a status code of CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be returned.
If a combination of supported bits is set by the client, and the server does not support the combination, the lowest supported single bit in the combination SHALL be set and active, and all other bits SHALL indicate zero.
4.4.6.12. AirflowDirection Attribute
The
bitmap
is
shown
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
current
airflow
direction
of
the
fan.
This
attribute
MAY
be
written
by
the
client
to
indicate
a
new
airflow
direction
for
the
fan.
This
attribute
SHALL
be
set
to
one
of
the
values
in
the
table
below.
AirflowDirectionEnum
table.
4.4.7. Commands
|
|
Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | Step | client ⇒ server | Y | O | STEP |
4.4.7.1. Step Command
This command speeds up or slows down the fan, in steps, without the client having to know the fan speed. This command supports, for example, a user operated wall switch, where the user provides the feedback or control to stop sending this command when the proper speed is reached. The step speed values are implementation specific. How many step speeds are implemented is implementation specific.
This command supports these fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
| Increase | M |
|||
|
1 |
| bool | false | O | ||
2 | LowestOff | bool | true | O |
4.4.7.1.1. Direction Field
This field SHALL indicate whether the fan speed increases or decreases to the next step value.
4.4.7.1.2. Wrap Field
This field SHALL indicate if the fan speed wraps between highest and lowest step value.
4.4.7.1.3. LowestOff Field
This field SHALL indicate that the fan being off (speed value 0) is included as a step value.
4.4.7.1.4. When Generated
The client sends this command to speed the fan up or down in a step by step fashion.
4.4.7.1.5. Effect Upon Receipt
This command SHALL be executed even if the fan speed is not currently at an implemented step value.
If the Direction field is Increase,
If the fan speed is lower than the highest step value, the fan speed SHALL change to the lowest step value that is higher than the current fan speed.
Else if Wrap is TRUE, the fan speed SHALL change to the lowest step value.
Else the fan speed SHALL change to (or remain at) the highest step value.
If the Direction field is Decrease,
If the fan speed is higher than the lowest step value, the fan speed SHALL change to the highest step value that is lower than the current fan speed.
Else if Wrap is TRUE, the fan speed SHALL change to the highest step value.
Else the fan speed SHALL change to (or remain at) the lowest step value.
Although the effect of the Step command is implementation specific, the effect on receipt of the Step command SHALL adhere to the conformance of the affected attributes.
4.5. Thermostat User Interface Configuration Cluster
This cluster provides an interface to allow configuration of the user interface for a thermostat, or a thermostat controller device, that supports a keypad and LCD screen.
4.5.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
New data model format and notation, added "Conversion of Temperature Values for Display" section |
4.5.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
TSUIC |
4.5.4. Conversion of Temperature Values for Display
When
converting
temperature
values
for
display
manufacturers
SHOULD
ensure
that
calculations
round
to
See
the
nearest
representable
value.
Particular
care
is
needed
when
using
integer
arithmetic.
Temperature
Conversion
section
in
the
Data
Model
for
unit
conversion
between
Fahrenheit
and
Celsius.
4.5.5. Data Types
4.5.5.1. TemperatureDisplayModeEnum Type
For
example,
assuming
a
display
resolution
of
0.5:
This
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.5.4.1.
Sample
Conversion
Code
4.5.5.2.
KeypadLockoutEnum
Type
Sample
code
provided
to
ensure
consistent
Fahrenheit
to
Celsius
and
vice-versa
conversion
between
devices
and
across
vendors.
For
degF:
the
value
is
a
int8u
representing
2x
temperature
value
in
Fahrenheit
(to
get
0.5
resolution).
For
degC:
the
value
This
data
type
is
a
int16s
representing
Celsius
in
0.01
resolution
as
expected
by
the
ZCL
format.
derived
from
enum8.
|
|
Name |
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
The interpretation of the various levels is device-dependent.
4.5.5.1.
TemperatureDisplayMode
Attribute
4.5.5.3.
ScheduleProgrammingVisibilityEnum
Type
The
TemperatureDisplayMode
attribute
specifies
the
units
of
the
temperature
displayed
on
the
thermostat
screen.
This
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
| Value | Name |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
4.5.5.2.
KeypadLockout
Attribute
The
KeypadLockout
attribute
specifies
the
level
of
functionality
that
is
available
to
the
user
via
the
keypad.
Table
102.
KeypadLockout
Attribute
Values
4.5.6.
Attributes
|
|
Name |
|
| Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.5.6.1. TemperatureDisplayMode Attribute
The
interpretation
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
units
of
the
various
levels
temperature
displayed
on
the
thermostat
screen.
4.5.6.2. KeypadLockout Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
level
of
functionality
that
is
device-dependent.
available
to
the
user
via
the
keypad.
4.5.5.3.
4.5.6.3.
ScheduleProgrammingVisibility
Attribute
The
ScheduleProgrammingVisibility
This
attribute
is
used
to
hide
the
weekly
schedule
programming
functionality
or
menu
on
a
thermostat
from
a
user
to
prevent
local
user
programming
of
the
weekly
schedule.
The
schedule
programming
MAY
still
be
performed
via
a
remote
interface,
and
the
thermostat
MAY
operate
in
schedule
programming
mode.
This attribute is designed to prevent local tampering with or disabling of schedules that MAY have been programmed by users or service providers via a more capable remote interface. The programming schedule SHALL continue to run even though it is not visible to the user locally at the thermostat.
5. Closures
The Cluster Library is made of individual chapters such as this one. References between chapters are made using a X.Y notation where X is the chapter and Y is the sub-section within that chapter.
5.1. General Description
5.1.1. Introduction
The clusters specified in this document are for use typically in applications involving closures (e.g., shades, windows, doors), but MAY be used in any application domain.
5.1.2. Cluster List
This
section
lists
the
closures
specific
clusters
as
specified
in
this
document,
and
gives
examples
of
typical
usage
for
the
purpose
of
clarification.
The
clusters
defined
in
this
document
are
listed
in
Table
104
.
chapter.
| Cluster ID | Cluster Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0x0101 |
An interface to a generic way to secure a door |
|
|
0x0102 |
Commands and attributes for controlling a window covering |
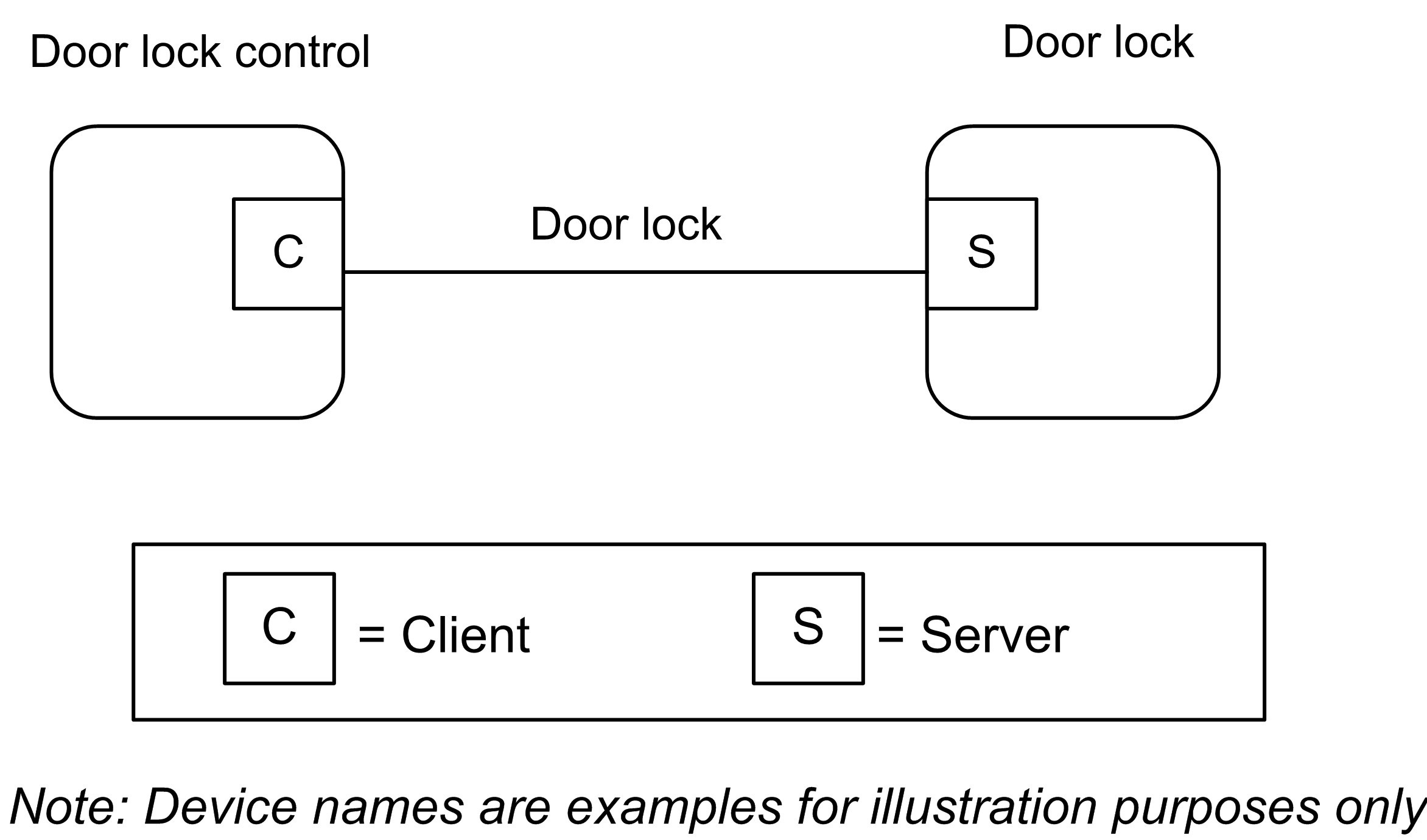
5.2. Door Lock
5.2.1. Overview
The door lock cluster provides an interface to a generic way to secure a door. The physical object that provides the locking functionality is abstracted from the cluster. The cluster has a small list of mandatory attributes and functions and a list of optional features.
5.2.1.1.
5.2.2.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
mandatory global ClusterRevision attribute added; CCB 1811 1812 1821 |
|
2 |
CCB 2430 |
|
3 |
CCB 2629 2630 |
|
4 |
All Hubs changes and added feature map |
|
5 |
|
|
6 |
New data model format and notation. Added User features. General cleanup of functionality |
|
7 | Added support for European door locks (unbolt feature) |
5.2.2.
5.2.5.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the Feature Map global attribute with these bits defined.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PIN |
PIN Credential |
O |
Lock supports PIN credentials (via keypad, or over-the-air) |
|
1 |
RID |
RFID Credential |
O |
Lock supports RFID credentials |
|
2 |
FGP |
Finger Credentials |
P, O |
Lock supports finger related credentials (fingerprint, finger vein) |
|
3 |
LOG |
Logging |
O |
Lock supports local/on-lock logging when Events are not supported |
|
4 |
WDSCH |
Week Day Access Schedules |
O |
Lock supports week day user access schedules |
|
5 |
DPS |
Door Position Sensor |
O |
Lock supports a door position sensor that indicates door’s state |
|
6 |
FACE |
Face Credentials |
P, O |
Lock supports face related credentials (face, iris, retina) |
|
7 |
COTA |
Credential Over-the-Air Access |
O |
PIN codes over-the-air supported for lock/unlock operations |
|
8 |
USR |
User |
[ PIN | RID | FGP | FACE ] |
Lock supports the user commands and database |
|
9 |
NOT |
Notification |
O |
Operation and Programming Notifications |
|
10 |
YDSCH |
Year Day Access Schedules |
O |
Lock supports year day user access schedules |
|
11 |
HDSCH |
Holiday Schedules |
O |
Lock supports holiday schedules |
|
12 | UBOLT | Unbolting | O | Lock supports unbolting |
5.2.2.1.
5.2.5.1.
PIN
Credential
Feature
If the User Feature is also supported then any PIN Code stored in the lock SHALL be associated with a User.
A lock MAY support multiple credential types so if the User feature is supported the UserType, UserStatus and Schedules are all associated with a User index and not directly with a PIN index. A User index may have several credentials associated with it.
5.2.2.2.
5.2.5.2.
RFID
Credential
Feature
If the User Feature is also supported then any RFID credential stored in the lock SHALL be associated with a User.
A lock MAY support multiple credential types so if the User feature is supported the UserType, UserStatus and Schedules are all associated with a User index and not directly with a RFID index. A User Index may have several credentials associated with it.
5.2.2.3.
5.2.5.3.
Finger
Credentials
Feature
Currently the cluster only defines the metadata format for notifications when a fingerprint/ finger vein credential is used to access the lock and doesn’t describe how to create fingerprint/finger vein credentials. If the Users feature is also supported then the User that a fingerprint/finger vein is associated with can also have its UserType, UserStatus and Schedule modified.
A lock MAY support multiple credential types so if the User feature is supported the UserType, UserStatus and Schedules are all associated with a User index and not directly with a Finger index. A User Index may have several credentials associated with it.
5.2.2.4.
5.2.5.4.
Logging
Feature
If Events are not supported the logging feature SHALL replace the Event reporting structure. If Events are supported the logging feature SHALL NOT be supported.
5.2.2.5.
5.2.5.5.
Week
Day
Access
Schedules
Feature
If the User feature is supported then Week Day Schedules are applied to a User and not a credential.
Week Day Schedules are used to restrict access to a specified time window on certain days of the week. The schedule is repeated each week. When a schedule is cleared this clears the access restrictions and grants unrestricted access to the user. The lock MAY automatically adjust the UserType when a schedule is created or cleared.
5.2.2.6.
5.2.5.6.
Door
Position
Sensor
Feature
If this feature is supported this indicates that the lock has the ability to determine the position of the door which is separate from the state of the lock.
5.2.2.7.
5.2.5.7.
Face
Credentials
Feature
Currently the cluster only defines the metadata format for notifications when a face recognition, iris, or retina credential is used to access the lock and doesn’t describe how to create face recognition, iris, or retina credentials. If the Users feature is also supported then the User that a face recognition, iris, or retina credential is associated with can also have its UserType, UserStatus and Schedule modified.
A lock MAY support multiple credential types so if the User feature is supported the UserType, UserStatus and Schedules are all associated with a User and not directly with a credential.
5.2.2.8.
5.2.5.8.
Credential
Over-the-Air
Access
Feature
If this feature is supported then the lock supports the ability to verify a credential provided in a lock/unlock command. Currently the cluster only supports providing the PIN credential to the lock/unlock commands. If this feature is supported then the PIN Credential feature SHALL also be supported.
5.2.2.9.
5.2.5.9.
User
Feature
If the User Feature is supported then a lock employs a User database. A User within the User database is used to associate credentials and schedules to single user record within the lock. This also means the UserType and UserStatus fields are associated with a User and not a credential.
5.2.2.10.
5.2.5.10.
Notification
Feature
This is a feature used before support of events. This feature supports notification commands and masks used to filter these notifications.
5.2.2.11.
5.2.5.11.
Year
Day
Access
Schedules
Feature
If the User feature is supported then Year Day Schedules are applied to a User and not a credential.
Year Day Schedules are used to restrict access to a specified date and time window. When a schedule is cleared this clears the access restrictions and grants unrestricted access to the user. The lock MAY automatically adjust the UserType when a schedule is created or cleared.
5.2.2.12.
5.2.5.12.
Holiday
Schedules
Feature
This feature is used to setup Holiday Schedule in the lock device. A Holiday Schedule sets a start and stop end date/time for the lock to use the specified operating mode set by the Holiday Schedule.
5.2.5.13. Unbolting Feature
Locks that support this feature differentiate between unbolting and unlocking. The Unbolt Door command retracts the bolt without pulling the latch. The Unlock Door command fully unlocks the door by retracting the bolt and briefly pulling the latch. While the latch is pulled, the lock state changes to Unlatched. Locks without unbolting support don’t differentiate between unbolting and unlocking and perform the same operation for both commands.
5.2.2.12.1.
5.2.5.13.1.
Recommended
steps
for
creating
a
new
User
It is RECOMMENDED that the Administrator query the door lock for what users already exist in its database to find an available UserIndex for creating a new User (see Get User Command ).
-
Use Set User Command with an available UserIndex to set the user record fields as applicable.
-
Use Set Credential Command with same UserIndex to add one or more credentials as applicable.
-
Use Set Week Day Schedule Command or Set Year Day Schedule Command with same UserIndex to add one or more schedule restrictions as applicable.
5.2.3.
5.2.6.
Attributes
| Id | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
LockState |
enum8 |
desc |
X P S |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0001 |
LockType |
enum8 |
desc |
R V |
M |
||
|
0x0002 |
ActuatorEnabled |
bool |
all |
R V |
M |
||
|
0x0003 |
DoorState |
enum8 |
desc |
X P |
R V |
DPS |
|
|
0x0004 |
DoorOpenEvents |
uint32 |
all |
RW VM |
[DPS] |
||
|
0x0005 |
DoorClosedEvents |
uint32 |
all |
RW VM |
[DPS] |
||
|
0x0006 |
OpenPeriod |
uint16 |
all |
RW VM |
[DPS] |
||
|
0x0010 |
NumberOfLogRecordsSupported |
uint16 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
LOG |
|
0x0011 |
NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
uint16 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
USR |
|
0x0012 |
NumberOfPINUsersSupported |
uint16 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
PIN |
|
0x0013 |
NumberOfRFIDUsersSupported |
uint16 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
RID |
|
0x0014 |
NumberOfWeekDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser |
uint8 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
WDSCH |
|
0x0015 |
NumberOfYearDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser |
uint8 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
YDSCH |
|
0x0016 |
NumberOfHolidaySchedulesSupported |
uint8 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
HDSCH |
|
0x0017 |
MaxPINCodeLength |
uint8 |
all |
F |
MS |
R V |
PIN |
|
0x0018 |
MinPINCodeLength |
uint8 |
all |
F |
MS |
R V |
PIN |
|
0x0019 |
MaxRFIDCodeLength |
uint8 |
all |
F |
MS |
R V |
RID |
|
|
MinRFIDCodeLength |
uint8 |
all |
F |
MS |
R V |
RID |
|
|
CredentialRulesSupport |
map8 |
all |
F |
1 |
R V |
USR |
|
|
NumberOfCredentialsSupportedPerUser |
uint8 |
all |
F |
0 |
R V |
USR |
|
0x0020 |
EnableLogging |
bool |
all |
P |
0 |
R[W] VA |
LOG |
|
0x0021 |
Language |
string |
max 3 |
P |
MS |
R[W] VM |
O |
|
0x0022 |
LEDSettings |
uint8 |
desc |
P |
0 |
R[W] VM |
O |
|
0x0023 |
AutoRelockTime |
uint32 |
all |
P |
MS |
R[W] VM |
O |
|
0x0024 |
SoundVolume |
uint8 |
desc |
P |
0 |
R[W] VM |
O |
|
0x0025 |
OperatingMode |
enum8 |
desc |
P |
0 |
R[W] VM |
M |
|
0x0026 |
SupportedOperatingModes |
map16 |
all |
F |
0xFFF6 |
R V |
M |
|
0x0027 |
DefaultConfigurationRegister |
map16 |
all |
P |
0 |
R V |
O |
|
0x0028 |
EnableLocalProgramming |
bool |
all |
P |
1 |
R[W] VA |
O |
|
0x0029 |
EnableOneTouchLocking |
bool |
all |
P |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
EnableInsideStatusLED |
bool |
all |
P |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
EnablePrivacyModeButton |
bool |
all |
P |
0 |
RW VM |
O |
|
|
LocalProgrammingFeatures |
map8 |
all |
P |
0 |
R[W] VA |
O |
|
0x0030 |
WrongCodeEntryLimit |
uint8 |
1 to 255 |
P |
MS |
R[W] VA |
PIN | RID |
|
0x0031 |
UserCodeTemporaryDisableTime |
uint8 |
1 to 255 |
P |
MS |
R[W] VA |
PIN | RID |
|
0x0032 |
SendPINOverTheAir |
bool |
all |
P |
0 |
R[W] VA |
|
|
0x0033 |
RequirePINforRemoteOperation |
bool |
all |
P |
0 |
R[W] VA |
COTA & PIN |
|
0x0034 |
SecurityLevel |
0 |
D |
||||
|
0x0035 |
ExpiringUserTimeout |
uint16 |
1 to 2880 |
P |
MS |
R[W] VA |
[USR] |
|
0x0040 |
AlarmMask |
map16 |
all |
P |
0xFFFF |
RW VA |
O |
|
0x0041 |
KeypadOperationEventMask |
map16 |
all |
P |
0xFFFF |
RW VA |
[NOT & PIN] |
|
0x0042 |
RemoteOperationEventMask |
map16 |
all |
P |
0xFFFF |
RW VA |
[NOT] |
|
0x0043 |
ManualOperationEventMask |
map16 |
all |
P |
0xFFFF |
RW VA |
[NOT] |
|
0x0044 |
RFIDOperationEventMask |
map16 |
all |
P |
0xFFFF |
RW VA |
[NOT & RID] |
|
0x0045 |
KeypadProgrammingEventMask |
map16 |
all |
P |
0xFFFF |
RW VA |
[NOT & PIN] |
|
0x0046 |
RemoteProgrammingEventMask |
map16 |
all |
P |
0xFFFF |
RW VA |
[NOT] |
|
0x0047 |
RFIDProgrammingEventMask |
map16 |
all |
P |
0xFFFF |
RW VA |
[NOT & RID] |
AutoRelockTime, OperatingMode and SupportedOperatingModes represent mandatory fields that were previously not present or optional. Implementors should be aware that older devices may not implement them.
5.2.3.1.
5.2.6.1.
Scene
Table
Extensions
If the Scenes server cluster is implemented on the same endpoint, the following attribute SHALL be part of the ExtensionFieldSetStruct of the Scene Table.
LockState
When the LockState attribute is part of a Scene table, the attribute is treated as a writable command; that is:
Setting the LockState to Locked SHALL command the lock to lock.
Setting the LockState to Unlocked SHALL command the lock to unlock.
If a lock supports the Unbolting Feature , setting the LockState to Unlocked SHALL unlock the door without pulling the latch.
Setting the LockState attribute to Unlatched SHALL command the lock to unlock and pull the latch.
Trying to write the LockState attribute to Not Fully Locked SHALL be ignored and not change the state of the lock.
The Transition Time field in the Scene table will be treated as a delay before setting the LockState attribute; that is, it is possible to activate a scene with the lock actuation some seconds later.
Locks that do not have an actuation mechanism SHOULD not support the Scene table extension.
5.2.6.2. LockState Attribute
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Not Fully Locked |
M |
Lock state is not fully locked |
|
1 |
Locked |
M |
Lock state is fully locked |
|
2 |
Unlocked |
M |
Lock state is fully unlocked |
|
3 | Unlatched | O | Lock state is fully unlocked and the latch is pulled |
The LockState Attribute may be NULL if the lock hardware does not currently know the status of the locking mechanism. For example, a lock may not know the LockState status after a power cycle until the first lock actuation is completed.
The Not Fully Locked value is used by a lock to indicate that the state of the lock is somewhere between Locked and Unlocked so it is only partially secured. For example, a deadbolt could be partially extended and not in a dead latched state.
5.2.3.2.
5.2.6.3.
LockType
Attribute
The LockType attribute is indicated by an enumeration:
| Value | Name |
|
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Dead bolt |
Physical lock type is dead bolt |
|
1 |
Magnetic |
Physical lock type is magnetic |
|
2 |
Other |
Physical lock type is other |
|
3 |
Mortise |
Physical lock type is mortise |
|
4 |
Rim |
Physical lock type is rim |
|
5 |
Latch Bolt |
Physical lock type is latch bolt |
|
6 |
Cylindrical Lock |
Physical lock type is cylindrical lock |
|
7 |
Tubular Lock |
Physical lock type is tubular lock |
|
8 |
Interconnected Lock |
Physical lock type is interconnected lock |
|
9 |
Dead Latch |
Physical lock type is dead latch |
|
10 |
Door Furniture |
Physical lock type is door furniture |
|
11 | Eurocylinder | Physical lock type is eurocylinder |
5.2.3.3.
5.2.6.4.
ActuatorEnabled
Attribute
The ActuatorEnabled attribute indicates if the lock is currently able to (Enabled) or not able to (Disabled) process remote Lock, Unlock, or Unlock with Timeout commands.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Boolean Value |
|
|---|---|
|
0 |
Disabled |
|
1 |
Enabled |
5.2.3.4.
5.2.6.5.
DoorState
Attribute
The current door state as defined in DoorStateEnum .
This attribute SHALL be null only if an internal error prevents the retrieval of the current door state.
5.2.3.5.
5.2.6.6.
DoorOpenEvents
Attribute
This attribute holds the number of door open events that have occurred since it was last zeroed.
5.2.3.6.
5.2.6.7.
DoorClosedEvents
Attribute
This attribute holds the number of door closed events that have occurred since it was last zeroed.
5.2.3.7.
5.2.6.8.
OpenPeriod
Attribute
This attribute holds the number of minutes the door has been open since the last time it transitioned from closed to open.
5.2.3.9.
5.2.6.10.
NumberOfTotalUsersSupported
Attribute
Number of total users supported by the lock.
5.2.3.12.
5.2.6.13.
NumberOfWeekDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser
Attribute
The number of configurable week day schedule supported per user.
5.2.3.13.
5.2.6.14.
NumberOfYearDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser
Attribute
The number of configurable year day schedule supported per user.
5.2.3.14.
5.2.6.15.
NumberOfHolidaySchedulesSupported
Attribute
The number of holiday schedules supported for the entire door lock device.
5.2.3.15.
5.2.6.16.
MaxPINCodeLength
Attribute
An 8 bit value indicates the maximum length in bytes of a PIN Code on this device.
5.2.3.16.
5.2.6.17.
MinPINCodeLength
Attribute
An 8 bit value indicates the minimum length in bytes of a PIN Code on this device.
5.2.3.17.
5.2.6.18.
MaxRFIDCodeLength
Attribute
An 8 bit value indicates the maximum length in bytes of a RFID Code on this device. The value depends on the RFID code range specified by the manufacturer, if media anti-collision identifiers (UID) are used as RFID code, a value of 20 (equals 10 Byte ISO 14443A UID) is recommended.
5.2.3.18.
5.2.6.19.
MinRFIDCodeLength
Attribute
An 8 bit value indicates the minimum length in bytes of a RFID Code on this device. The value depends on the RFID code range specified by the manufacturer, if media anti-collision identifiers (UID) are used as RFID code, a value of 8 (equals 4 Byte ISO 14443A UID) is recommended.
5.2.3.19.
5.2.6.20.
CredentialRulesSupport
Attribute
This bitmap contains a bit for every value of CredentialRuleEnum supported on this device.
| Bit |
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Single |
Only one credential is required for lock operation |
|
1 |
Dual |
Any two credentials are required for lock operation |
|
2 |
Tri |
Any three credentials are required for lock operation |
5.2.3.20.
5.2.6.21.
NumberOfCredentialsSupportedPerUser
Attribute
The number of credentials that could be assigned for each user.
Depending on the value of NumberOfRFIDUsersSupported and NumberOfPINUsersSupported it may not be possible to assign that number of credentials for a user.
For example, if the device supports only PIN and RFID credential types, NumberOfCredentialsSupportedPerUser is set to 10, NumberOfPINUsersSupported is set to 5 and NumberOfRFIDUsersSupported is set to 3, it will not be possible to actually assign 10 credentials for a user because maximum number of credentials in the database is 8.
5.2.3.21.
5.2.6.22.
EnableLogging
Attribute
Enable/disable event logging. When event logging is enabled, all event messages are stored on the lock for retrieval. Logging events can be but not limited to Tamper Alarm, Lock, Unlock, AutoRelock, User Code Added, User Code Cleared, Schedule Added, and Schedule Cleared. For a full detail of all the possible alarms and events, please refer to the full list in the Alarm and Event Masks Attribute Set.
5.2.3.22.
5.2.6.23.
Language
Attribute
Modifies the language for the on-screen or audible user interface using a 2-byte language code from ISO-639-1.
5.2.3.23.
5.2.6.24.
OperatingMode
Attribute
The current operating mode of the lock (see OperatingModeEnum ).
5.2.3.24.
5.2.6.25.
SupportedOperatingModes
Attribute
This bitmap contains all operating bits of the Operating Mode Attribute supported by the lock. All operating modes NOT supported by a lock SHALL be set to one. The value of the OperatingMode enumeration defines the related bit to be set, as shown below:
| Bit |
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Normal |
M |
|
1 |
Vacation |
O |
|
2 |
Privacy |
O |
|
3 |
NoRemoteLockUnlock |
M |
|
4 |
Passage |
O |
5.2.3.25.
5.2.6.26.
LEDSettings
Attribute
The settings for the LED support three different modes, shown below:
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
0 |
Never use LED for signalization |
|
1 |
Use LED signalization except for access allowed events |
|
2 |
Use LED signalization for all events |
5.2.3.26.
5.2.6.27.
AutoRelockTime
Attribute
The number of seconds to wait after unlocking a lock before it automatically locks again. 0=disabled. If set, unlock operations from any source will be timed. For one time unlock with timeout use the specific command.
5.2.3.27.
5.2.6.28.
SoundVolume
Attribute
The sound volume on a door lock has four possible settings: silent, low, high and medium volumes, shown below:
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
0 |
Silent Mode |
|
1 |
Low Volume |
|
2 |
High Volume |
|
3 |
Medium Volume |
5.2.3.28.
5.2.6.29.
DefaultConfigurationRegister
Attribute
This attribute represents the default configurations as they are physically set on the device (example: hardware dip switch setting, etc…) and represents the default setting for some of the attributes within this cluster (for example: LED, Auto Lock, Sound Volume, and Operating Mode attributes).
This is a read-only attribute and is intended to allow clients to determine what changes MAY need to be made without having to query all the included attributes. It MAY be beneficial for the clients to know what the device’s original settings were in the event that the device needs to be restored to factory default settings.
If the Client device would like to query and modify the door lock server’s operating settings, it SHOULD send read and write attribute requests to the specific attributes.
For example, the Sound Volume attribute default value is Silent Mode. However, it is possible that the current Sound Volume is High Volume. Therefore, if the client wants to query/modify the current Sound Volume setting on the server, the client SHOULD read/write to the Sound Volume attribute.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Bit |
| Summary |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Local Programming |
0 - Enable Local Programming Attribute default value is 0 (disabled) 1 - Enable Local Programming Attribute default value is 1 (enabled) |
|
1 |
Keypad Interface |
0 –Keypad Interface default access is disabled 1 - Keypad Interface default access is enabled |
|
2 |
Remote Interface |
0 - Remote Interface default access is disabled 1 - Remote Interface default access is enabled |
|
5 |
Sound Volume |
0 – Sound Volume attribute default value is 0 (Silent Mode) 1 – Sound Volume attribute default value is equal to something other than 0 |
|
6 |
Auto Relock |
0 – Auto Relock Time attribute default value = 0 1 – Auto Relock Time attribute default value is equal to something other than 0 |
|
7 |
LED Settings |
0
–
1
–
|
5.2.3.29.
5.2.6.30.
EnableLocalProgramming
Attribute
Enable/disable local programming on the door lock of certain features (see LocalProgrammingFeatures attribute). If this value is set to TRUE then local programming is enabled on the door lock for all features. If it is set to FALSE then local programming is disabled on the door lock for those features whose bit is set to 0 in the LocalProgrammingFeatures attribute. Local programming SHALL be enabled by default.
5.2.3.30.
5.2.6.31.
EnableOneTouchLocking
Attribute
Enable/disable the ability to lock the door lock with a single touch on the door lock.
5.2.3.31.
5.2.6.32.
EnableInsideStatusLED
Attribute
Enable/disable an inside LED that allows the user to see at a glance if the door is locked.
5.2.3.32.
5.2.6.33.
EnablePrivacyModeButton
Attribute
Enable/disable a button inside the door that is used to put the lock into privacy mode. When the lock is in privacy mode it cannot be manipulated from the outside.
5.2.3.33.
5.2.6.34.
LocalProgrammingFeatures
Attribute
The local programming features that will be disabled when EnableLocalProgramming attribute is set to False. If a door lock doesn’t support disabling one aspect of local programming it SHALL return CONSTRAINT_ERROR during a write operation of this attribute. If the EnableLocalProgramming attribute is set to True then all local programming features SHALL be enabled regardless of the bits set to 0 in this attribute.
The features that can be disabled from local programming are defined in the following bitmap.
| Bit |
| Summary |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Add Locally | 0 - The ability to add Users/credentials/Schedules locally is disabled 1 - The ability to add Users/Credentials/Schedules locally is enabled |
|
1 |
Modify Locally | 0 - The ability to modify Users/credentials/Schedules locally is disabled 1 - The ability to modify Users/Credentials/Schedules locally is enabled |
|
2 |
Clear Locally | 0 - The ability to clear Users/credentials/Schedules locally is disabled 1 - The ability to clear Users/Credentials/Schedules locally is enabled |
|
3 |
Adjust Locally | 0 - The ability to adjust lock settings locally is disabled 1 - The ability to adjust lock settings locally is enabled |
5.2.3.34.
5.2.6.35.
WrongCodeEntryLimit
Attribute
The number of incorrect Pin codes or RFID presentment attempts a user is allowed to enter before the lock will enter a lockout state. The value of this attribute is compared to all failing forms of credential presentation, including Pin codes used in an Unlock Command when RequirePINforRemoteOperation is set to true. Valid range is 1-255 incorrect attempts. The lockout state will be for the duration of UserCodeTemporaryDisableTime. If the attribute accepts writes and an attempt to write the value 0 is made, the device SHALL respond with CONSTRAINT_ERROR.
The lock MAY reset the counter used to track incorrect credential presentations as required by internal logic, environmental events, or other reasons. The lock SHALL reset the counter if a valid credential is presented.
5.2.3.35.
5.2.6.36.
UserCodeTemporaryDisableTime
Attribute
The number of seconds that the lock shuts down following wrong code entry. Valid range is 1-255 seconds. Device can shut down to lock user out for specified amount of time. (Makes it difficult to try and guess a PIN for the device.) If the attribute accepts writes and an attempt to write the attribute to 0 is made, the device SHALL respond with CONSTRAINT_ERROR.
5.2.3.36.
5.2.6.37.
SendPINOverTheAir
Attribute
Boolean set to True if it is ok for the door lock server to send PINs over the air. This attribute determines the behavior of the server’s TX operation. If it is false, then it is not ok for the device to send PIN in any messages over the air.
The PIN field within any door lock cluster message SHALL keep the first octet unchanged and masks the actual code by replacing with 0xFF. For example (PIN "1234" ): If the attribute value is True, 0x04 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 SHALL be used in the PIN field in any door lock cluster message payload. If the attribute value is False, 0x04 0xFF 0xFF 0xFF 0xFF SHALL be used.
5.2.3.37.
5.2.6.38.
RequirePINForRemoteOperation
Attribute
Boolean set to True if the door lock server requires that an optional PINs be included in the payload of remote lock operation events like Lock, Unlock, Unlock with Timeout and Toggle in order to function.
5.2.3.38.
5.2.6.39.
ExpiringUserTimeout
Attribute
Number of minutes a PIN, RFID, Fingerprint, or other credential associated with a user of type ExpiringUser SHALL remain valid after its first use before expiring. When the credential expires the UserStatus for the corresponding user record SHALL be set to OccupiedDisabled.
5.2.3.39.
5.2.6.40.
AlarmMask
Attribute
This attribute is only supported if the Alarms cluster is on the same endpoint. The alarm mask is used to turn on/off alarms for particular functions. Alarms for an alarm group are enabled if the associated alarm mask bit is set. Each bit represents a group of alarms. Entire alarm groups can be turned on or off by setting or clearing the associated bit in the alarm mask.
This attribute has the following possible values:
This mask DOES NOT apply to the Events mechanism of this cluster.
|
|
Bit |
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Alarm Code 0 |
0 |
Locking Mechanism Jammed |
M |
|
Alarm Code 1 |
1 |
Lock Reset to Factory Defaults |
O |
|
Alarm Code 2 |
2 |
Reserved |
O |
|
Alarm Code 3 |
3 |
RF Module Power Cycled |
O |
|
Alarm Code 4 |
4 |
Tamper Alarm - wrong code entry limit |
PIN | RID |
|
Alarm Code 5 |
5 |
Tamper Alarm - front escutcheon removed from main |
O |
|
Alarm Code 6 |
6 |
Forced Door Open under Door Locked Condition |
O |
5.2.3.40.
5.2.6.41.
KeypadOperationEventMask
Attribute
Event mask used to turn on and off the transmission of keypad operation events. This mask DOES NOT apply to the storing of events in the event log. This mask only applies to the Operation Event Notification Command.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Event Source |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Operation Event Code 0 |
|
Unknown or manufacturer-specific keypad operation event |
|
0 |
Operation Event Code 1 |
|
Lock, source: keypad |
|
0 |
Operation Event Code 2 |
|
Unlock, source: keypad |
|
0 |
Operation Event Code 3 |
|
Lock, source: keypad, error: invalid PIN |
|
0 |
Operation Event Code 4 |
|
Lock, source: keypad, error: invalid schedule |
|
0 |
Operation Event Code 5 |
|
Unlock, source: keypad, error: invalid code |
|
0 |
Operation Event Code 6 |
|
Unlock, source: keypad, error: invalid schedule |
|
0 |
Operation Event Code 15 |
|
Non-Access User operation event, source keypad. |
This mask DOES NOT apply to the Events mechanism of this cluster.
5.2.3.41.
5.2.6.42.
RemoteOperationEventMask
Attribute
Event mask used to turn on and off the transmission of remote operation events. This mask DOES NOT apply to the storing of events in the event log. This mask only applies to the Operation Event Notification Command.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Event Source |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Operation Event Code 0 |
|
Unknown or manufacturer-specific remote operation event |
|
1 |
Operation Event Code 1 |
|
Lock, source: remote |
|
1 |
Operation Event Code 2 |
|
Unlock, source: remote |
|
1 |
Operation Event Code 3 |
|
Lock, source: remote, error: invalid code |
|
1 |
Operation Event Code 4 |
|
Lock, source: remote, error: invalid schedule |
|
1 |
Operation Event Code 5 |
|
Unlock, source: remote, error: invalid code |
|
1 |
Operation Event Code 6 |
|
Unlock, source: remote, error: invalid schedule |
This mask DOES NOT apply to the Events mechanism of this cluster.
5.2.3.42.
5.2.6.43.
ManualOperationEventMask
Attribute
Event mask used to turn on and off manual operation events. This mask DOES NOT apply to the storing of events in the event log. This mask only applies to the Operation Event Notification Command.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Event Source |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 0 |
|
Unknown or manufacturer-specific manual operation event |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 1 |
|
Thumbturn Lock |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 2 |
|
Thumbturn Unlock |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 7 |
|
One touch lock |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 8 |
|
Key Lock |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 9 |
|
Key Unlock |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 10 |
|
Auto lock |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 11 |
|
Schedule Lock |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 12 |
|
Schedule Unlock |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 13 |
|
Manual Lock (Key or Thumbturn) |
|
2 |
Operation Even Code 14 |
|
Manual Unlock (Key or Thumbturn) |
This mask DOES NOT apply to the Events mechanism of this cluster.
5.2.3.43.
5.2.6.44.
RFIDOperationEventMask
Attribute
Event mask used to turn on and off RFID operation events. This mask DOES NOT apply to the storing of events in the event log. This mask only applies to the Operation Event Notification Command.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Event Source |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
3 |
Operation Event Code 0 |
|
Unknown or manufacturer-specific keypad operation event |
|
3 |
Operation Event Code 1 |
|
Lock, source: RFID |
|
3 |
Operation Event Code 2 |
|
Unlock, source: RFID |
|
3 |
Operation Event Code 3 |
|
Lock, source: RFID, error: invalid RFID ID |
|
3 |
Operation Event Code 4 |
|
Lock, source: RFID, error: invalid schedule |
|
3 |
Operation Event Code 5 |
|
Unlock, source: RFID, error: invalid RFID ID |
|
3 |
Operation Event Code 6 |
|
Unlock, source: RFID, error: invalid schedule |
This mask DOES NOT apply to the Events mechanism of this cluster.
5.2.3.44.
5.2.6.45.
KeypadProgrammingEventMask
Attribute
Event mask used to turn on and off keypad programming events. This mask DOES NOT apply to the storing of events in the event log. This mask only applies to the Programming Event Notification Command.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Event Source |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Program Event Code 0 |
|
Unknown or manufacturer-specific keypad programming event |
|
0 |
Program Event Code 1 |
|
Programming PIN code changed, source: keypad User ID: programming user ID. PIN: default or programming PIN code if codes can be sent over the air per attribute. User type: default User Status: default |
|
0 |
Program Event Code 2 |
|
PIN added, source: keypad User ID: user ID that was added. PIN: code that was added (if codes can be sent over the air per attribute.) User type: default or type added. User Status: default or status added. |
|
0 |
Program Event Code 3 |
|
PIN cleared, source: keypad User ID: user ID that was cleared. PIN: code that was cleared (if codes can be sent over the air per attribute.) User type: default or type cleared. User Status: default or status cleared. |
|
0 |
Program Event Code 4 |
|
PIN changed Source: keypad User ID: user ID that was changed PIN: code that was changed (if codes can be sent over the air per attribute.) User type: default or type changed. User Status: default or status changed. |
This mask DOES NOT apply to the Events mechanism of this cluster.
5.2.3.45.
5.2.6.46.
RemoteProgrammingEventMask
Attribute
Event mask used to turn on and off remote programming events. This mask DOES NOT apply to the storing of events in the event log. This mask only applies to the Programming Event Notification Command.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Event Source |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Program Event Code 0 |
|
Unknown or manufacturer-specific remote programming event. |
|
1 |
Program Event Code 2 |
|
PIN added, source remote Same as keypad source above |
|
1 |
Program Event Code 3 |
|
PIN cleared, source remote Same as keypad source above. |
|
1 |
Program Event Code 4 |
|
PIN changed Source remote Same as keypad source above |
|
1 |
Program Event Code 5 |
|
RFID code added, Source remote |
|
1 |
Program Event Code 6 |
|
RFID code cleared, Source remote |
This mask DOES NOT apply to the Events mechanism of this cluster.
5.2.3.46.
5.2.6.47.
RFIDProgrammingEventMask
Attribute
Event mask used to turn on and off RFID programming events. This mask DOES NOT apply to the storing of events in the event log. This mask only applies to the Programming Event Notification Command.
This attribute has the following possible values:
| Event Source |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
3 |
Program Event Code 0 |
|
Unknown or manufacturer-specific keypad programming event |
|
3 |
Program Event Code 5 |
|
ID Added, Source: RFID User ID: user ID that was added. ID: ID that was added (if codes can be sent over the air per attribute.) User Type: default or type added. User Status: default or status added. |
|
3 |
Program Event Code 6 |
|
ID cleared, Source: RFID User ID: user ID that was cleared. ID: ID that was cleared (if codes can be sent over the air per attribute.) User Type: default or type cleared. User Status: default or status cleared. |
This mask DOES NOT apply to the Events mechanism of this cluster.
5.2.4.
5.2.7.
Commands
| Id | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
Lock Door |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T O |
M |
|
0x01 |
Unlock Door |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T O |
M |
|
0x02 |
Toggle |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T O |
X |
|
0x03 |
Unlock with Timeout |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T O |
O |
|
0x04 |
Get Log Record |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get Log Record Response |
M |
LOG |
|
0x04 |
Get Log Record Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
LOG |
|
|
0x05 |
Set PIN Code |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
!USR & PIN |
|
0x06 |
Get PIN Code |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get PIN Code Response |
A |
!USR & PIN |
|
0x06 |
Get PIN Code Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
!USR & PIN |
|
|
0x07 |
Clear PIN Code |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
!USR & PIN |
|
0x08 |
Clear All PIN Codes |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
!USR & PIN |
|
0x09 |
Set User Status |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
A |
!USR & (PIN | RID | FGP) |
|
|
Get User Status |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get User Status Response |
A |
!USR & (PIN | RID | FGP) |
|
|
Get User Status Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
!USR |
|
|
|
Set Week Day Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
A |
WDSCH |
|
|
Get Week Day Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get Week Day Schedule Response |
A |
WDSCH |
|
|
Get Week Day Schedule Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
WDSCH |
|
|
|
Clear Week Day Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
A |
WDSCH |
|
|
Set Year Day Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
A |
YDSCH |
|
|
Get Year Day Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get Year Day Schedule Response |
A |
YDSCH |
|
|
Get Year Day Schedule Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
YDSCH |
|
|
0x10 |
Clear Year Day Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
A |
YDSCH |
|
0x11 |
Set Holiday Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
A |
HDSCH |
|
0x12 |
Get Holiday Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get Holiday Schedule Response |
A |
HDSCH |
|
0x12 |
Get Holiday Schedule Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
HDSCH |
|
|
0x13 |
Clear Holiday Schedule |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
A |
HDSCH |
|
0x14 |
Set User Type |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
A |
!USR & (PIN | RID | FGP) |
|
0x15 |
Get User Type |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get User Type Response |
A |
!USR & (PIN | RID | FGP) |
|
0x15 |
Get User Type Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
!USR |
|
|
0x16 |
Set RFID Code |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
!USR & RID |
|
0x17 |
Get RFID Code |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get RFID Code Response |
A |
!USR & RID |
|
0x17 |
Get RFID Code Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
!USR & RID |
|
|
0x18 |
Clear RFID Code |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
!USR & RID |
|
0x19 |
Clear All RFID Codes |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
!USR & RID |
|
|
Set User |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
USR |
|
|
Get User |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get User Response |
A |
USR |
|
|
Get User Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
USR |
|
|
|
Clear User |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
USR |
|
0x20 |
Operating Event Notification |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
[NOT] |
|
|
0x21 |
Programming Event Notification |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
[NOT] |
|
|
0x22 |
Set Credential |
Client ⇒ Server |
Set Credential Response |
T A |
USR |
|
0x23 |
Set Credential Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
USR |
|
|
0x24 |
Get Credential Status |
Client ⇒ Server |
Get Credential Status Response |
A |
USR |
|
0x25 |
Get Credential Status Response |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
USR |
|
|
0x26 |
Clear Credential |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
USR |
|
0x27 | Unbolt Door | Client ⇒ Server | Y | T O | UBOLT |
5.2.4.1.
5.2.7.1.
Lock
Door
Command
This
command
causes
the
lock
device
to
lock
the
door.
This
command
includes
an
optional
code
for
the
lock.
The
door
lock
MAY
require
a
PIN
depending
on
the
value
of
the
[Require
PIN
for
Remote
Operation
attribute].
RequirePINForRemoteOperation
attribute
.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PINCode PIN/RFID Code† |
octstr |
[COTA & PIN] |
† The PIN/RFID Code is an obsolete field name, use PINCode instead.
5.2.4.1.1.
5.2.7.1.1.
PINCode
Field
If the RequirePINforRemoteOperation attribute is True then PINCode field SHALL be provided and the door lock SHALL NOT grant access if it is not provided.
If the PINCode field is provided, the door lock SHALL verify PINCode before granting access regardless of the value of RequirePINForRemoteOperation attribute.
When the PINCode field is provided an invalid PIN will count towards the WrongCodeEntryLimit and the UserCodeTemporaryDisableTime will be triggered if the WrongCodeEntryLimit is exceeded. The lock SHALL ignore any attempts to lock/unlock the door until the UserCodeTemporaryDisableTime expires.
5.2.4.2.
5.2.7.2.
Unlock
Door
Command
This
command
causes
the
lock
device
to
unlock
the
door.
This
command
includes
an
optional
code
for
the
lock.
The
door
lock
MAY
require
a
code
depending
on
the
value
of
the
[Require
PIN
for
Remote
Operation
attribute].
RequirePINForRemoteOperation
attribute
.
Note: If the attribute AutoRelockTime is supported the lock will transition to the locked state when the auto relock time has expired.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PINCode PIN/RFID Code† |
octstr |
[COTA & PIN] |
† The PIN/RFID Code is an obsolete field name, use PINCode instead.
5.2.4.2.1.
5.2.7.2.1.
PINCode
Field
See PINCode Field .
5.2.4.3.
5.2.7.3.
Unlock
with
Timeout
Command
This command causes the lock device to unlock the door with a timeout parameter. After the time in seconds specified in the timeout field, the lock device will relock itself automatically. This timeout parameter is only temporary for this message transition and overrides the default relock time as specified in the AutoRelockTime attribute. If the door lock device is not capable of or does not want to support temporary Relock Timeout, it SHOULD NOT support this optional command.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Timeout |
uint16 |
M |
|||
|
1 |
PINCode PIN/RFID Code† |
octstr |
[COTA & PIN] |
† The PIN/RFID Code is an obsolete field name, use PINCode instead.
5.2.4.3.1.
5.2.7.3.1.
Timeout
Field
The timeout in seconds to wait before relocking the door lock. This value is independent of the AutoRelockTime attribute value.
5.2.4.3.2.
5.2.7.3.2.
PINCode
Field
See PINCode Field .
5.2.4.4.
5.2.7.4.
Get
Log
Record
Command
Request a log record. Log number is between 1 – [Number of Log Records Supported attribute]. If log number 0 is requested then the most recent log entry is returned.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Log Index |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
Log record format: The log record format is defined in the description of the Get Log Record Response command.
5.2.4.5.
5.2.7.5.
Get
Log
Record
Response
Command
Returns the specified log record. If an invalid log entry ID was requested, it is set to 0 and the most recent log entry will be returned.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Log Entry ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Timestamp |
epoch-s |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
Event Type |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
3 |
Source
|
uint8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
4 |
Event
ID/Alarm
Code
|
uint8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
5 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
6 |
PIN |
octstr |
M |
5.2.7.5.1.
Log
Entry
ID:
ID
Field
This is the index into the log table where this log entry is stored. If the log entry requested is 0, the most recent log is returned with the appropriate log entry ID.
5.2.7.5.2. Timestamp Field
Timestamp:
A
This
is
a
timestamp
for
all
events
and
alarms
on
the
door
lock
in
Epoch
Time
in
Seconds
with
local
time
offset
based
on
the
local
timezone
and
DST
offset
on
the
day
of
the
event.
5.2.7.5.3.
Event
Type:
Indicates
Type
Field
This indicates the type of event that took place on the door lock.
| Value | Name |
|---|---|
0
|
Operation |
|
1
|
Programming |
|
2
|
Alarm |
5.2.7.5.4. Source Field
Source:
A
This
is
a
source
value
where
available
sources
are:
are
(see
Operation
Event
Sources).
| Value | Name |
|---|---|
0x00
|
Keypad |
|
0x01
|
Remote |
|
0x02
|
Manual |
|
0x03
|
RFID |
|
0xFF
|
Indeterminate |
If
the
Event
type
is
0x02
(Alarm)
then
the
source
SHOULD
be
be,
but
does
not
have
to
be
0xff
0xFF
(Indeterminate).
5.2.7.5.5.
Event
ID:
A
one-byte
value
indicating
ID
Field
This indicates the type of event that took place on the door lock depending on the event code table provided for a given event type and source. See Operation Event Codes.
5.2.4.6.
5.2.7.6.
Set
PIN
Code
Command
Set a PIN Code into the lock.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
User Status |
uint8 |
X |
OccupiedEnabled |
M |
|
|
2 |
User Type |
enum8 |
X |
UnrestrictedUser |
M |
|
|
3 |
PIN |
octstr |
M |
User ID is between 0 - [# of PIN Users Supported attribute]. Only the values 1 (Occupied/Enabled) and 3 (Occupied/Disabled) are allowed for User Status.
Return status is a global status code or a cluster-specific status code from the DoorLockStatus table and SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Setting PIN code was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Setting PIN code failed. |
|
CONSTRAINT_ERROR |
Setting PIN code failed because User ID requested was out of range. |
|
DUPLICATE |
Setting PIN code failed because it would create a duplicate PIN code. |
5.2.4.7.
5.2.7.7.
Get
PIN
Code
Command
Retrieve a PIN Code. User ID is between 0 - [# of PIN Users Supported attribute].
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
5.2.4.8.
5.2.7.8.
Get
PIN
Code
Response
Command
Returns the PIN for the specified user ID.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
User Status |
uint8 |
X |
Available |
M |
|
|
2 |
User Type |
enum8 |
X |
M |
||
|
3 |
PIN Code |
octstr |
X |
empty |
M |
If the requested User ID is valid and the Code doesn’t exist, Get RFID Code Response SHALL have the following format:
User ID = requested User ID
UserStatus = 0 (available)
UserType = 0xFF (not supported)
PIN Code = 0 (zero length)
If the requested User ID is invalid, send Default Response with an error status. The error status SHALL be equal to CONSTRAINT_ERROR when User_ID is less than the max number of users supported, and NOT_FOUND if greater than or equal to the max number of users supported.
5.2.4.9.
5.2.7.9.
Clear
PIN
Code
Command
Clear a PIN code or all PIN codes.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
PINSlotIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfPINUsersSupported, 0xFFFE |
M |
† The User ID is an obsolete field name, use PINSlotIndex instead.
For each PIN Code cleared whose user doesn’t have a RFID Code or other credential type, then corresponding user record’s UserStatus value SHALL be set to Available, and UserType value SHALL be set to UnrestrictedUser and all schedules SHALL be cleared.
5.2.4.10.
5.2.7.10.
Clear
All
PIN
Codes
Command
Clear out all PINs on the lock.
Note: On the server, the clear all PIN codes command SHOULD have the same effect as the Clear PIN Code command with respect to the setting of user status, user type and schedules.
5.2.4.11.
5.2.7.11.
Set
User
Status
Command
Set the status of a user ID. User Status value of 0 is not allowed. In order to clear a user id, the Clear ID Command SHALL be used. For user status value please refer to User Status Value.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
User Status |
uint8 |
M |
5.2.4.12.
5.2.7.12.
Get
User
Status
Command
Get the status of a user.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
5.2.4.13.
5.2.7.13.
Get
User
Status
Response
Command
Returns the user status for the specified user ID. If the requested User ID is invalid, the Status field SHALL be set to FAILURE. If the command is successful, the Status field SHALL be set to SUCCESS.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
User Status |
enum8 |
M |
5.2.4.14.
5.2.7.14.
Set
Week
Day
Schedule
Command
Set a weekly repeating schedule for a specified user.
| Id |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
WeekDayIndex Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfWeekDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
||
|
2 |
DaysMask |
M |
||||
|
3 |
StartHour |
uint8 |
0 to 23 |
M |
||
|
4 |
StartMinute |
uint8 |
0 to 59 |
M |
||
|
5 |
EndHour |
uint8 |
0 to 23 |
M |
||
|
6 |
EndMinute |
uint8 |
0 to 59 |
M |
† The Schedule ID and User ID are obsolete field names, use WeekDayIndex and UserIndex instead, respectively.
The associated UserType MAY be changed to ScheduleRestrictedUser by the lock when a Week Day schedule is set.
Return status SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Setting Week Day schedule was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Some unexpected internal error occurred setting Week Day schedule. |
|
INVALID_COMMAND |
One or more fields violates constraints or is invalid. Door lock is unable to set Week Day schedule for more than one day in DaysMask map (e.g. need to use separate schedules for each day). |
5.2.4.15.
5.2.7.15.
Get
Week
Day
Schedule
Command
Retrieve the specific weekly schedule for the specific user.
|
|
Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
WeekDayIndex Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfWeekDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
† The Schedule ID and User ID are obsolete field names, use WeekDayIndex and UserIndex instead, respectively.
5.2.4.16.
5.2.7.16.
Get
Week
Day
Schedule
Response
Command
Returns the weekly repeating schedule data for the specified schedule index.
|
|
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
WeekDayIndex Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfWeekDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
||
|
2 |
Status |
enum8 |
desc |
SUCCESS |
M |
|
|
3 |
DaysMask |
O |
||||
|
4 |
StartHour |
uint8 |
0 to 23 |
O |
||
|
5 |
StartMinute |
uint8 |
0 to 59 |
O |
||
|
6 |
EndHour |
uint8 |
0 to 23 |
O |
||
|
7 |
EndMinute |
uint8 |
0 to 59 |
O |
† The Schedule ID and User ID are obsolete field names, use WeekDayIndex and UserIndex instead, respectively.
5.2.4.16.1.
5.2.7.16.1.
Status
Status SHALL be one of the following values:
-
SUCCESS if both WeekDayIndex and UserIndex are valid and there is a corresponding schedule entry.
-
INVALID_COMMAND if either WeekDayIndex and/or UserIndex values are not within valid range
-
NOT_FOUND if
both WeekDayIndex and UserIndex are within the valid range, however, there is notno corresponding schedule entryfound.found for WeekDayIndex. NOT_FOUND if no corresponding user entry found for UserIndex.
Only
if
the
status
If
this
field
is
SUCCESS
that
other
remaining
SUCCESS,
the
optional
fields
are
included.
for
this
command
SHALL
be
present.
For
other
(error)
status
values,
only
the
fields
up
to
the
status
field
SHALL
be
present.
5.2.4.17.
5.2.7.17.
Clear
Week
Day
Schedule
Command
Clear the specific weekly schedule or all weekly schedules for the specific user.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
WeekDayIndex Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfWeekDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser, 0xFE |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
† The Schedule ID and User ID are obsolete field names, use WeekDayIndex and UserIndex instead, respectively.
Return status SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Clearing Week Day schedule(s) was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Some unexpected internal error occurred clearing Week Day schedule. |
|
INVALID_COMMAND |
One or more fields violates constraints or is invalid. |
5.2.4.18.
5.2.7.18.
Set
Year
Day
Schedule
Command
Set a time-specific schedule ID for a specified user.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
YearDayIndex Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfYearDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
||
|
2 |
LocalStartTime |
epoch-s |
all |
M |
||
|
3 |
LocalEndTime |
epoch-s |
all |
M |
† The Schedule ID and User ID are obsolete field names, use YearDayIndex and UserIndex instead, respectively.
The associated UserType MAY be changed to ScheduleRestrictedUser by the lock when a Year Day schedule is set.
Return status SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Setting Year Day schedule was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Some unexpected internal error occurred setting Year Day schedule. |
|
INVALID_COMMAND |
One or more fields violates constraints or is invalid. |
5.2.4.19.
5.2.7.19.
Get
Year
Day
Schedule
Command
Retrieve the specific year day schedule for the specific schedule and user indexes.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
YearDayIndex Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfYearDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
† The Schedule ID and User ID are obsolete field names, use YearDayIndex and UserIndex instead, respectively.
5.2.4.20.
5.2.7.20.
Get
Year
Day
Schedule
Response
Command
Returns the year day schedule data for the specified schedule and user indexes.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
YearDayIndex Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfYearDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
||
|
2 |
Status |
enum8 |
desc |
SUCCESS |
M |
|
|
2 |
LocalStartTime |
epoch-s |
all |
|
|
|
|
3 |
LocalEndTime |
epoch-s |
all |
|
|
† The Schedule ID and User ID are obsolete field names, use YearDayIndex and UserIndex instead, respectively.
5.2.4.20.1.
5.2.7.20.1.
Status
Status SHALL be one of the following values:
-
SUCCESS if both YearDayIndex and UserIndex are valid and there is a corresponding schedule entry.
-
INVALID_COMMAND if either YearDayIndex and/or UserIndex values are not within valid range
-
NOT_FOUND if
both YearDayIndex and UserIndex are within the valid range, however, there is notno corresponding schedule entryfound.found for YearDayIndex. NOT_FOUND if no corresponding user entry found for UserIndex.
All
If
this
field
is
SUCCESS,
the
optional
fields
for
this
command
SHALL
be
included
irrespective
of
the
value
of
the
Status
field.
present.
For
error
other
(error)
status
values,
only
the
LocalStartTime
and
LocalEndTime
fields
up
to
the
status
field
SHALL
be
set
to
null.
present.
5.2.4.20.2.
5.2.7.20.2.
LocalStartTime
The starting time for the Year Day schedule in Epoch Time in Seconds with local time offset based on the local timezone and DST offset on the day represented by the value. This SHALL be null if the schedule is not set for the YearDayIndex and UserIndex provided.
5.2.4.20.3.
5.2.7.20.3.
LocalEndTime
The ending time for the Year Day schedule in Epoch Time in Seconds with local time offset based on the local timezone and DST offset on the day represented by the value. LocalEndTime SHALL be greater than LocalStartTime. This SHALL be null if the schedule is not set for the YearDayIndex and UserIndex provided.
5.2.4.21.
5.2.7.21.
Clear
Year
Day
Schedule
Command
Clears the specific year day schedule or all year day schedules for the specific user.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
YearDayIndex Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfYearDaySchedulesSupportedPerUser, 0xFE |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
† The Schedule ID and User ID are obsolete field names, use YearDayIndex and UserIndex instead, respectively.
Return status SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Clearing Year Day schedule(s) was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Some unexpected internal error occurred clearing Year Day schedule. |
|
INVALID_COMMAND |
One or more fields violates constraints or is invalid. |
5.2.4.22.
5.2.7.22.
Set
Holiday
Schedule
Command
Set the holiday Schedule by specifying local start time and local end time with respect to any Lock Operating Mode.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
HolidayIndex Holiday Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfHolidaySchedulesSupported |
M |
||
|
1 |
LocalStartTime |
epoch-s |
all |
M |
||
|
2 |
LocalEndTime |
epoch-s |
all |
M |
||
|
3 |
OperatingMode |
all |
M |
† The Holiday Schedule ID is an obsolete field name, use HolidayIndex instead.
Return status SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Setting Holiday schedule was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Some unexpected internal error occurred setting Holiday schedule. |
|
INVALID_COMMAND |
One or more fields violates constraints or is invalid. |
5.2.4.22.1.
5.2.7.22.1.
LocalStartTime
The starting time for the Holiday Day schedule in Epoch Time in Seconds with local time offset based on the local timezone and DST offset on the day represented by the value.
5.2.4.23.
5.2.7.23.
Get
Holiday
Schedule
Command
Get the holiday schedule for the specified index.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
HolidayIndex Holiday Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfHolidaySchedulesSupported |
M |
† The Holiday Schedule ID is an obsolete field name, use HolidayIndex instead.
5.2.4.24.
5.2.7.24.
Get
Holiday
Schedule
Response
Command
Returns the Holiday Schedule Entry for the specified Holiday ID.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
HolidayIndex Holiday Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfHolidaySchedulesSupported |
M |
||
|
1 |
Status |
enum8 |
desc |
SUCCESS |
M |
|
|
2 |
LocalStartTime |
epoch-s |
all |
X |
O |
|
|
3 |
Local End Time |
epoch-s |
all |
X |
O |
|
|
4 |
OperatingMode |
all |
X |
O |
† The Holiday Schedule ID is an obsolete field name, use HolidayIndex instead.
5.2.4.24.1.
5.2.7.24.1.
Status
Status SHALL be one of the following values:
-
FAILURE if the attribute NumberOfHolidaySchedulesSupported is zero.
-
SUCCESS if the HolidayIndex is valid and there is a corresponding schedule entry.
-
INVALID_COMMAND if the HolidayIndex is not within valid range
-
NOT_FOUND if the HolidayIndex is within the valid range, however, there is not corresponding schedule entry found.
Only
if
the
status
If
this
field
is
SUCCESS
that
other
remaining
SUCCESS,
the
optional
fields
are
included.
for
this
command
SHALL
be
present.
For
other
(error)
status
values,
only
the
fields
up
to
the
status
field
SHALL
be
present.
5.2.4.24.2.
5.2.7.24.2.
LocalStartTime
The starting time for the Holiday schedule in Epoch Time in Seconds with local time offset based on the local timezone and DST offset on the day represented by the value. This SHALL be null if the schedule is not set for the HolidayIndex provided.
5.2.4.24.3.
5.2.7.24.3.
LocalEndTime
The ending time for the Holiday schedule in Epoch Time in Seconds with local time offset based on the local timezone and DST offset on the day represented by the value. LocalEndTime SHALL be greater than LocalStartTime. This SHALL be null if the schedule is not set for the HolidayIndex provided.
5.2.4.25.
5.2.7.25.
Clear
Holiday
Schedule
Command
Clears the holiday schedule or all holiday schedules.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
HolidayIndex Holiday Schedule ID† |
uint8 |
1 to NumberOfHolidaySchedulesSupported, 0xFE |
M |
† The Holiday Schedule ID is an obsolete field name, use HolidayIndex instead.
5.2.4.26.
5.2.7.26.
Set
User
Type
Command
Set the user type for a specified user.
For user type value please refer to User Type Value.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
User Type |
enum8 |
M |
If UserType is currently YearDayScheduleUser, WeekDayScheduleUser, or ScheduleRestrictedUser and the new UserType is UnrestrictedUser then all existing Year Day and/or Week Day schedules SHALL be ignored or disabled (if this transition is supported by the door lock). If UserType is ScheduleRestrictedUser and the new UserType is ScheduleRestrictedUser then all existing Year Day and/or Week Day schedules SHALL be applied or enabled.
Return status SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Setting User Type was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Some unexpected internal error occurred setting User Type. |
|
INVALID_COMMAND |
One or more fields violates constraints or is invalid. Door lock is unable to switch from restricted to unrestricted user (e.g. need to clear schedules to switch). |
5.2.4.27.
5.2.7.27.
Get
User
Type
Command
Retrieve the user type for a specific user.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
5.2.4.28.
5.2.7.28.
Get
User
Type
Response
Command
Returns the user type for the specified user ID. If the requested User ID is invalid, send Default Response with an error status equal to FAILURE.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
User Type |
enum8 |
M |
5.2.4.29.
5.2.7.29.
Set
RFID
Code
Command
Set an ID for RFID access into the lock.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
User Status |
uint8 |
X |
OccupiedEnabled |
M |
|
|
2 |
User Type |
enum8 |
X |
UnrestrictedUser |
M |
|
|
3 |
RFID Code |
octstr |
M |
User ID : Between 0 - [# of RFID Users Supported attribute]. Only the values 1 (Occupied/Enabled) and 3 (Occupied/Disabled) are allowed for User Status.
User Status: Used to indicate what the status is for a specific user ID. The values are according to “Set PIN” while not all are supported.
| Value | User Status Byte | Conformance |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Occupied / Enabled (Access Given) |
M |
|
3 |
Occupied / Disabled |
M |
User Type: The values are the same as used for “Set PIN Code.”
Return status is a global status code or a cluster-specific status code from the DoorLockStatus table and SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Setting RFID code was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Setting RFID code failed. |
|
CONSTRAINT_ERROR |
Setting RFID code failed because User ID requested was out of range. |
|
DUPLICATE |
Setting RFID code failed because it would create a duplicate RFID code. |
5.2.4.30.
5.2.7.30.
Get
RFID
Code
Command
Retrieve an RFID code. User ID is between 0 - [# of RFID Users Supported attribute].
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
5.2.4.31.
5.2.7.31.
Get
RFID
Code
Response
Command
Returns the RFID code for the specified user ID.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
User Status |
enum8 |
X |
Available |
M |
|
|
2 |
User Type |
enum8 |
X |
M |
||
|
3 |
RFID Code |
octstr |
X |
empty |
M |
If the requested User ID is valid and the Code doesn’t exist, Get RFID Code Response SHALL have the following format:
User ID = requested User ID
UserStatus = 0 (available)
UserType = 0xFF (not supported)
RFID Code = 0 (zero length)
If
requested
User
ID
is
invalid,
send
Default
Response
with
an
error
status.
The
error
status
shall
SHALL
be
equal
to
CONSTRAINT_ERROR
when
User_ID
is
less
than
the
max
number
of
users
supported,
and
NOT_FOUND
if
greater
than
or
equal
to
the
max
number
of
users
supported.
5.2.4.32.
5.2.7.32.
Clear
RFID
Code
Command
Clear an RFID code or all RFID codes.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
RFIDSlotIndex User ID† |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfRFIDUsersSupported, 0xFFFE |
M |
† The User ID is an obsolete field name, use RFIDSlotIndex instead.
For each RFID Code cleared whose user doesn’t have a PIN Code or other credential type, then the corresponding user record’s UserStatus value SHALL be set to Available, and UserType value SHALL be set to UnrestrictedUser and all schedules SHALL be cleared.
5.2.4.33.
5.2.7.33.
Clear
All
RFID
Codes
Command
Clear out all RFIDs on the lock. If you clear all RFID codes and this user didn’t have a PIN code, the user status has to be set to "0 Available", the user type has to be set to the default value, and all schedules which are supported have to be set to the default values.
5.2.4.34.
5.2.7.34.
Set
User
Command
Set User into the lock.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
OperationType |
Add, Modify |
M |
|||
|
1 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
||
|
2 |
UserName |
string |
max 10 |
X |
empty |
M |
|
3 |
UserUniqueID |
uint32 |
all |
X |
0xFFFFFFFF |
M |
|
4 |
UserStatus |
OccupiedEnabled, OccupiedDisabled |
X |
OccupiedEnabled |
M |
|
|
5 |
UserType |
UnrestrictedUser, NonAccessUser, ForcedUser, DisposableUser, ExpiringUser, ScheduleRestrictedUser, RemoteOnlyUser |
X |
UnrestrictedUser |
M |
|
|
6 |
CredentialRule |
|
X |
Single |
M |
Fields used for different use cases:
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
|
Create a new user record |
CreatorFabricIndex and LastModifiedFabricIndex in the new user record SHALL be set to the accessing fabric index.
A
LockUserChange
event
SHALL
be
|
|
Modify an existing user record |
CreatorFabricIndex SHALL NOT be changed in the user record. LastModifiedFabricIndex in the new user record SHALL be set to the accessing fabric index.
A
LockUserChange
event
SHALL
be
|
Return status is a global status code or a cluster-specific status code from the DoorLockStatus table and SHALL be one of the following values:
-
SUCCESS, if setting User was successful.
-
FAILURE, if some unexpected internal error occurred setting User.
-
OCCUPIED, if OperationType is Add and UserIndex points to an occupied slot.
-
INVALID_COMMAND, if one or more fields violate constraints or are invalid or if OperationType is Modify and UserIndex points to an available slot.
5.2.4.34.1.
5.2.7.34.1.
UserName
A string to use as a human readable identifier for the user.
If UserName is null then:
-
If the OperationType is Add, the UserName in the resulting user record SHALL be set to an empty string.
-
If the OperationType is Modify, the UserName in the user record SHALL NOT be changed from the current value.
If UserName is not null, the UserName in the user record SHALL be set to the provided value.
5.2.4.34.2.
5.2.7.34.2.
UserUniqueID
A fabric assigned number to use for connecting this user to other users on other devices from the fabric’s perspective.
If UserUniqueID is null then:
-
If the OperationType is Add, the UserUniqueID in the resulting user record SHALL be set to default value specified above.
-
If the OperationType is Modify, the UserUniqueID in the user record SHALL NOT be changed from the current value.
If UserUniqueID is not null, the UserUniqueID in the user record SHALL be set to the provided value.
5.2.4.34.3.
5.2.7.34.3.
UserStatus
A UserStatus to assign to this user when created or modified.
If UserStatus is null then:
-
If the OperationType is Add, the UserStatus in the resulting user record SHALL be set to default value specified above.
-
If the OperationType is Modify, the UserStatus in the user record SHALL NOT be changed from the current value.
If UserStatus is not null, the UserStatus in the user record SHALL be set to the provided value.
5.2.4.34.4.
5.2.7.34.4.
UserType
A UserType to assign to this user when created or modified.
If UserType is null then:
-
If the OperationType is Add, the UserType in the resulting user record SHALL be set to default value specified above.
-
If the OperationType is Modify, the UserType in the user record SHALL NOT be changed from the current value.
If UserType is not null, the UserType in the user record SHALL be set to the provided value.
5.2.4.34.5.
5.2.7.34.5.
CredentialRule
The CredentialRule to use for this user.
The valid CredentialRule enumeration values depends on the bits in the CredentialRulesSupport map. Each bit in the map identifies a valid CredentialRule that can be used.
If CredentialRule is null then:
-
If the OperationType is Add, the CredentialRule in the resulting user record SHALL be set to default value specified above.
-
If the OperationType is Modify, the CredentialRule in the user record SHALL NOT be changed from the current value.
If CredentialRule is not null, the CredentialRule in the user record SHALL be set to the provided value.
5.2.4.35.
5.2.7.35.
Get
User
Command
Retrieve User.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
An InvokeResponse command SHALL be sent with an appropriate error (e.g. FAILURE, INVALID_COMMAND, etc.) as needed otherwise the Get User Response Command SHALL be sent implying a status of SUCCESS.
5.2.4.36.
5.2.7.36.
Get
User
Response
Command
Returns the User for the specified UserIndex.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserName |
string |
max 10 |
X |
empty |
M |
|
2 |
UserUniqueID |
uint32 |
all |
X |
0 |
M |
|
3 |
UserStatus |
all |
X |
Available |
M |
|
|
4 |
UserType |
all |
X |
UnrestrictedUser |
M |
|
|
5 |
CredentialRule |
|
X |
Single |
M |
|
|
6 |
Credentials |
list[ CredentialStruct ] |
0 to NumberOfCredentialsSupportedPerUser |
X |
M |
|
|
7 |
CreatorFabricIndex |
fabric-idx |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
8 |
LastModifiedFabricIndex |
fabric-idx |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
9 |
NextUserIndex |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
X |
M |
If the requested UserIndex is valid and the UserStatus is Available for the requested UserIndex then UserName, UserUniqueID, UserStatus, UserType, CredentialRule, Credentials, CreatorFabricIndex, and LastModifiedFabricIndex SHALL all be null in the response.
5.2.4.36.1.
5.2.7.36.1.
CreatorFabricIndex
The
user’s
creator
fabric
index.
CreatorFabricIndex
SHALL
be
null
if
UserStatus
is
set
to
Available
or
when
the
creator
fabric
cannot
be
determined
(for
example,
when
user
was
created
outside
the
Interaction
Model)
and
SHALL
NOT
be
null
otherwise.
This
value
SHALL
be
set
to
0
if
the
original
creator
fabric
was
deleted.
5.2.4.36.2.
5.2.7.36.2.
LastModifiedFabricIndex
The
user’s
last
modifier
fabric
index.
LastModifiedFabricIndex
SHALL
be
null
if
UserStatus
is
set
to
Available
or
when
the
modifier
fabric
cannot
be
determined
(for
example,
when
user
was
modified
outside
the
Interaction
Model)
and
SHALL
NOT
be
null
otherwise.
This
value
SHALL
be
set
to
0
if
the
last
modifier
fabric
was
deleted.
5.2.4.36.3.
5.2.7.36.3.
NextUserIndex
The next occupied UserIndex in the database which is useful for quickly identifying occupied user slots in the database. This SHALL NOT be null if there is at least one occupied entry after the requested UserIndex in the User database and SHALL be null if there are no more occupied entries.
5.2.4.37.
5.2.7.37.
Clear
User
Command
Clears a User or all Users.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported, 0xFFFE |
M |
For each User to clear, all associated credentials (e.g. PIN, RFID, fingerprint, etc.) SHALL be cleared and the User entry values SHALL be reset to their default values (e.g. UserStatus SHALL be Available, UserType SHALL be UnrestrictedUser) and all associated schedules SHALL be cleared.
A LockUserChange event with the provided UserIndex SHALL be generated after successfully clearing users.
5.2.4.38.
5.2.7.38.
Operation
Event
Notification
Command
The door lock server sends out operation event notification when the event is triggered by the various event sources. The specific operation event will only be sent out if the associated bitmask is enabled in the various attributes in the Event Masks Attribute Set.
All events are optional.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Operation Event Source |
uint8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Operation Event Code |
uint8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
2 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
3 |
PIN |
octstr |
M |
|||
|
4 |
LocalTime |
epoch-s |
all |
M |
||
|
5 |
Data |
string |
O |
5.2.4.38.1.
5.2.7.38.1.
Operation
Event
Sources
This field indicates where the event was triggered from.
| Value | Source |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Keypad |
|
1 |
Remote |
|
2 |
Manual |
|
3 |
RFID |
|
0xFF |
Indeterminate |
5.2.4.38.2.
5.2.7.38.2.
Operation
Event
Codes
The door lock optionally sends out notifications (if they are enabled) whenever there is a significant operational event on the lock. When combined with a source from the Event Source table above, the following operational event codes constitute an event on the door lock that can be both logged and sent to a bound device using the Operation Event Notification command.
Not all operation event codes are applicable to each of the event source. The following table marks each event code with “A” if the event code is applicable to the event source.
| Value | Name | Conformance | Applicable | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Keypad |
Remote |
Manual |
RFID |
|||
|
0 |
UnknownOrMfgSpecific |
O |
A |
A |
A |
A |
|
1 |
Lock |
O |
A |
A |
A |
A |
|
2 |
Unlock |
O |
A |
A |
A |
A |
|
3 |
LockFailureInvalidPINorRFID |
O |
A |
A |
A |
|
|
4 |
LockFailureInvalidSchedule |
O |
A |
A |
A |
|
|
5 |
UnlockFailureInvalidPINorRFID |
O |
A |
A |
A |
|
|
6 |
UnlockFailureInvalidSchedule |
O |
A |
A |
A |
|
|
7 |
OneTouchLock |
O |
A |
|||
|
8 |
KeyLock |
O |
A |
|||
|
9 |
KeyUnlock |
O |
A |
|||
|
10 |
AutoLock |
O |
A |
|||
|
11 |
ScheduleLock |
|
A |
|||
|
12 |
ScheduleUnlock |
|
A |
|||
|
13 |
Manual Lock (Key or Thumbturn) |
O |
A |
|||
|
14 |
Manual Unlock (Key or Thumbturn) |
O |
A |
|||
|
15 |
Non-access User Operation Event |
O |
A |
|||
5.2.4.38.5.
5.2.7.38.5.
LocalTime
The time when the event was triggered in Epoch Time in Seconds with local time offset based on the local timezone and DST offset on the day represented by the value. If time is not supported, the field SHALL be populated with default not used value 0xFFFFFFFF.
5.2.4.38.6.
5.2.7.38.6.
Data
The operation event notification command contains a variable string, which can be used to pass data associated with a particular event. Generally this field will be left empty. However, manufacturer can choose to use this field to store/display manufacturer-specific information.
5.2.4.38.7.
5.2.7.38.7.
Keypad
Operation
Event
Notification
Keypad Operation Event Notification feature is enabled by setting the associated bitmasks in the [Keypad Operation Event Mask attribute].
5.2.4.38.8.
5.2.7.38.8.
Remote
Operation
Event
Notification
Remote Operation Event Notification feature is enabled by setting the associated bitmasks in the [Remote Operation Event Mask attribute].
5.2.4.39.
5.2.7.39.
Programming
Event
Notification
Command
The door lock server sends out a programming event notification whenever a programming event takes place on the door lock.
As with operational events, all programming events can be turned on and off by flipping bits in the associated event mask.
The programming event notification command includes an optional string of data that can be used by the manufacturer to pass some manufacturer-specific information if that is required.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Program Event Source |
uint8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
Program Event Code |
uint8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
2 |
User ID |
uint16 |
desc |
M |
||
|
3 |
PIN |
octstr |
M |
|||
|
4 |
User Type |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
5 |
User Status |
enum8 |
desc |
M |
||
|
6 |
LocalTime |
epoch-s |
all |
M |
||
|
7 |
Data |
string |
O |
5.2.4.39.1.
5.2.7.39.1.
Operation
Event
Sources
This field indicates where the event was triggered from.
| Value | Source |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Keypad |
|
1 |
Remote |
|
2 |
Reserved (Manual in Operation Event) |
|
3 |
RFID |
|
0xFF |
Indeterminate |
5.2.4.39.2.
5.2.7.39.2.
Programming
Event
Codes
The door lock optionally sends out notifications (if they are enabled) whenever there is a significant programming event on the lock. When combined with a source from the Event Source table above, the following programming event codes constitute an event on the door lock that can be both logged and sent to a bound device using the Programming Event Notification command.
Not all event codes are applicable to each of the event source. The following table marks each event code with “A” if the event code is applicable to the event source.
| Value | Programming Event Code | Keypad | Remote | RFID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
UnknownOrMfgSpecific |
A |
A |
A |
|
1 |
ProgrammingCodeChanged |
A |
||
|
2 |
PINCodeAdded |
A |
A |
|
|
3 |
PINCodeCleared |
A |
A |
|
|
4 |
PINCodeChanged |
A |
A |
|
|
5 |
RFIDCodeAdded |
A |
||
|
6 |
RFIDCodeCleared |
A |
5.2.4.39.5.
5.2.7.39.5.
User
Type
The User Type that is associated with the User ID who performed the event
5.2.4.39.6.
5.2.7.39.6.
User
Status
The User Status that is associated with the User ID who performed the event
5.2.4.39.7.
5.2.7.39.7.
LocalTime
The time when the event was triggered in Epoch Time in Seconds with local time offset based on the local timezone and DST offset on the day represented by the value. If time is not supported, the field SHALL be populated with default not used value 0xFFFFFFFF.
5.2.4.39.8.
5.2.7.39.8.
Data
The programming event notification command contains a variable string, which can be used to pass data associated with a particular event. Generally this field will be left empty. However, manufacturer can choose to use this field to store/display manufacturer-specific information.
5.2.4.39.9.
5.2.7.39.9.
Keypad
Programming
Event
Notification
Keypad Programming Event Notification feature is enabled by setting the associated bitmasks in the [Keypad Programming Event Mask attribute].
5.2.4.40.
5.2.7.40.
Set
Credential
Command
Set a credential (e.g. PIN, RFID, Fingerprint, etc.) into the lock for a new user, existing user, or ProgrammingUser.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
OperationType |
Add, Modify |
M |
|||
|
1 |
Credential |
M |
||||
|
2 |
CredentialData |
octstr |
desc |
M |
||
|
3 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
X |
M |
|
|
4 |
UserStatus |
OccupiedEnabled, OccupiedDisabled |
X |
OccupiedEnabled |
M |
|
|
5 |
UserType |
UnrestrictedUser, ProgrammingUser, NonAccessUser, ForcedUser, DisposableUser, ExpiringUser, RemoteOnlyUser |
X |
UnrestrictedUser |
M |
Fields used for different use cases:
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
|
Create a new credential and a new user record |
CreatorFabricIndex and LastModifiedFabricIndex in new user and credential records SHALL be set to the accessing fabric index.
A
LockUserChange
event
SHALL
be
|
|
Add a new credential to existing user record |
CreatorFabricIndex SHALL NOT be changed in the user record. LastModifiedFabricIndex in the user record SHALL be set to the accessing fabric index. CreatorFabricIndex and LastModifiedFabricIndex in the new credential record SHALL be set to the accessing fabric index.
A
LockUserChange
event
SHALL
be
|
|
Modify credential for an existing user record |
CreatorFabricIndex SHALL NOT be changed in user and credential records. LastModifiedFabricIndex in user and credential records SHALL be set to the accessing fabric index.
A
LockUserChange
event
SHALL
be
|
|
Modify credential for a Programming User |
CreatorFabricIndex SHALL NOT be changed in the credential record. LastModifiedFabricIndex in the credential record SHALL be set to the accessing fabric index.
A
LockUserChange
event
SHALL
be
|
5.2.4.40.2.
5.2.7.40.2.
Credential
A credential structure that contains the CredentialTypeEnum and the credential index (if applicable or 0 if not) to set.
5.2.4.40.3.
5.2.7.40.3.
CredentialData
The credential data to set for the credential being added or modified. The length of the credential data SHALL conform to the limits of the CredentialType specified in the Credential structure otherwise an INVALID_COMMAND status SHALL be returned in the Set Credential Response Command .
5.2.4.40.4.
5.2.7.40.4.
UserIndex
The user index to the user record that corresponds to the credential being added or modified. This SHALL be null if OperationType is add and a new credential and user is being added at the same time.
5.2.4.41.
5.2.7.41.
Set
Credential
Response
Command
Returns the status for setting the specified credential.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
status |
desc |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
X |
0 |
M |
|
2 |
NextCredentialIndex |
uint16 |
desc |
X |
O |
5.2.4.41.1.
5.2.7.41.1.
Status
Status comes from the DoorLockStatus table and SHALL be one of the following values:
-
SUCCESS, if setting user credential was successful.
-
FAILURE, if some unexpected internal error occurred setting user credential.
-
OCCUPIED, if OperationType is Add and CredentialIndex in Credential structure points to an occupied slot.
-
OCCUPIED, if OperationType is Modify and CredentialIndex in Credential structure does not match the CredentialIndex that is already associated with the provided UserIndex.
-
DUPLICATE, if CredentialData provided is a duplicate of another credential (e.g. duplicate PIN code).
-
RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED, if OperationType is Add and the user referred to by UserIndex already has NumberOfCredentialsSupportedPerUser credentials associated.
-
INVALID_COMMAND, if one or more fields violate constraints or are invalid or if OperationType is Modify and UserIndex points to an available slot.
5.2.4.41.2.
5.2.7.41.2.
UserIndex
The user index that was created with the new credential. If the status being returned is not success then this SHALL be null. This SHALL be null if OperationType was Modify; if the OperationType was Add and a new User was created this SHALL NOT be null and SHALL provide the UserIndex created. If the OperationType was Add and an existing User was associated with the new credential then this SHALL be null.
5.2.4.41.3.
5.2.7.41.3.
NextCredentialIndex
The next available index in the database for the credential type set, which is useful for quickly identifying available credential slots in the database. This SHALL NOT be null if there is at least one available entry after the requested credential index in the corresponding database and SHALL be null if there are no more available entries. The NextCredentialIndex reported SHALL NOT exceed the maximum number of credentials for a particular credential type.
5.2.4.42.
5.2.7.42.
Get
Credential
Status
Command
Retrieve the status of a particular credential (e.g. PIN, RFID, Fingerprint, etc.) by index.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Credential |
M |
An InvokeResponse command SHALL be sent with an appropriate error (e.g. FAILURE, INVALID_COMMAND, etc.) as needed otherwise the Get Credential Status Response Command SHALL be sent implying a status of SUCCESS.
5.2.4.42.1.
5.2.7.42.1.
Credential
A credential structure that contains the CredentialTypeEnum and the credential index (if applicable or 0 if not) to retrieve the status for.
5.2.4.43.
5.2.7.43.
Get
Credential
Status
Response
Command
Returns the status for the specified credential.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
CredentialExists |
bool |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
1 to NumberOfTotalUsersSupported |
X |
M |
|
|
2 |
CreatorFabricIndex |
fabric-idx |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
3 |
LastModifiedFabricIndex |
fabric-idx |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
4 |
NextCredentialIndex |
uint16 |
desc |
X |
O |
5.2.4.43.1.
5.2.7.43.1.
CredentialExists
A boolean value indicating the requested credential type and index exists and is populated for a given user index.
5.2.4.43.2.
5.2.7.43.2.
UserIndex
The
credential’s
corresponding
user
index
value
if
the
credential
exists.
If
CredentialType
requested
was
ProgrammingUser
ProgrammingPIN
then
UserIndex
SHALL
be
null;
otherwise,
UserIndex
SHALL
be
null
if
CredentialExists
is
set
to
False
and
SHALL
NOT
be
null
if
CredentialExists
is
set
to
True.
5.2.4.43.3.
5.2.7.43.3.
CreatorFabricIndex
The
credential’s
creator
fabric
index.
CreatorFabricIndex
SHALL
be
null
if
CredentialExists
is
set
to
False
or
when
the
creator
fabric
cannot
be
determined
(for
example,
when
credential
was
created
outside
the
Interaction
Model)
and
SHALL
NOT
be
null
otherwise.
This
value
SHALL
be
set
to
0
if
the
original
creator
fabric
was
deleted.
5.2.4.43.4.
5.2.7.43.4.
LastModifiedFabricIndex
The
credential’s
last
modifier
fabric
index.
LastModifiedFabricIndex
SHALL
be
null
if
CredentialExists
is
set
to
False
or
when
the
modifier
fabric
cannot
be
determined
(for
example,
when
credential
was
modified
outside
the
Interaction
Model)
and
SHALL
NOT
be
null
otherwise.
This
value
SHALL
be
set
to
0
if
the
last
modifier
fabric
was
deleted.
5.2.4.43.5.
5.2.7.43.5.
NextCredentialIndex
The next occupied index in the database for the credential type requested, which is useful for quickly identifying occupied credential slots in the database. This SHALL NOT be null if there is at least one occupied entry after the requested credential index in the corresponding database and SHALL be null if there are no more occupied entries. The NextCredentialIndex reported SHALL NOT exceed the maximum number of credentials for a particular credential type.
5.2.4.44.
5.2.7.44.
Clear
Credential
Command
Clear one, one type, or all credentials except ProgrammingPIN credential.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Credential |
desc |
X |
M |
Fields used for different use cases:
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
|
Clear a single credential |
A
LockUserChange
event
SHALL
be
|
|
Clear all credentials of one type |
A
single
LockUserChange
event
SHALL
be
|
|
Clear all credentials of all types |
The ProgrammingPIN credential SHALL NOT be cleared.
|
For each credential cleared whose user doesn’t have another valid credential, the corresponding user record SHALL be reset back to default values and its UserStatus value SHALL be set to Available and UserType value SHALL be set to UnrestrictedUser and all schedules SHALL be cleared. In this case a LockUserChange event SHALL be generated for the user being cleared.
Return status SHALL be one of the following values:
| Name |
|
|---|---|
|
SUCCESS |
Clearing credential(s) was successful. |
|
FAILURE |
Some unexpected internal error occurred clearing credential(s). |
|
INVALID_COMMAND |
One or more fields violate constraints or are invalid. |
5.2.4.44.1.
5.2.7.44.1.
Credential
A credential structure that contains the CredentialTypeEnum and the credential index (0xFFFE for all credentials or 0 if not applicable) to clear. This SHALL be null if clearing all credential types otherwise it SHALL NOT be null.
5.2.7.45. Unbolt Door Command
This command causes the lock device to unlock the door without pulling the latch. This command includes an optional code for the lock. The door lock MAY require a code depending on the value of the RequirePINForRemoteOperation attribute .
Note: If the attribute AutoRelockTime is supported, the lock will transition to the locked state when the auto relock time has expired.
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | PINCode | octstr | [COTA & PIN] |
5.2.7.45.1. PINCode Field
See PINCode Field .
5.2.5.
5.2.8.
Events
This cluster SHALL support these events:
| Id | Name | Priority | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
DoorLockAlarm |
CRITICAL |
V |
M |
|
1 |
DoorStateChange |
desc |
V |
DPS |
|
2 |
LockOperation |
desc |
V |
M |
|
3 |
LockOperationError |
desc |
V |
M |
|
4 |
LockUserChange |
INFO |
V |
USR |
The Events specified in this cluster are not intended to define the user experience. The events are only intended to define the metadata format used to notify any nodes that have subscribed for updates.
If the DoorState reported in the DoorStateChange event is not DoorClosed then the priority SHALL be CRITICAL; otherwise it MAY be INFO.
If the LockOperationType reported in the LockOperation event is Unlock or ForcedUserEvent then the priority SHALL be CRITICAL; otherwise it MAY be INFO.
If the OperationError reported in the LockOperationError event is DisabledUserDenied or the LockOperationType is Lock the priority SHALL be CRITICAL; otherwise it MAY be INFO.
5.2.5.1.
5.2.8.1.
DoorLockAlarm
Event
The door lock cluster provides several alarms which can be sent when there is a critical state on the door lock. The alarms available for the door lock cluster are listed in the AlarmCodeEnum section below.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
AlarmCode |
all |
M |
5.2.5.2.
5.2.8.2.
DoorStateChange
Event
The door lock server sends out a DoorStateChange event when the door lock door state changes.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
DoorState |
all |
M |
5.2.5.3.
5.2.8.3.
LockOperation
Event
The door lock server sends out a LockOperation event when the event is triggered by the various lock operation sources.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
LockOperationType |
all |
M |
|||
|
1 |
OperationSource |
all |
M |
|||
|
2 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
3 |
FabricIndex |
fabric-idx |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
4 |
SourceNode |
node-id |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
5 |
Credentials |
list[ CredentialStruct ] |
1 to NumberOfCredentialsSupportedPerUser |
X |
[USR] |
-
If the door lock server supports the Unbolt Door command, it SHALL generate a LockOperation event with LockOperationType set to Unlock after an Unbolt Door command succeeds.
If the door lock server supports the Unbolting Feature and an Unlock Door command is performed, it SHALL generate a LockOperation event with LockOperationType set to Unlatch when the unlatched state is reached and a LockOperation event with LockOperationType set to Unlock when the lock successfully completes the unlock → hold latch → release latch and return to unlock state operation.
If the command fails during holding or releasing the latch but after passing the unlocked state, the door lock server SHALL generate a LockOperationError event with LockOperationType set to Unlatch and a LockOperation event with LockOperationType set to Unlock.
If it fails before reaching the unlocked state, the door lock server SHALL generate only a LockOperationError event with LockOperationType set to Unlock.
Upon manual actuation, a door lock server that supports the Unbolting Feature :
SHALL generate a LockOperation event of LockOperationType Unlatch when it is actuated from the outside.
MAY generate a LockOperation event of LockOperationType Unlatch when it is actuated from the inside.
5.2.5.3.3.
5.2.8.3.3.
UserIndex
The lock UserIndex who performed the lock operation. This SHALL be null if there is no user index that can be determined for the given operation source. This SHALL NOT be null if a user index can be determined. In particular, this SHALL NOT be null if the operation was associated with a valid credential.
5.2.5.3.4.
5.2.8.3.4.
FabricIndex
The fabric index of the fabric that performed the lock operation. This SHALL be null if there is no fabric that can be determined for the given operation source. This SHALL NOT be null if the operation source is "Remote".
5.2.5.4.
5.2.8.4.
LockOperationError
Event
The door lock server sends out a LockOperationError event when a lock operation fails for various reasons.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
LockOperationType |
all |
M |
|||
|
1 |
OperationSource |
all |
M |
|||
|
2 |
OperationError |
all |
M |
|||
|
3 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
4 |
FabricIndex |
fabric-idx |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
5 |
SourceNode |
node-id |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
6 |
Credentials |
list[ CredentialStruct ] |
1 to NumberOfCredentialsSupportedPerUser |
X |
[USR] |
5.2.5.4.3.
5.2.8.4.3.
OperationError
The lock operation error triggered when the operation was performed.
5.2.5.4.4.
5.2.8.4.4.
UserIndex
The lock UserIndex who performed the lock operation. This SHALL be null if there is no user id that can be determined for the given operation source.
5.2.5.4.5.
5.2.8.4.5.
FabricIndex
The fabric index of the fabric that performed the lock operation. This SHALL be null if there is no fabric that can be determined for the given operation source. This SHALL NOT be null if the operation source is "Remote".
5.2.5.5.
5.2.8.5.
LockUserChange
Event
The door lock server sends out a LockUserChange event when a lock user, schedule, or credential change has occurred.
The data of this event SHALL contain the following information:
| Id | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
LockDataType |
all |
M |
|||
|
1 |
DataOperationType |
all |
M |
|||
|
2 |
OperationSource |
Unspecified, Keypad, Remote |
M |
|||
|
3 |
UserIndex |
uint16 |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
4 |
FabricIndex |
fabric-idx |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
5 |
SourceNode |
node-id |
all |
X |
M |
|
|
6 |
DataIndex |
uint16 |
all |
X |
M |
5.2.5.5.4.
5.2.8.5.4.
UserIndex
The lock UserIndex associated with the change (if any). This SHALL be null if there is no specific user associated with the data operation. This SHALL be 0xFFFE if all users are affected (e.g. Clear Users).
5.2.5.5.5.
5.2.8.5.5.
FabricIndex
The fabric index of the fabric that performed the change (if any). This SHALL be null if there is no fabric that can be determined to have caused the change. This SHALL NOT be null if the operation source is "Remote".
5.2.5.5.6.
5.2.8.5.6.
SourceNode
The Node ID that that performed the change (if any). The Node ID of the node that performed the change. This SHALL be null if there was no Node involved in the change. This SHALL NOT be null if the operation source is "Remote".
5.2.5.5.7.
5.2.8.5.7.
DataIndex
This is the index of the specific item that was changed (e.g. schedule, PIN, RFID, etc.) in the list of items identified by LockDataType. This SHALL be null if the LockDataType does not correspond to a list that can be indexed into (e.g. ProgrammingUser). This SHALL be 0xFFFE if all indices are affected (e.g. Clear PIN Code, Clear RFID Code, Clear Week Day Schedule, Clear Year Day Schedule, etc.).
5.2.6.
5.2.9.
Data
Types
5.2.6.1.
5.2.9.1.
AlarmCodeEnum
The Alarm Code enum SHALL indicate the alarm type. The data type of the Alarm Code enum is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
LockJammed |
M |
Locking Mechanism Jammed |
|
1 |
LockFactoryReset |
O |
Lock Reset to Factory Defaults |
|
3 |
LockRadioPowerCycled |
O |
Lock Radio Power Cycled |
|
4 |
WrongCodeEntryLimit |
[USR] |
Tamper Alarm - wrong code entry limit |
|
5 |
FrontEsceutcheonRemoved |
O |
Tamper Alarm - front escutcheon removed from main |
|
6 |
DoorForcedOpen |
[DPS] |
Forced Door Open under Door Locked Condition |
|
7 |
DoorAjar |
[DPS] |
Door ajar |
|
8 |
ForcedUser |
[USR] |
Force User SOS alarm |
5.2.6.2.
5.2.9.2.
CredentialRuleEnum
The CredentialRule enum used in various commands SHALL indicate the credential rule that can be applied to a particular user. The data type of the CredentialRule enum is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Single |
USR |
Only one credential is required for lock operation |
|
1 |
Dual |
[USR] |
Any two credentials are required for lock operation |
|
2 |
Tri |
[USR] |
Any three credentials are required for lock operation |
5.2.6.3.
5.2.9.3.
CredentialStruct
The CredentialStruct is used in LockOperation event and Get User Record Response command and SHALL indicate the credential types and their corresponding indices (if any) for the event or user record.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
CredentialType |
all |
M |
|||
|
1 |
CredentialIndex |
uint16 |
all |
0 |
M |
5.2.6.3.2.
5.2.9.3.2.
CredentialIndex
This is the index of the specific credential used to authorize the lock operation in the list of credentials identified by CredentialType (e.g. schedule, PIN, RFID, etc.). This SHALL be set to 0 if CredentialType is ProgrammingPIN or does not correspond to a list that can be indexed into.
5.2.6.4.
5.2.9.4.
CredentialTypeEnum
The Credential Type enum SHALL indicate the credential type. The data type of the Credential Type enum is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
ProgrammingPIN |
O |
Programming PIN code credential type |
|
1 |
PIN |
PIN |
PIN code credential type |
|
2 |
RFID |
RID |
RFID identifier credential type |
|
3 |
Fingerprint |
FGP |
Fingerprint identifier credential type |
|
4 |
FingerVein |
FGP |
Finger vein identifier credential type |
|
5 |
Face |
FACE |
Face identifier credential type |
5.2.6.5.
5.2.9.5.
DataOperationTypeEnum
The DataOperationType enum SHALL indicate the data operation performed. The data type of the DataOperationType enum is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Add |
M |
Data is being added or was added |
|
1 |
Clear |
M |
Data is being cleared or was cleared |
|
2 |
Modify |
M |
Data is being modified or was modified |
5.2.6.6.
5.2.9.6.
DaysMaskMap
The DaysMask field used in various commands and SHALL indicate the days of the week the Week Day schedule applies for. The data type of the DaysMask field is derived from map8.
| Bit |
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Sunday |
M |
|
1 |
Monday |
M |
|
2 |
Tuesday |
M |
|
3 |
Wednesday |
M |
|
4 |
Thursday |
M |
|
5 |
Friday |
M |
|
6 |
Saturday |
M |
5.2.6.7.
5.2.9.7.
DoorStateEnum
The DoorState enumeration SHALL indicate the current door state. The data type of the DoorState enum field is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
DoorOpen |
DPS |
Door state is open |
|
1 |
DoorClosed |
DPS |
Door state is closed |
|
2 |
DoorJammed |
[DPS] |
Door state is jammed |
|
3 |
DoorForcedOpen |
[DPS] |
Door state is currently forced open |
|
4 |
DoorUnspecifiedError |
[DPS] |
Door state is invalid for unspecified reason |
|
5 |
DoorAjar |
[DPS] |
Door state is ajar |
5.2.6.8.
5.2.9.8.
DoorLockStatus
The cluster-specific status codes for the Door Lock cluster are as follows:
| Value | Status Code |
|
|---|---|---|
|
2 |
DUPLICATE |
Entry would cause a duplicate credential/ID. |
|
3 |
OCCUPIED |
Entry would replace an occupied slot. |
5.2.6.9.
5.2.9.9.
LockDataTypeEnum
The LockDataType enum SHALL indicate the data type that is being or has changed. The data type of the DataType enum is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Unspecified |
O |
Unspecified or manufacturer specific lock user data added, cleared, or modified. |
|
1 |
ProgrammingCode |
O |
Lock programming PIN code was added, cleared, or modified. |
|
2 |
UserIndex |
M |
Lock user index was added, cleared, or modified. |
|
3 |
WeekDaySchedule |
WDSCH |
Lock user week day schedule was added, cleared, or modified. |
|
4 |
YearDaySchedule |
YDSCH |
Lock user year day schedule was added, cleared, or modified. |
|
5 |
HolidaySchedule |
HDSCH |
Lock holiday schedule was added, cleared, or modified. |
|
6 |
PIN |
PIN |
Lock user PIN code was added, cleared, or modified. |
|
7 |
RFID |
RID |
Lock user RFID code was added, cleared, or modified. |
|
8 |
Fingerprint |
FGP |
Lock user fingerprint was added, cleared, or modified. |
|
9 | FingerVein | FGP | Lock user finger-vein information was added, cleared, or modified. |
10 | Face | FACE | Lock user face information was added, cleared, or modified. |
5.2.6.10.
5.2.9.10.
LockOperationTypeEnum
The LockOperationType enumeration SHALL indicate the type of Lock operation performed. The data type of the LockOperationType enum field is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Lock |
M |
Lock operation |
|
1 |
Unlock |
M |
Unlock operation |
|
2 |
NonAccessUserEvent |
O |
Triggered by keypad entry for user with User Type set to Non Access User |
|
3 |
ForcedUserEvent |
O |
Triggered by using a user with UserType set to Forced User |
|
4 | Unlatch | M | Unlatch operation |
5.2.6.11.
5.2.9.11.
OperationErrorEnum
The OperationError enumeration SHALL indicate the error cause of the Lock/Unlock operation performed. The data type of the OperationError enum field is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Unspecified |
O |
Lock/unlock error caused by unknown or unspecified source |
|
1 |
InvalidCredential |
USR |
Lock/unlock error caused by invalid PIN, RFID, fingerprint or other credential |
|
2 |
DisabledUserDenied |
M |
Lock/unlock error caused by disabled USER or credential |
|
3 |
Restricted |
|
Lock/unlock error caused by schedule restriction |
|
4 |
InsufficientBattery |
O |
Lock/unlock error caused by insufficient battery power left to safely actuate the lock |
5.2.6.12.
5.2.9.12.
OperatingModeEnum
The OperatingMode enumeration SHALL indicate the lock operating mode. The data type of the OperatingMode enum field is derived from enum8.
The table below shows the operating mode and which interfaces are enabled, if supported, for each mode.
| Value | Name | Conformance | Keypad * | Remote * | RFID * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Normal |
M |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Vacation |
O |
|
|
|
|
2 |
Privacy |
O |
|
|
|
|
3 |
NoRemoteLockUnlock |
M |
|
|
|
|
4 |
Passage |
O |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
* Interface Operational: Yes, No or N/A
Note: For modes that disable the remote interface, the door lock SHALL respond to Lock, Unlock, Toggle, and Unlock with Timeout commands with a response status Failure and not take the action requested by those commands. The door lock SHALL NOT disable the radio or otherwise unbind or leave the network. It SHALL still respond to all other commands and requests.
5.2.6.12.2.
5.2.9.12.2.
Vacation
Only remote interaction is enabled. The keypad SHALL only be operable by the master user.
5.2.6.12.3.
5.2.9.12.3.
Privacy
This mode is only possible if the door is locked. Manual unlocking changes the mode to Normal operating mode. All external interaction with the door lock is disabled. This mode is intended to be used so that users, presumably inside the property, will have control over the entrance.
5.2.6.13.
5.2.9.13.
OperationSourceEnum
The OperationSource enumeration SHALL indicate the source of the Lock/Unlock operation performed. The data type of the OperationSource enum field is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Conformance |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Unspecified |
O |
Lock/unlock operation came from unspecified source |
|
1 |
Manual |
O |
Lock/unlock operation came from manual operation (key, thumbturn, handle, etc). |
|
2 |
ProprietaryRemote |
O |
Lock/unlock operation came from prioretary remote source (e.g. vendor app/cloud) |
|
3 |
Keypad |
O |
Lock/unlock operation came from keypad |
|
4 |
Auto |
O |
Lock/unlock operation came from lock automatically (e.g. relock timer) |
|
5 |
Button |
O |
Lock/unlock operation came from lock button (e.g. one touch or button) |
|
6 |
Schedule |
HDSCH |
Lock/unlock operation came from lock due to a schedule |
|
7 |
Remote |
M |
Lock/unlock operation came from remote node |
|
8 |
RFID |
RID |
Lock/unlock operation came from RFID card |
|
9 |
Biometric |
[USR] |
Lock/unlock operation came from biometric source (e.g. face, fingerprint/fingervein) |
5.2.6.14.
5.2.9.14.
PIN/RFID
Code
Format
The
PIN/RFID
codes
defined
in
this
specification
are
all
in
Octet
String
format.
The
first
octet
in
the
string
specifies
the
number
of
octets
contained
in
the
remaining
of
the
data
field
not
including
itself.
strings.
All value in the PIN/RFID code SHALL be ASCII encoded regardless if the PIN/RFID codes are number or characters. For example, code of “1, 2, 3, 4” SHALL be represented as 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34.
5.2.6.15.
5.2.9.15.
UserStatusEnum
The UserStatus enum used in various commands SHALL indicate what the status is for a specific user ID.
|
|
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Available |
M |
|
1 |
OccupiedEnabled |
M |
|
3 |
OccupiedDisabled |
O |
5.2.6.16.
5.2.9.16.
UserTypeEnum
The UserType enum used in various commands SHALL indicate what the type is for a specific user ID.
|
|
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
UnrestrictedUser |
M |
|
1 |
YearDayScheduleUser |
O |
|
2 |
WeekDayScheduleUser |
O |
|
3 |
ProgrammingUser |
O |
|
4 |
NonAccessUser |
O |
|
5 |
ForcedUser |
[USR] |
|
6 |
DisposableUser |
[USR] |
|
7 |
ExpiringUser |
[USR] |
|
8 |
ScheduleRestrictedUser |
|
|
|
RemoteOnlyUser |
USR & COTA & PIN |
5.2.6.16.1.
5.2.9.16.1.
UnrestrictedUser
User has access 24/7 provided proper PIN or RFID is supplied (e.g., owner).
5.2.6.16.2.
5.2.9.16.2.
YearDayScheduleUser
User has ability to open lock within a specific time period (e.g., guest).
5.2.6.16.3.
5.2.9.16.3.
WeekDayScheduleUser
User has ability to open lock based on specific time period within a reoccurring weekly schedule (e.g., cleaning worker).
5.2.6.16.4.
5.2.9.16.4.
ProgrammingUser
User has ability to both program and operate the door lock. This user can manage the users and user schedules. In all other respects this user matches the unrestricted (default) user. ProgrammingUser is the only user that can disable the user interface (keypad, remote, etc…).
5.2.6.16.5.
5.2.9.16.5.
NonAccessUser
User is recognized by the lock but does not have the ability to open the lock. This user will only cause the lock to generate the appropriate event notification to any bound devices.
5.2.6.16.6.
5.2.9.16.6.
ForcedUser
User has ability to open lock but a ForcedUser LockOperationType and ForcedUser silent alarm will be emitted to allow a notified Node to alert emergency services or contacts on the user account when used.
5.2.6.16.7.
5.2.9.16.7.
DisposableUser
User has ability to open lock once after which the lock SHALL change the corresponding user record UserStatus value to OccupiedDisabled automatically.
5.2.6.16.8.
5.2.9.16.8.
ExpiringUser
User has ability to open lock for ExpiringUserTimeout attribute minutes after the first use of the PIN code, RFID code, Fingerprint, or other credential. After ExpiringUserTimeout minutes the corresponding user record UserStatus value SHALL be set to OccupiedDisabled automatically by the lock. The lock SHALL persist the timeout across reboots such that the ExpiringUserTimeout is honored.
5.2.6.16.9.
5.2.9.16.9.
ScheduleRestrictedUser
User access is restricted by Week Day and/or Year Day schedule.
5.2.6.16.10.
5.2.9.16.10.
RemoteOnlyUser
User access and PIN code is restricted to remote lock/unlock commands only. This type of user might be useful for regular delivery services or voice assistant unlocking operations to prevent a PIN code credential created for them from being used at the keypad. The PIN code credential would only be provided over-the-air for the lock/unlock commands.
5.3. Window Covering Cluster
The window covering cluster provides an interface for controlling and adjusting automatic window coverings such as drapery motors, automatic shades, curtains and blinds.
5.3.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
CCB 2328 |
|
3 |
CCB 2477 2555 2845 3028 |
|
4 |
All Hubs changes with FeatureMap & OperationalStatus attribute |
|
5 |
New
data
model
format
and
notation.
Created
plus
clarified
|
5.3.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
|
|
5.3.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
LF |
Lift
|
|
Lift
|
|
1 |
TL |
Tilt
|
|
Tilt
|
|
2 |
PA_LF |
|
|
Position
|
|
3 |
ABS |
|
|
Absolute positioning is supported. |
|
4 |
PA_TL |
|
|
Position
|
*
At
least
one
of
the
Lift
and
Tilt
features
SHALL
be
supported.
Due
to
backward
compatibility
reasons
this
feature
map
SHALL
match
the
advertised
Type
Attribute
Supported
Features.
5.3.4.1. Lift Feature
The
Lift
feature
applies
to
window
coverings
that
lift
up
and
down
(ex:
(e.g.
for
a
rollershade,
roller
shade,
Up
and
Down
is
Lift
lift
Open
and
Close)
or
slide
left
to
right
(ex:
(e.g.
for
a
sliding
curtain,
Left
and
Right
is
Lift
lift
Open
and
Close).
5.3.4.2. Tilt Feature
The Tilt feature applies to window coverings with vertical or horizontal strips.
5.3.4.3.
Position
Aware
PositionAware
Features
Relative
positioning
with
percent100ths
(min
step
0.01%)
attribute
is
mandatory,
E.g
e.g.
Max
10000
equals
100.00%
and
relative
positioning
with
percent
(min
step
1%)
attribute
is
for
backward
compatibility.
The CurrentPosition attributes SHALL always reflects the physical position of an actuator and the TargetPosition attribute SHALL reflect the requested position of an actuator once a positioning command is received.
5.3.4.4.
Absolute
Position
AbsolutePosition
Feature
The percentage attributes SHALL indicate the position as a percentage between the InstalledOpenLimits and InstalledClosedLimits attributes of the window covering starting at the open (0.00%).
As a general rule, absolute positioning (in centimeters or tenth of a degrees) SHOULD NOT be supported for new implementations.
5.3.5.
Attributes
Data
Types
5.3.5.1. ConfigStatusBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map8.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Device is operational. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supports the PositionAwareLift feature (PA_LF). |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
LiftEncoderControlled | Uses an encoder for lift. |
6 | TiltEncoderControlled | Uses an encoder for tilt. |
5.3.5.1.1. Operational Bit
This bit SHALL indicate whether the window covering is operational for regular use:
0 = Not Operational
1 = Operational
5.3.5.1.2. LiftMovementReversed Bit
This bit SHALL indicate whether the lift movement is reversed:
0 = Lift movement is normal
1 = Lift movement is reversed
5.3.5.1.3. LiftPositionAware Bit
This bit SHALL indicate whether the window covering supports the PositionAwareLift feature:
0 = Lift control is not position aware
1 = Lift control is position aware (PA_LF)
5.3.5.1.4. TiltPositionAware Bit
This bit SHALL indicate whether the window covering supports the PositionAwareTilt feature:
0 = Tilt control is not position aware
1 = Tilt control is position aware (PA_TL)
5.3.5.2. ModeBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Perform a calibration. |
|
2 |
|
Freeze all motions for maintenance. |
|
|
LedFeedback | Control the LEDs feedback. |
5.3.5.2.1. MotorDirectionReversed Bit
This bit SHALL control the motor direction:
0 = Lift movement is normal
1 = Lift movement is reversed
5.3.5.2.2. CalibrationMode Bit
This bit SHALL set the window covering into calibration mode:
0 = Normal mode
1 = Calibration mode
5.3.5.3. OperationalStatusBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map8.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0..1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Lift operational state. |
|
4..5 |
|
|
The OperationalStatusBitmap is using several internal operational state fields (composed of 2 bits) following this definition:
00b = Currently not moving
01b = Currently opening (e.g. moving from closed to
InstalledClosedLimitLiftopen).10b = Currently closing (e.g. moving from open to closed).
11b = Reserved
5.3.5.3.1. Global Bits
These bits SHALL indicate in which direction the covering is currently moving or if it has stopped. Global operational state SHALL always reflect the overall motion of the device.
5.3.5.4. SafetyStatusBitmap
This data type is derived from map16.
| Bit | Name | Summary |
|---|---|---|
0 |
|
|
|
|
| Tampering detected on sensors or any other safety equipment. Ex: a device has been forcedly moved without its actuator(s). |
|
|
|
Communication failure to sensors or other safety equipment. |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ObstacleDetected | An obstacle is preventing actuator movement. |
|
|
|
Device has power related issue or limitation e.g. device is running w/ the help of a backup battery or power might not be fully available at the moment. |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PCB, fuse and other electrics problems. |
|
|
|
Actuator is manually operated and is preventing actuator movement (e.g. actuator is disengaged/decoupled). |
|
11 |
|
|
5.3.5.5. TypeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RollerShade - 2 Motor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| RollerShadeExterior2Motor | RollerShade - Exterior - 2 Motor | LF |
|
|
| Drapery (curtain) | LF |
|
5 | Awning |
Awning |
LF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Tilt Blind - Tilt Only | TL |
|
|
|
Tilt Blind - Lift & Tilt | LF & TL |
9 | ProjectorScreen |
Projector Screen |
LF |
|
|
Unknown | Unknown | O |
5.3.5.6. EndProductTypeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0
|
|
|
|
|
| RomanShade | Roman Shade | LF |
|
|
|
Balloon Shade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PleatedShade | Pleated Shade | LF |
|
|
| Cellular Shade |
LF |
6 | LayeredShade |
Layered Shade |
LF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SheerShade | Sheer Shade |
LF
&
|
|
|
|
Tilt Only Interior Blind |
TL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VerticalBlindStripCurtain | Vertical Blind, Strip Curtain |
LF & TL |
|
12 | InteriorVenetianBlind | Interior Venetian Blind |
LF
&
|
|
|
|
Exterior Venetian Blind |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LateralRightCurtain | Lateral Right Curtain | LF |
|
|
| Central Curtain | LF |
17 | RollerShutter |
Roller Shutter |
LF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AwningTerracePatio | Awning Terrace (Patio) |
LF
|
|
|
| Awning Vertical Screen | LF |
21 | TiltOnlyPergola |
Tilt Only Pergola |
LF | TL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SlidingShutter | Sliding Shutter |
LF
|
TL
|
|
|
|
Unknown |
O |
5.3.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Type | desc | F |
0
|
|
M | |
0x0001 | PhysicalClosedLimitLift | uint16 | all | F |
0 |
R V |
|
|
|
|
uint16 |
all |
|
0 |
R V | [TL & PA_TL & ABS] |
0x0003 | CurrentPositionLift 1 | uint16 |
InstalledOpenLimitLift
to
|
|
|
R V |
|
|
|
|
uint16 |
InstalledOpenLimitTilt to InstalledClosedLimitTilt | XN | null | R V | [TL & PA_TL & ABS] |
0x0005 | NumberOfActuationsLift |
uint16 |
|
N |
0 |
R V |
|
|
|
|
uint16 |
all |
|
0
|
R V | [TL] |
0x0007 | ConfigStatus | desc |
N |
|
R V |
|
|
|
|
|
percent |
XNSP |
null |
R V |
|
|
|
|
|
percent |
0 to 100 |
XNSP |
null |
R V |
|
|
|
|
0b00xx xxxx |
P |
0 |
R V |
M |
|
|
| TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths 2 | percent100ths | XSP | null | R V | LF & PA_LF |
|
|
|
|
percent100ths |
XSP |
|
|
|
|
|
0x000D | EndProductType | desc | F |
0 |
|
M |
|
|
|
|
percent100ths |
0 to 10000 |
XNP |
null |
R V |
|
|
|
|
percent100ths |
0 to 10000 |
XNP |
null |
R V |
|
|
|
|
uint16 |
|
|
|
R V | LF & PA_LF & ABS |
0x0011 | InstalledClosedLimitLift | uint16 |
0 to 65534 |
N | 65534 |
R V |
|
|
0x0012 |
InstalledOpenLimitTilt |
uint16 |
0
to
|
|
|
| TL & PA_TL & ABS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| R V | TL & PA_TL & ABS |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| RW VM | M |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
desc | P | 0 | R V | O |
|
Note
|
Nullable
positions
1 - The null value indicates that the current position is unknown, e.g. calibration is needed. 2 - The null value indicates that the value is unavailable, e.g. no target position has been set. |
5.3.6.1. Scene Table Extensions
If the Scenes server cluster is implemented on the same endpoint, the following attributes SHALL be part of the ExtensionFieldSetStruct of the Scene Table. If the implicit form of the ExtensionFieldSetStruct is used, the order of the attributes in the AttributeValueList is in the given order, i.e., the attribute listed as 1 is added first:
CurrentPositionLiftPercentage
CurrentPositionTiltPercentage
TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths
TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths
When a Percentage attribute is part of a Scene Table, the attribute is treated as a writeable command, that is, activate a motion (lift or tilt) on the window covering device to the percentage specified in the Scene Table over the specified transition time.
The device MAY treat the commands as linear transitions if appropriate or MAY accelerate and decelerate as it deems necessary.
For position aware devices, a percentage written by a scene to either the current or target lift/tilt attributes MUST be treated as a GoToLiftPercentage/GoToTiltPercentage command. Using the CurrentPosition Attribute results in writing the received percentage to the associated TargetPosition and activate the motion (lift or tilt) of the window covering device to the specified percentage.
For position unaware devices, a percentage of 0 is treated as a UpOrOpen command and a non-zero percentage is treated as an DownOrClose command and the device will ignore the transition time and transition as fast as appropriate for that device.
Attributes in the Scene Table that are not supported by the device (according to the FeatureMap attribute) SHALL be present in the scene table but ignored.
5.3.5.2.
5.3.6.3.
PhysicalClosedLimitLift
Attribute
The
PhysicalClosedLimitLift
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
possible
encoder
position
possible
(in
(Unit
cm
,
centimeters)
to
position
the
height
of
the
window
covering
Lift.
lift.
5.3.5.3.
5.3.6.4.
PhysicalClosedLimitTilt
Attribute
The
PhysicalClosedLimitTilt
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
maximum
possible
encoder
position
possible
(tenth
(Unit
0.1°
,
tenths
of
a
degrees)
degree)
to
position
the
angle
of
the
window
covering
Tilt.
tilt.
5.3.5.4.
5.3.6.5.
CurrentPositionLift
Attribute
The
CurrentPositionLift
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
actual
Lift
lift
position
(in
(Unit
cm
,
centimeters)
of
the
window
covering
from
the
fully-open
position.
5.3.5.5.
5.3.6.6.
CurrentPositionTilt
Attribute
The
CurrentPositionTilt
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
actual
Tilt
tilt
position
(in
tenth
(Unit
0.1°
,
tenths
of
an
a
degree)
of
the
window
covering
from
the
fully-open
position.
5.3.5.6.
5.3.6.7.
NumberOfActuationsLift
Attribute
The
NumberOfActuationsLift
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
total
number
of
lift/slide
actuations
applied
to
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
since
the
device
was
installed.
5.3.5.7.
5.3.6.8.
NumberOfActuationsTilt
Attribute
The
NumberOfActuationsTilt
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
total
number
of
tilt
actuations
applied
to
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
since
the
device
was
installed.
5.3.5.8.
5.3.6.9.
ConfigStatus
Attribute
The
ConfigStatus
This
attribute
makes
specifies
the
configuration
and
status
information
available.
of
the
window
covering.
To
change
settings,
devices
SHALL
write
to
the
Mode
attribute
of
the
Window
Covering
Settings
Attribute
Set.
attribute.
The
behavior
causing
the
setting
or
clearing
of
each
bit
is
vendor
specific.
See
table
below
for
details
on
each
bit.
0
=
Not
Operational
1
=
5.3.6.9.1.
Operational
Operational:
This
status
bit
defines
if
the
Window
Covering
is
operational.
Bit
The SafetyStatus & Mode attributes might affect this bit state.
M
1
Reserved
deprecated
D
2
0
=
Lift
movement
are
normal
1
=
Lift
movement
is
reversed
Reversal:
5.3.6.9.2.
LiftMovementReversed
Bit
This
status
bit
identifies
if
the
directions
of
the
lift/slide
movements
have
been
reversed
in
order
for
commands
(e.g:
Open,
Close,
GoTos)
to
match
the
physical
installation
conditions
This
bit
can
be
adjusted
by
setting
the
appropriate
reversal
MotorDirectionReversed
bit
value
in
the
Mode
attribute
LF
3
0
=
Lift
control
is
not
Position
Aware
1
=
Lift
control
is
Position
Aware
Control
-
Lift:
This
status
bit
identifies
if
the
window
covering
supports
the
Position
Aware
Lift
Control
LF
4
0
=
Tilt
control
is
not
Position
Aware
1
=
Tilt
control
is
Position
Aware
Control
-
Tilt:
This
status
bit
identifies
if
the
window
covering
supports
the
Position
Aware
Tilt
Control
TL
5
attribute.
0
=
Timer
Controlled
1
=
Encoder
Controlled
5.3.6.9.3.
LiftEncoderControlled
Bit
This
bit
is
Ignored
ignored
if
the
device
does
not
support
the
Position
Aware
for
Lift.
Encoder
-
Lift:
This
status
bit
identifies
if
a
Position
Aware
Controlled
Window
Covering
is
employing
an
encoder
for
positioning
the
height
of
the
window
covering.
LF
&
PA_LF
6
PositionAwareLift
feature
(PA_LF).
0
=
Timer
Controlled
1
=
Encoder
Controlled
5.3.6.9.4.
TiltEncoderControlled
Bit
This
bit
is
Ignored
ignored
if
the
device
does
not
support
the
Position
Aware
for
Tilt.
Encoder
-
Tilt:
This
status
bit
identifies
if
a
Position
Aware
Controlled
Window
Covering
is
employing
an
encoder
for
tilting
the
window
covering.
TL
&
PA_TL
PositionAwareTilt
feature
(PA_TL).
5.3.5.9.
5.3.6.10.
CurrentPositionLiftPercent100ths
Attribute
The
CurrentPositionLiftPercent100ths
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
actual
position
as
a
percentage
with
a
minimal
step
of
0.01%.
E.g
Max
10000
equals
100.00%.
5.3.5.10.
5.3.6.11.
CurrentPositionTiltPercent100ths
Attribute
The
CurrentPositionTiltPercent100ths
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
actual
position
as
a
percentage
with
a
minimal
step
of
0.01%.
E.g
Max
10000
equals
100.00%.
5.3.5.11.
5.3.6.12.
CurrentPositionLiftPercentage
Attribute
The
CurrentPositionLiftPercentage
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
actual
position
as
a
percentage
from
0%
to
100%
with
1%
default
step.
This
attribute
is
equal
to
CurrentPositionLiftPercent100ths
attribute
divided
by
100.
5.3.5.12.
5.3.6.13.
CurrentPositionTiltPercentage
Attribute
The
CurrentPositionTiltPercentage
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
actual
position
as
a
percentage
from
0%
to
100%
with
1%
default
step.
This
attribute
is
equal
to
CurrentPositionTiltPercent100ths
attribute
divided
by
100.
5.3.5.13.
5.3.6.14.
TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths
Attribute
The
TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
position
where
the
Window
Covering
Lift
window
covering
lift
will
go
or
is
moving
to
as
a
percentage.
percentage
(Unit
0.01%
).
5.3.5.14.
5.3.6.15.
TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths
Attribute
The
TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
position
where
the
Window
Covering
Tilt
window
covering
tilt
will
go
or
is
moving
to
as
a
percentage.
percentage
(Unit
0.01%
).
5.3.5.15.
5.3.6.16.
OperationalStatus
Attribute
The
OperationalStatus
This
attribute
keeps
track
of
SHALL
indicate
the
currently
ongoing
operations
and
applies
to
all
type
of
devices.
See
below
for
details
about
the
meaning
of
individual
bits.
5.3.5.16.
5.3.6.17.
EndProductType
Attribute
The
EndProductType
This
attribute
identifies
SHOULD
provide
more
detail
about
the
product
type
in
complement
of
than
can
be
determined
from
the
main
category
indicated
by
the
Type
attribute.
The
window
covering
SHALL
set
this
value
table
below
helps
to
one
of
match
the
values
in
EndProductType
attribute
with
the
table
below.
Type
attribute.
| Value |
|
Indoor Outdoor | Indicative Dimension |
Recommended
Type
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
2D |
|
|
|
|
I |
2D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
2D |
|
|
|
|
I |
2D |
|
|
|
|
I |
2D |
|
|
|
|
O |
2D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
I |
1D |
|
|
|
|
O |
1D |
|
|
|
|
O |
1D |
|
|
|
|
O |
1D |
|
|
|
|
O |
1D |
|
|
|
|
O |
1D |
|
|
|
|
O |
1D |
|
|
|
|
O |
1D |
|
|
|
Unknown |
Unknown |
5.3.5.17.
5.3.6.18.
InstalledOpenLimitLift
Attribute
The
InstalledOpenLimitLift
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
Open
Limit
open
limit
for
Lifting
lifting
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
whether
position
(in
centimeters)
is
encoded
or
timed.
5.3.5.18.
5.3.6.19.
InstalledClosedLimitLift
Attribute
The
InstalledClosedLimitLift
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
Closed
Limit
closed
limit
for
Lifting
lifting
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
whether
position
(in
centimeters)
is
encoded
or
timed.
5.3.5.19.
5.3.6.20.
InstalledOpenLimitTilt
Attribute
The
InstalledOpenLimitTilt
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
Open
Limit
open
limit
for
Tilting
tilting
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
whether
position
(in
tenth
of
a
degree)
is
encoded
or
timed.
5.3.5.20.
5.3.6.21.
InstalledClosedLimitTilt
Attribute
The
InstalledClosedLimitTilt
This
attribute
identifies
SHALL
indicate
the
Closed
Limit
closed
limit
for
Tilting
tilting
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
whether
position
(in
tenth
of
a
degree)
is
encoded
or
timed.
5.3.5.21.
5.3.6.22.
Mode
Attribute
The
Mode
attribute
allows
configuration
of
the
Window
Covering,
window
covering,
such
as:
reversing
the
motor
direction,
placing
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
into
calibration
mode,
placing
the
motor
into
maintenance
mode,
disabling
the
network,
and
disabling
status
LEDs.
See
below
for
details.
In
the
case
a
device
does
not
support
or
implement
a
specific
mode,
e.g.
the
device
has
a
specific
installation
method
and
reversal
is
not
relevant
or
the
device
does
not
include
a
maintenance
mode,
any
write
interaction
to
the
Mode
attribute
,
attribute,
with
an
unsupported
mode
bit
or
any
out
of
bounds
bits
set,
must
be
ignored
and
a
response
containing
the
status
of
CONSTRAINT_ERROR
will
be
returned.
0
=
Lift
movement
is
normal
1
=
Lift
movement
is
reversed
Disables
(0)
or
Enables
(1)
Lift
reversal
5.3.6.22.1.
MotorDirectionReversed
Bit
This
bit
SHALL
control
the
LiftMovementReversed
Bit
1
0
=
normal
mode
1
=
calibration
mode
bit
in
the
ConfigStatus
Attribute
attribute.
Disabled
(0)
or
Enabled
(1)
placing
the
Window
Covering
into
calibration
Mode
where
limits
are
either
setup
using
tools
or
learned
by
the
Window
Covering
by
doing
self-calibration.
5.3.6.22.2.
CalibrationMode
Bit
If
in
calibration
mode,
all
commands
(e.g:
UpOrOpen
,
DownOrClose
,
GoTos
)
UpOrOpen,
DownOrClose,
GoTos)
that
can
result
in
movement,
could
be
accepted
and
result
in
a
self-calibration
being
initiated
before
the
command
is
executed.
In
case
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
does
not
have
the
ability
or
is
not
able
to
perform
a
self-calibration,
the
command
SHOULD
be
ignored
and
a
FAILURE
status
SHOULD
be
returned.
In a write interaction, setting this bit to 0, while the device is in calibration mode, is not allowed and SHALL generate a FAILURE error status. In order to leave calibration mode, the device must perform its calibration routine, either as a self-calibration or assisted by external tool(s), depending on the device/manufacturer implementation.
A
manufacturer
might
choose
to
set
the
operational
Operational
Bit
bit
of
the
ConfigStatus
Attribute
attribute
to
its
not
operational
value,
if
applicable
during
calibration
mode
2
0
=
normal
mode
1
=
maintenance
mode
mode.
Disables
(0)
or
Enables
(1)
placing
the
Window
Covering
into
Maintenance
Mode
where
it
cannot
be
moved
over
the
network
or
by
a
switch
connected
to
a
Local
Switch
Input.
5.3.6.22.3.
MaintenanceMode
Bit
While
in
maintenance
mode,
all
commands
(e.g:
UpOrOpen
,
DownOrClose
,
GoTos
)
UpOrOpen,
DownOrClose,
GoTos)
or
local
inputs
that
can
result
in
movement,
must
be
ignored
and
respond
with
a
BUSY
status.
Additionally,
the
operational
bit
Operational
Bit
bit
of
the
ConfigStatus
Attribute
attribute
should
be
set
to
its
not
operational
value.
5.3.5.22.
5.3.6.23.
SafetyStatus
Attribute
The
SafetyStatus
attribute
reflects
the
state
of
the
safety
sensors
and
the
common
issues
preventing
movements.
By
default
for
nominal
operation
all
flags
are
cleared
(0).
A
device
might
support
none,
one
or
several
bit
flags
from
this
attribute
(all
optional).
See
below
for
details
about
the
meaning
of
individual
bits.
5.3.6.
5.3.7.
Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
UpOrOpen |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
DownOrClose |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x02 |
StopMotion |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x04 |
GoToLiftValue |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
[LF & ABS] |
|
0x05 |
GoToLiftPercentage |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
LF & PA_LF, [LF] |
|
0x07 |
GoToTiltValue |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
[TL & ABS] |
|
0x08 |
GoToTiltPercentage |
client ⇒ server |
Y |
O |
TL & PA_TL, [TL] |
5.3.6.1.
5.3.7.1.
UpOrOpen
Command
Upon
receipt
of
this
command,
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
will
adjust
its
position
so
the
physical
lift/slide
and
tilt
is
at
the
maximum
open/up
position.
This
will
happen
as
fast
as
possible.
The
server
attributes
SHALL
be
updated
as
follows:
if
Position
Aware
the
PositionAware
feature
is
supported:
-
TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths attribute SHALL be set to 0.00%.
-
TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths attribute SHALL be set to 0.00%.
The server positioning attributes will follow the movements, once the movement has successfully finished, the server attributes SHALL be updated as follows:
if
Position
Aware
the
PositionAware
feature
is
supported:
-
CurrentPositionLiftPercent100ths attribute SHALL be 0.00%.
-
CurrentPositionLiftPercentage attribute SHALL be 0%.
-
CurrentPositionTiltPercent100ths attribute SHALL be 0.00%.
-
CurrentPositionTiltPercentage attribute SHALL be 0%.
if
Absolute
Position
the
AbsolutePosition
feature
is
supported:
-
CurrentPositionLift attribute SHALL be equal to the InstalledOpenLimitLift attribute.
-
CurrentPositionTilt attribute SHALL be equal to the InstalledOpenLimitTilt attribute.
5.3.6.2.
5.3.7.2.
DownOrClose
Command
Upon
receipt
of
this
command,
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
will
adjust
its
position
so
the
physical
lift/slide
and
tilt
is
at
the
maximum
closed/down
position.
This
will
happen
as
fast
as
possible.
The
server
attributes
supported
SHALL
be
updated
as
follows:
if
Position
Aware
the
PositionAware
feature
is
supported:
-
TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths attribute SHALL be set to 100.00%.
-
TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths attribute SHALL be set to 100.00%.
The server positioning attributes will follow the movements, once the movement has successfully finished, the server attributes SHALL be updated as follows:
if
Position
Aware
the
PositionAware
feature
is
supported:
-
CurrentPositionLiftPercent100ths attribute SHALL be 100.00%.
-
CurrentPositionLiftPercentage attribute SHALL be 100%.
-
CurrentPositionTiltPercent100ths attribute SHALL be 100.00%.
-
CurrentPositionTiltPercentage attribute SHALL be 100%.
if
Absolute
Position
the
AbsolutePosition
feature
is
supported:
-
CurrentPositionLift attribute SHALL be equal to the InstalledClosedLimitLift attribute.
-
CurrentPositionTilt attribute SHALL be equal to the InstalledClosedLimitTilt attribute.
5.3.6.3.
5.3.7.3.
StopMotion
Command
Upon
receipt
of
this
command,
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
will
stop
any
adjusting
to
the
physical
tilt
and
lift/slide
that
is
currently
occurring.
The
server
attributes
supported
SHALL
be
updated
as
follows:
-
TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths attribute will be set to CurrentPositionLiftPercent100ths attribute value.
-
TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths attribute will be set to CurrentPositionTiltPercent100ths attribute value.
5.3.6.4.
5.3.7.4.
GoToLiftValue
Command
The
GoToLiftValue
This
command
SHALL
have
the
following
data
fields:
| ID | Name |
|
Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
uint16 |
desc |
M |
5.3.7.4.1. LiftValue Field
This field SHALL specify the requested physical lift/slide position in unit cm (centimeters).
5.3.7.4.2. Effect on Receipt
Upon
receipt
of
this
command,
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
will
adjust
the
window
so
the
physical
lift/slide
is
at
lift
position
to
the
value
specified
in
the
payload
of
this
command
LiftValue
field,
as
long
as
that
value
is
not
larger
than
InstalledOpenLimitLift
thanInstalledOpenLimitLift
attribute
and
not
smaller
than
InstalledClosedLimitLift
attribute.
Once
the
command
is
received
the
The
TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths
attribute
will
SHALL
update
its
value
accordingly.
If the value is out of bounds a response containing the status of CONSTRAINT_ERROR will be returned.
5.3.6.5.
5.3.7.5.
GoToLiftPercentage
Command
The
GoToLiftPercentage
This
command
SHALL
have
the
following
data
fields:
| ID | Name |
|
Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
percent |
desc |
|
||
|
1 |
|
percent100ths |
desc |
|
Upon receipt of this command, the server will adjust the window covering to the lift/slide percentage specified in the payload of this command.
If the command includes LiftPercent100thsValue, then TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths attribute SHALL be set to LiftPercent100thsValue. Otherwise the TargetPositionLiftPercent100ths attribute SHALL be set to LiftPercentageValue * 100.
If
a
client
includes
LiftPercent100thsValue
in
the
command,
the
LiftPercentageValue
SHALL
be
set
to
to
LiftPercent100thsValue
/
100,
so
a
legacy
server
which
only
supports
LiftPercentageValue
(not
LiftPercent100thsValue)
has
a
value
to
set
the
target
position.
If
the
server
does
not
support
the
Position
Aware
PositionAware
feature,
then
a
zero
percentage
SHALL
be
treated
as
a
UpOrOpen
command
and
a
non-zero
percentage
SHALL
be
treated
as
an
DownOrClose
command.
If
the
device
is
only
a
tilt
control
device,
then
the
command
SHOULD
be
ignored
and
a
UNSUPPORTED_COMMAND
status
SHOULD
be
returned.
5.3.6.6.
5.3.7.6.
GoToTiltValue
Command
The
GoToTiltValue
This
command
SHALL
have
the
following
data
fields:
| ID | Name |
|
Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
uint16 |
desc |
M |
5.3.7.6.1. TiltValue
This field SHALL specify the requested physical tilt position in unit 0.1° (tenth of a degrees).
5.3.7.6.2. Effect on Receipt
Upon
receipt
of
this
command,
the
Window
Covering
window
covering
will
adjust
the
window
so
the
physical
tilt
is
at
position
to
the
tilt
value
specified
in
the
payload
of
this
command
TiltValue
field,
as
long
as
that
value
is
not
larger
than
InstalledOpenLimitTilt
attribute
and
not
smaller
than
InstalledClosedLimitTilt
attribute.
Once
the
command
is
received
the
The
TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths
attribute
will
SHALL
update
its
value
accordingly.
If the tilt value is out of bounds a response containing the status of CONSTRAINT_ERROR will be returned.
5.3.6.7.
5.3.7.7.
GoToTiltPercentage
Command
The
GoToTiltPercentage
This
command
SHALL
have
the
following
data
fields:
| ID | Name |
|
Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
percent |
desc |
|
||
|
1 |
|
percent100ths |
desc |
|
Upon receipt of this command, the server will adjust the window covering to the tilt percentage specified in the payload of this command.
If the command includes TiltPercent100thsValue, then TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths attribute SHALL be set to TiltPercent100thsValue. Otherwise the TargetPositionTiltPercent100ths attribute SHALL be set to TiltPercentageValue * 100.
If
a
client
includes
TiltPercent100thsValue
in
the
command,
the
TiltPercentageValue
SHALL
be
set
to
to
TiltPercent100thsValue
/
100,
so
a
legacy
server
which
only
supports
TiltPercentageValue
(not
TiltPercent100thsValue)
has
a
value
to
set
the
target
position.
If
the
server
does
not
support
the
Position
Aware
PositionAware
feature,
then
a
zero
percentage
SHALL
be
treated
as
a
UpOrOpen
command
and
a
non-zero
percentage
SHALL
be
treated
as
an
DownOrClose
command.
If
the
device
is
only
a
tilt
control
device,
then
the
command
SHOULD
be
ignored
and
a
UNSUPPORTED_COMMAND
status
SHOULD
be
returned.
6. Media
The Cluster Library is made of individual chapters such as this one. See Document Control in the Cluster Library for a list of all chapters and documents. References between chapters are made using a X.Y notation where X is the chapter and Y is the sub-section within that chapter. References to external documents are contained in Chapter 1 and are made using [ Rn ] notation.
6.1. General Description
6.1.1. Introduction
The clusters specified in this document are for use typically in applications involving media (e.g., Video Players, Content Apps, Speakers), but MAY be used in any application domain.
6.1.2. Cluster List
This
section
lists
the
media
specific
clusters
as
specified
in
this
document,
and
gives
examples
of
typical
usage
for
the
purpose
of
clarification.
The
clusters
defined
in
this
document
are
listed
in
Table
105,
“Media
Clusters”
.
chapter.
| Cluster ID | Cluster Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
This cluster provides an interface for facilitating user account login on an application or a node. |
|
|
|
Provides information about a Content App running on a Video Player device which is represented as an endpoint. |
|
|
|
This cluster provides an interface for launching content on a Video Player device. |
|
|
|
This cluster provides an interface for controlling the Output on a Video Player device. |
|
|
0x0504 |
This cluster provides an interface for controlling the current Channel on an endpoint. |
|
|
|
This cluster provides an interface for launching content on a Video Player device or a Content App. |
|
|
0x0509 |
This cluster provides an interface for controlling a Video Player or a Content App using action commands such as UP, DOWN, and SELECT. |
|
|
0x0507 |
This cluster provides an interface for controlling the Input Selector on a Video Player device. |
|
|
0x0506 |
This cluster provides an interface for controlling Media Playback (PLAY, PAUSE, etc) on a Video Player device. |
|
|
0x0505 |
This cluster provides an interface for UX navigation within a set of targets on a Video Player device or Content App endpoint. |
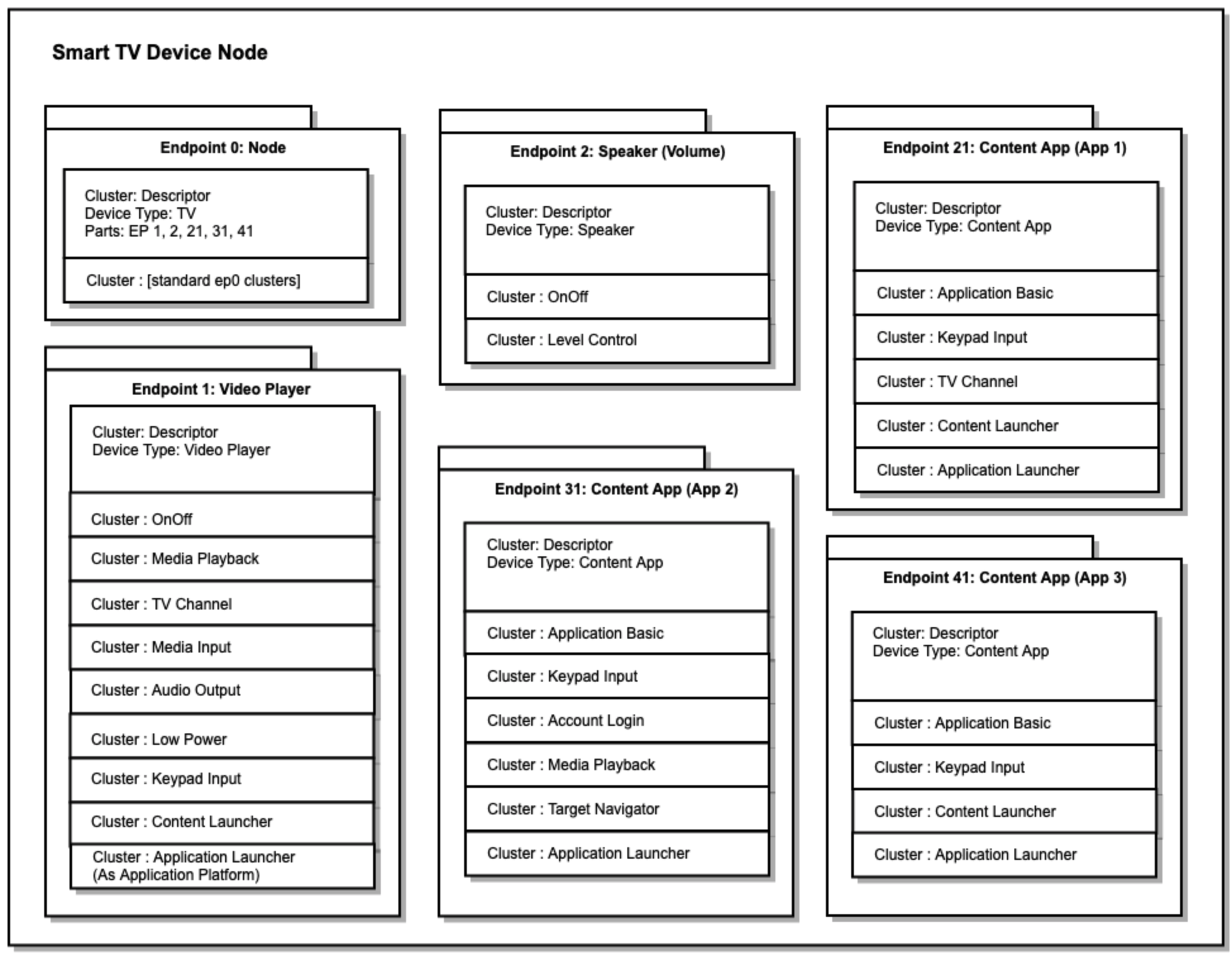
6.2. Account Login Cluster
This cluster provides commands that facilitate user account login on a Content App or a node. For example, a Content App running on a Video Player device, which is represented as an endpoint (see Device Type Library document), can use this cluster to help make the user account on the Content App match the user account on the Client.
The cluster server for this cluster may be supported on each endpoint that represents a Content App on a Video Player device.
See Device Type Library document for details of how a Content App, represented as an endpoint on the Video Player device, may implement the cluster server for this cluster to simplify account login for its users.
6.2.1.1.
6.2.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial Release |
6.2.1.2.
6.2.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
ALOGIN |
6.2.4. Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
GetSetupPIN |
Client ⇒ Server |
GetSetupPINResponse |
T A |
M |
|
0x01 |
GetSetupPINResponse |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
M |
|
|
0x02 |
Login |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T A |
M |
|
0x03 |
Logout |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
T O |
M |
6.2.4.1. GetSetupPIN Command
The purpose of this command is to determine if the active user account of the given Content App matches the active user account of a given Commissionee, and when it does, return a Setup PIN code which can be used for password-authenticated session establishment (PASE) with the Commissionee.
For example, a Video Player with a Content App Platform may invoke this command on one of its Content App endpoints to facilitate commissioning of a Phone App made by the same vendor as the Content App. If the accounts match, then the Content App may return a setup code that can be used by the Video Player to commission the Phone App without requiring the user to physically input a setup code.
The account match is determined by the Content App using a method which is outside the scope of this specification and will typically involve a central service which is in communication with both the Content App and the Commissionee. The GetSetupPIN command is needed in order to provide the Commissioner/Admin with a Setup PIN when this Commissioner/Admin is operated by a different vendor from the Content App.
This method is used to facilitate Setup PIN exchange (for PASE) between Commissioner and Commissionee when the same user account is active on both nodes. With this method, the Content App satisfies proof of possession related to commissioning by requiring the same user account to be active on both Commissionee and Content App, while the Commissioner/Admin ensures user consent by prompting the user prior to invocation of the command.
Upon receipt of this command, the Content App checks if the account associated with the Temporary Account Identifier sent by the client is the same account that is active on itself. If the accounts are the same, then the Content App returns the GetSetupPIN Response which includes a Setup PIN that may be used for PASE with the Commissionee.
The
Temporary
Account
Identifier
for
a
Commissionee
may
be
populated
with
the
Rotating
ID
field
of
the
client’s
commissionable
node
advertisement
(see
Rotating
Device
Identifier
section
in
[MatterCore]
[MatterCore]
)
encoded
as
an
octet
string
where
the
octets
of
the
Rotating
Device
Identifier
are
encoded
as
2-character
sequences
by
representing
each
octet’s
value
as
a
2-digit
hexadecimal
number,
using
uppercase
letters.
The
Setup
PIN
is
an
11
character
string
so
that
it
can
accommodate
different
future
formats,
including
alpha-numeric
encodings.
For
a
Commissionee
it
SHALL
be
populated
with
the
Manual
Pairing
Code
(see
Manual
Pairing
Code
section
in
[MatterCore]
[MatterCore]
)
encoded
as
a
string.
The
Server
server
SHALL
implement
rate
limiting
to
prevent
brute
force
attacks.
No
more
than
10
unique
requests
in
a
10
minute
period
SHALL
be
allowed;
a
command
response
status
of
FAILURE
should
sent
for
additional
commands
received
within
the
10
minute
period.
Because
access
to
this
command
is
limited
to
nodes
with
Admin-level
access,
and
the
user
is
prompted
for
consent
prior
to
Commissioning,
there
are
in
place
multiple
obstacles
to
successfully
mounting
a
brute
force
attack.
A
Content
App
that
supports
this
command
SHALL
ensure
that
the
Temporary
Account
Identifier
used
by
its
clients
is
not
valid
for
more
than
10
minutes.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
TempAccountIdentifier |
string |
|
M |
6.2.4.2. GetSetupPINResponse Command
This message is sent in response to the GetSetupPIN command, and contains the Setup PIN code, or null when the account identified in the request does not match the active account of the running Content App.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
SetupPIN |
string |
min 11 |
X |
M |
6.2.4.3. Login Command
The purpose of this command is to allow the Content App to assume the user account of a given Commissionee by leveraging the Setup PIN code input by the user during the commissioning process.
For example, a Video Player with a Content App Platform may invoke this command on one of its Content App endpoints after the commissioning has completed of a Phone App made by the same vendor as the Content App. The Content App may determine whether the Temporary Account Identifier maps to an account with a corresponding Setup PIN and, if so, it may automatically login to the account for the corresponding user. The end result is that a user performs commissioning of a Phone App to a Video Player by inputting the Setup PIN for the Phone App into the Video Player UX. Once commissioning has completed, the Video Player invokes this command to allow the corresponding Content App to assume the same user account as the Phone App.
The verification of Setup PIN for the given Temporary Account Identifier is determined by the Content App using a method which is outside the scope of this specification and will typically involve a central service which is in communication with both the Content App and the Commissionee. Implementations of such a service should impose aggressive time outs for any mapping of Temporary Account Identifier to Setup PIN in order to prevent accidental login due to delayed invocation.
Upon receipt, the Content App checks if the account associated with the client’s Temp Account Identifier has a current active Setup PIN with the given value. If the Setup PIN is valid for the user account associated with the Temp Account Identifier, then the Content App MAY make that user account active.
The Temporary Account Identifier for a Commissionee may be populated with the Rotating ID field of the client’s commissionable node advertisement encoded as an octet string where the octets of the Rotating Device Identifier are encoded as 2-character sequences by representing each octet’s value as a 2-digit hexadecimal number, using uppercase letters.
The Setup PIN for a Commissionee may be populated with the Manual Pairing Code encoded as a string of decimal numbers.
The
Server
server
SHALL
implement
rate
limiting
to
prevent
brute
force
attacks.
No
more
than
10
unique
requests
in
a
10
minute
period
SHALL
be
allowed;
a
command
response
status
of
FAILURE
should
sent
for
additional
commands
received
within
the
10
minute
period.
Because
access
to
this
command
is
limited
to
nodes
with
Admin-level
access,
and
the
user
is
involved
when
obtaining
the
SetupPIN,
there
are
in
place
multiple
obstacles
to
successfully
mounting
a
brute
force
attack.
A
Content
App
that
supports
this
command
SHALL
ensure
that
the
Temporary
Account
Identifier
used
by
its
clients
is
not
valid
for
more
than
10
minutes.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
TempAccountIdentifier |
string |
|
M |
||
|
1 |
SetupPIN |
string |
min 11 |
M |
6.3. Application Basic Cluster
This cluster provides information about a Content App running on a Video Player device which is represented as an endpoint (see Device Type Library document).
The cluster server for this cluster should be supported on each endpoint that represents a Content App on a Video Player device. This cluster provides identification information about the Content App such as vendor and product.
6.3.1.1.
6.3.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial Release |
6.3.1.2.
6.3.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
APBSC |
6.3.2.
Features
6.3.4.
Data
Types
6.3.4.1. ApplicationStatusEnum Type
This
cluster
SHALL
support
the
FeatureMap
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 | Stopped | Application is not running. | M |
1 | ActiveVisibleFocus | Application is running, is visible to the user, and is the active target for input. | M |
2 | ActiveHidden | Application is running but not visible to the user. | M |
3 | ActiveVisibleNotFocus | Application is running and visible, but is not the active target for input. | M |
6.3.4.2. ApplicationStruct Type
This indicates a global identifier for an Application given a catalog.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | CatalogVendorID | uint16 | all | M | |||
1 | ApplicationID | string | all | M |
6.3.4.2.1. CatalogVendorID Field
This field SHALL indicate the Connectivity Standards Alliance issued vendor ID for the catalog. The DIAL registry SHALL use value 0x0000.
It is assumed that Content App Platform providers (see Video Player Architecture section in [MatterDevLib] ) will have their own catalog vendor ID (set to their own Vendor ID) and will assign an ApplicationID to each Content App.
6.3.3.
6.3.5.
Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
VendorName |
string |
max 32 |
F |
empty |
R V |
O |
|
0x0001 |
VendorID |
vendor-id |
all |
F |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0002 |
ApplicationName |
string |
desc |
F |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0003 |
ProductID |
uint16 |
all |
F |
R V |
O |
|
|
0x0004 |
Application |
|
desc |
F |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0005 |
Status |
desc |
|
R V |
M |
||
|
0x0006 |
ApplicationVersion |
string |
max 32 |
F |
R V |
M |
|
|
0x0007 |
AllowedVendorList |
list[vendor-id] |
|
F |
R A |
M |
6.3.3.1.
6.3.5.1.
VendorName
Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify a human readable (displayable) name of the vendor for the Content App.
6.3.3.2.
6.3.5.2.
VendorID
Attribute
This attribute, if present, SHALL specify the Connectivity Standards Alliance assigned Vendor ID for the Content App.
6.3.3.3.
6.3.5.3.
ApplicationName
Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify a human readable (displayable) name of the Content App assigned by the vendor. For example, "NPR On Demand". The maximum length of the ApplicationName attribute is 256 bytes of UTF-8 characters.
6.3.3.4.
6.3.5.4.
ProductID
Attribute
This attribute, if present, SHALL specify a numeric ID assigned by the vendor to identify a specific Content App made by them. If the Content App is certified by the Connectivity Standards Alliance, then this would be the Product ID as specified by the vendor for the certification.
6.3.3.5.
6.3.5.5.
Application
Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify a Content App which consists of an Application ID using a specified catalog.
6.3.3.6.
6.3.5.6.
Status
Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify the current running status of the application.
6.4. Application Launcher Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for launching applications on a Video Player device such as a TV.
This cluster is supported on endpoints that can launch Applications, such as a Casting Video Player device with a Content App Platform. It supports identifying an Application by global identifier from a given catalog, and launching it. It also supports tracking the currently in-focus Application.
Depending on the support for the Application Platform feature, the cluster can either support launching the application corresponding to the endpoint on which the cluster is supported (AP feature not supported) or it can support launching any application (AP feature supported).
6.3.4.
6.4.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial Release |
6.4.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | AP | ApplicationPlatform | Support for attributes and commands required for endpoint to support launching any application within the supported application catalogs |
6.4.5. Data Types
6.3.4.1.
Application
6.4.5.1.
StatusEnum
Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Success | Command succeeded | M |
1 | AppNotAvailable | Requested app is not available. | M |
2 | SystemBusy | Video platform unable to honor command. | M |
6.4.5.2. ApplicationStruct Type
This indicates a global identifier for an Application given a catalog.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
CatalogVendorID |
uint16 |
all |
M |
|||
|
1 |
ApplicationID |
string |
all |
M |
6.3.4.1.1.
6.4.5.2.1.
CatalogVendorID
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
Connectivity
Standards
Alliance
issued
CSA-issued
vendor
ID
for
the
catalog.
The
DIAL
registry
SHALL
use
value
0x0000.
It
is
assumed
that
Content
App
Platform
providers
(see
Video
Player
Architecture
section
in
[MatterDevLib]
)
will
have
their
own
catalog
vendor
ID
(set
to
their
own
Vendor
ID)
and
will
assign
an
ApplicationID
to
each
Content
App.
6.3.4.1.2.
6.4.5.2.2.
ApplicationID
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
application
identifier,
expressed
as
a
string,
such
as
"123456-5433",
"PruneVideo"
or
"Company
X".
This
field
SHALL
be
unique
within
a
catalog.
For
the
DIAL
registry
catalog,
this
value
SHALL
be
the
DIAL
prefix.
prefix
(see
[
DIAL
Registry
]).
6.3.4.2.
ApplicationStatusEnum
6.4.5.3.
ApplicationEPStruct
Type
ApplicationStatusEnum
Data
Type
is
derived
from
enum8.
This
specifies
an
app
along
with
its
corresponding
endpoint.
|
|
Name |
|
| Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
M |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.4.3.
6.4.6.
Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
CatalogList |
list[uint16] |
|
N |
R V |
AP |
|
|
0x0001 |
CurrentApp |
|
desc |
X |
null |
R V |
O |
6.4.3.1.
6.4.6.1.
CatalogList
Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify the list of supported application catalogs, where each entry in the list is the CSA-issued vendor ID for the catalog. The DIAL registry (see [ DIAL Registry ]) SHALL use value 0x0000.
It is expected that Content App Platform providers will have their own catalog vendor ID (set to their own Vendor ID) and will assign an ApplicationID to each Content App.
6.4.3.2.
6.4.6.2.
CurrentApp
Attribute
This attribute SHALL specify the current in-focus application, identified using an Application ID, catalog vendor ID and the corresponding endpoint number when the application is represented by a Content App endpoint. A null SHALL be used to indicate there is no current in-focus application.
6.4.4.
6.4.7.
Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
LaunchApp |
Client ⇒ Server |
LauncherResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
StopApp |
Client ⇒ Server |
LauncherResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x02 |
HideApp |
Client ⇒ Server |
LauncherResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x03 |
LauncherResponse |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
M |
6.4.4.1.
6.4.7.1.
LaunchApp
Command
Upon receipt of this command, the server SHALL launch the application with optional data. The application SHALL be either
-
the specified application, if the Application Platform feature is supported;
-
otherwise the application corresponding to the endpoint.
The
endpoint
SHALL
launch
and
bring
to
foreground
the
requisite
application
if
the
application
is
not
already
launched
and
in
foreground.
The
Status
attribute
SHALL
be
updated
to
ACTIVE_VISIBLE_FOCUS
ActiveVisibleFocus
on
the
Application
Basic
cluster
of
the
Endpoint
corresponding
to
the
launched
application.
The
Status
attribute
SHALL
be
updated
on
any
other
application
whose
Status
MAY
have
changed
as
a
result
of
this
command.
The
CurrentApp
attribute,
if
supported,
SHALL
be
updated
to
reflect
the
new
application
in
the
foreground.
This command returns a Launcher Response.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Application |
|
desc |
AP |
||
|
1 |
Data |
octstr |
|
|
O |
6.4.4.1.2.
6.4.7.1.2.
Data
Field
This field SHALL specify optional app-specific data to be sent to the app.
Note: This format and meaning of this value is proprietary and outside the specification. It provides a transition path for device makers that use other protocols (like DIAL) which allow for proprietary data. Apps that are not yet Matter aware can be launched via Matter, while retaining the existing ability to launch with proprietary data.
6.4.4.2.
6.4.7.2.
StopApp
Command
Upon receipt of this command, the server SHALL stop the application if it is running. The application SHALL be either
-
the specified application, if the Application Platform feature is supported;
-
otherwise the application corresponding to the endpoint.
The
Status
attribute
SHALL
be
updated
to
STOPPED
Stopped
on
the
Application
Basic
cluster
of
the
Endpoint
corresponding
to
the
stopped
application.
The
Status
attribute
SHALL
be
updated
on
any
other
application
whose
Status
MAY
have
changed
as
a
result
of
this
command.
This command returns a Launcher Response.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Application |
|
desc |
|
AP |
6.4.4.3.
6.4.7.3.
HideApp
Command
Upon receipt of this command, the server SHALL hide the application. The application SHALL be either
-
the specified application, if the Application Platform feature is supported;
-
otherwise the application corresponding to the endpoint.
The
endpoint
MAY
decide
to
stop
the
application
based
on
manufacturer
specific
behavior
or
resource
constraints
if
any.
The
Status
attribute
SHALL
be
updated
to
ACTIVE_HIDDEN
ActiveHidden
or
STOPPED
,
Stopped,
depending
on
the
action
taken,
on
the
Application
Basic
cluster
of
the
Endpoint
corresponding
to
the
application
on
which
the
action
was
taken.
The
Status
attribute
SHALL
be
updated
on
any
other
application
whose
Status
MAY
have
changed
as
a
result
of
this
command.
This command returns a Launcher Response.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Application |
|
desc |
|
AP |
6.4.4.4.
6.4.7.4.
LauncherResponse
Command
This command SHALL be generated in response to LaunchApp/StopApp/HideApp commands.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
all |
M |
|||
|
1 |
Data |
octstr |
|
|
O |
6.4.5.
Data
Types
6.5.
Audio
Output
Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for controlling the Output on a Video Player device such as a TV.
This cluster would be supported on a device with audio outputs like a Video Player device (Smart TV, TV Setup Top Box, Smart Speaker, etc).
This cluster provides the list of available outputs and provides commands for selecting and renaming them.
The cluster server for Audio Output is implemented by a device that has configurable audio output.
6.4.5.1.
StatusEnum
6.5.1.
Revision
History
StatusEnum
Data
Type
is
derived
from
enum8.
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
be
the
highest
revision
number
in
the
table
below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial Release |
6.5.2. Classification
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
M
6.5.4.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
6.5.5. Data Types
6.4.5.2.
Application
6.5.5.1.
OutputTypeEnum
Type
This
indicates
a
global
identifier
for
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
The
type
of
output,
expressed
as
an
Application
given
a
catalog.
enum,
with
the
following
values:
|
|
Name |
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
1 | BT |
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Headphone |
M |
|
|
4 |
Internal
|
M |
|
|
5 |
Other |
M |
6.4.5.3.
ApplicationEP
6.5.5.2.
OutputInfoStruct
Type
This
specifies
contains
information
about
an
app
along
with
its
corresponding
endpoint.
output.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.5.2.
Features
6.5.5.2.1.
Index
Field
This
cluster
field
SHALL
support
indicate
the
FeatureMap
bitmap
attribute
as
defined
below.
unique
index
into
the
list
of
outputs.
NU
6.5.5.2.2.
OutputType
Field
This field SHALL indicate the type of output.
6.5.3.
6.5.6.
Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
OutputList |
|
|
R V |
M |
||
|
0x0001 |
CurrentOutput |
uint8 |
all |
R V |
M |
6.5.3.1.
6.5.6.1.
OutputList
Attribute
This
list
attribute
provides
the
list
of
outputs
supported
by
the
device.
6.5.3.2.
6.5.6.2.
CurrentOutput
Attribute
This
field
attribute
contains
the
value
of
the
index
field
of
the
currently
selected
OutputInfo
.
OutputInfoStruct
.
6.5.4.
6.5.7.
Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
SelectOutput |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
RenameOutput |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
M |
NU |
6.5.4.1.
SelectAudioOutput
6.5.7.1.
SelectOutput
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL change the output on the device to the output at a specific index in the Output List.
Note that when the current output is set to an output of type HDMI, adjustments to volume via a Speaker endpoint on the same node MAY cause HDMI volume up/down commands to be sent to the given HDMI output.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Index |
uint8 |
all |
M |
6.5.4.1.1.
6.5.7.1.1.
Index
Field
This
SHALL
indicate
the
index
field
of
the
OutputInfo
OutputInfoStruct
from
the
OutputList
attribute
in
which
to
change
to.
6.5.4.2.
6.5.7.2.
RenameOutput
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL rename the output at a specific index in the Output List.
Updates to the output name SHALL appear in the device’s settings menus. Name updates MAY automatically be sent to the actual device to which the output connects.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Index |
uint8 |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
Name |
string |
all |
M |
6.5.5.
Data
Types
6.6.
Channel
Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for controlling the current Channel on a device or endpoint.
This cluster server would be supported on Video Player devices or endpoints that allow Channel control such as a Content App. This cluster provides a list of available channels and provides commands for absolute and relative channel changes.
The cluster server for Channel is implemented by an endpoint that controls the current Channel.
6.5.5.1.
OutputInfo
6.6.1.
Revision
History
This
contains
information
about
an
output.
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
be
the
highest
revision
number
in
the
table
below.
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
1 | Initial Release |
6.6.2. Classification
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
6.6.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.5.5.1.1.
Index
This
SHALL
indicate
the
unique
index
into
the
list
of
outputs.
6.6.5.
Data
Types
6.5.5.1.2.
OutputType
6.6.5.1.
LineupInfoTypeEnum
Type
This
SHALL
indicate
the
data
type
of
output
is
derived
from
enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
MSO
|
Multi System Operator | M |
6.5.5.2.
OutputTypeEnum
6.6.5.2.
StatusEnum
Type
OutputType
Data
Type
This
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
| Value | Name |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
M |
|
| MultipleMatches | More than one equal match for the ChannelInfoStruct passed in. | M |
|
2 |
|
|
M |
6.6.5.3. ChannelInfoStruct Type
This indicates a channel in a channel lineup.
While the major and minor numbers in the ChannelInfoStruct support use of ATSC channel format, a lineup MAY use other formats which can map into these numeric values.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | MajorNumber | uint16 | all |
M |
|||
|
1 |
|
|
|
M |
|||
|
2 |
|
|
|
O |
|||
|
3 |
|
|
|
O |
|||
|
4 |
|
|
|
O |
6.6.
Channel
Cluster
6.6.5.3.1.
MajorNumber
Field
This
cluster
provides
an
interface
for
controlling
field
SHALL
indicate
the
current
Channel
on
channel
major
number
value
(for
example,
using
ATSC
format).
When
the
channel
number
is
expressed
as
a
device
string,
such
as
"13.1"
or
endpoint.
"256",
the
major
number
would
be
13
or
256,
respectively.
6.6.1.
Overview
6.6.5.3.2.
MinorNumber
Field
This
cluster
server
field
SHALL
indicate
the
channel
minor
number
value
(for
example,
using
ATSC
format).
When
the
channel
number
is
expressed
as
a
string,
such
as
"13.1"
or
"256",
the
minor
number
would
be
supported
on
Video
Player
devices
1
or
endpoints
that
allow
Channel
control
such
as
a
Content
App.
This
cluster
provides
a
list
of
available
channels
and
provides
commands
for
absolute
and
relative
channel
changes.
0,
respectively.
6.6.5.3.3. Name Field
The
cluster
server
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
marketing
name
for
Channel
is
implemented
by
an
endpoint
that
controls
the
current
Channel.
channel,
such
as
“The
CW"
or
"Comedy
Central".
This
field
is
optional,
but
SHOULD
be
provided
when
known.
6.6.1.1.
Revision
History
6.6.5.3.4.
CallSign
Field
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
This
field
SHALL
be
indicate
the
highest
revision
number
in
call
sign
of
the
table
below.
channel,
such
as
"PBS".
This
field
is
optional,
but
SHOULD
be
provided
when
known.
Initial
Release
6.6.5.3.5.
AffiliateCallSign
Field
This field SHALL indicate the local affiliate call sign, such as "KCTS". This field is optional, but SHOULD be provided when known.
6.6.1.2.
Classification
6.6.5.4.
LineupInfoStruct
Type
The Lineup Info allows references to external lineup sources like Gracenote. The combination of OperatorName, LineupName, and PostalCode MUST uniquely identify a lineup.
|
|
|
|
| Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
1 |
|
|
|
empty |
O |
|
|
2 |
PostalCode |
|
|
|
||
|
3 |
LineupInfoType |
|
|
6.6.5.4.1. OperatorName Field
This field SHALL indicate the name of the operator, for example “Comcast”.
6.6.5.4.2. LineupName Field
This field SHALL indicate the name of the provider lineup, for example "Comcast King County". This field is optional, but SHOULD be provided when known.
6.6.3.
6.6.6.
Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
ChannelList |
|
|
empty |
R V |
CL |
|
|
0x0001 |
Lineup |
|
desc |
R V |
LI |
||
|
0x0002 |
CurrentChannel |
|
desc |
X |
null |
R V |
O |
6.6.3.1.
6.6.6.1.
ChannelList
Attribute
This
optional
list
provides
attribute
SHALL
provide
the
channels
supported.
list
of
supported
channels.
6.6.4.
6.6.7.
Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
ChangeChannel |
Client ⇒ Server |
ChangeChannelResponse |
O |
CL
|
|
0x01 |
ChangeChannelResponse |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
CL
|
|
|
0x02 |
ChangeChannelByNumber |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x03 |
SkipChannel |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
O |
M |
6.6.4.1.
6.6.7.1.
ChangeChannel
Command
Change the channel to the channel case-insensitive exact matching the value passed as an argument.
The match priority order SHALL be: AffiliateCallSign ("KCTS"), CallSign ("PBS"), Name ("Comedy Central"), Number ("13.1")
Upon receipt, this SHALL generate a ChangeChannelResponse command.
Upon success, the CurrentChannel attribute, if supported, SHALL be updated to reflect the change.
The data for this command SHALL be as follows:
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Match |
string |
M |
6.6.4.2.
6.6.7.2.
ChangeChannelResponse
Command
This command SHALL be generated in response to a ChangeChannel command. The data for this command SHALL be as follows:
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
desc |
M |
|||
|
1 |
Data |
|
any |
O |
6.6.4.3.
6.6.7.3.
ChangeChannelByNumber
Command
Change the channel to the channel with the given Number in the ChannelList attribute.
The data for this command SHALL be as follows:
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
uint16 |
all |
M |
||
|
1 |
|
uint16 |
all |
M |
6.6.4.4.
6.6.7.4.
SkipChannel
Command
This command provides channel up and channel down functionality, but allows channel index jumps of size Count .
When the value of the increase or decrease is larger than the number of channels remaining in the given direction, then the behavior SHALL be to return to the beginning (or end) of the channel list and continue. For example, if the current channel is at index 0 and count value of -1 is given, then the current channel should change to the last channel.
The data for this command is as follows:
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Count |
int16 |
all |
M |
6.7. Content Launcher Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for launching content on a Video Player device such as a Streaming Media Player, Smart TV or Smart Screen.
This cluster would be supported on a Video Player device or devices that can playback content, such as a Streaming Media Player, Smart TV or Smart Screen. This cluster supports playing back content referenced by URL. It supports finding content by type and global identifier, and either playing the content or displaying the search results.
The cluster server for Content Launcher is implemented by an endpoint that can launch content, such as a Video Player, or an endpoint representing a Content App on such a device.
When this cluster is implemented for an Content App Endpoint (Endpoint with type “Content App” and having an Application Basic cluster), the Video Player device SHALL launch the application when a client invokes the LaunchContent or LaunchURL commands.
6.7.1.1.
6.7.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial Release |
6.7.1.2.
6.7.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
CONTENTLAUNCHER |
6.7.2.
6.7.4.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
CS |
|
Device supports content search (non-app specific) |
|
1 |
UP |
|
Device supports basic URL-based file playback |
6.7.3.
Attributes
6.7.5.
Data
Types
6.7.5.1. SupportedProtocolsBitmap Type
This data type is derived from map32.
|
|
Name |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SupportedStreamingProtocols
6.7.5.2.
StatusEnum
Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.7.4.
Commands
6.7.5.3.
ParameterEnum
Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
|
|
Name |
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Genre represents the genre of video media content such as action, drama or comedy. |
M |
|
|
|
|
M |
|
|
|
Popularity
indicates
whether
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Video
represents
the
|
M |
6.7.4.3.
LauncherResponse
Command
6.7.5.4.
MetricTypeEnum
Type
This
command
SHALL
be
generated
in
response
to
LaunchContent
and
LaunchURL
commands.
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
|
|
|
|
Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
M |
|
1 |
|
|
|
6.7.4.3.1.
Status
6.7.5.4.1.
Pixels
Value
This
SHALL
indicate
the
status
of
the
command
which
resulted
value
is
used
for
dimensions
defined
in
this
response.
a
number
of
Pixels.
6.7.4.3.2.
Data
6.7.5.4.2.
Percentage
Value
This
value
is
for
dimensions
defined
as
a
percentage
of
the
overall
display
dimensions.
For
example,
if
using
a
Percentage
Metric
type
for
a
Width
measurement
of
50.0,
against
a
display
width
of
1920
pixels,
then
the
resulting
value
used
would
be
960
pixels
(50.0%
of
1920)
for
that
dimension.
Whenever
a
measurement
uses
this
Metric
type,
the
resulting
values
SHALL
indicate
Optional
app-specific
data.
be
rounded
("floored")
towards
0
if
the
measurement
requires
an
integer
final
value.
6.7.5.1.
StatusEnum
6.7.5.5.
AdditionalInfoStruct
Type
StatusEnum
Data
Type
is
derived
from
enum8.
This
object
defines
additional
name=value
pairs
that
can
be
used
for
identifying
content.
|
|
Name |
|
| Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
M |
6.7.5.3.
Parameter
6.7.5.6.
ParameterStruct
Type
This object defines inputs to a search for content for display or playback.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Type |
all |
M |
||||
|
1 |
Value |
string |
max 1024 |
M |
|||
|
2 |
ExternalIDList |
|
all |
empty |
O |
6.7.5.4.
ParameterEnum
6.7.5.7.
ContentSearchStruct
Type
Parameter
Data
Type
is
derived
from
enum8.
This
object
defines
inputs
to
a
search
for
content
for
display
or
playback.
|
|
Name |
|
| Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M |
A
director
of
6.7.5.7.1.
ParameterList
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
video
media
content;
for
example,
“Spike
Lee”
4
Event
M
An
event
is
a
reference
to
a
type
of
event;
examples
would
include
sports,
music,
or
other
types
list
of
events.
For
example,
searching
for
"Football
games"
would
parameters
comprising
the
search.
If
multiple
parameters
are
provided,
the
search
for
a
'game'
event
entity
and
a
'football'
sport
entity.
5
Franchise
M
parameters
SHALL
be
joined
with
'AND'
logic.
e.g.
action
movies
with
Tom
Cruise
will
be
represented
as
[{Actor:
'Tom
Cruise'},
{Type:
'Movie'},
{Genre:
'Action'}]
A
franchise
is
a
video
entity
which
can
represent
a
number
of
video
entities,
like
movies
or
TV
shows.
For
example,
take
the
fictional
franchise
"Intergalactic
Wars"
which
represents
a
collection
of
movie
trilogies,
as
well
as
animated
and
live
action
TV
shows.
6.7.5.8.
DimensionStruct
Type
This
entity
type
was
introduced
to
account
for
requests
by
customers
such
as
"Find
Intergalactic
Wars
movies",
object
defines
dimension
which
would
search
can
be
used
for
all
'Intergalactic
Wars'
programs
defining
Size
of
the
MOVIE
MediaType,
rather
than
attempting
to
match
to
a
single
title.
background
images.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Video
6.7.5.8.1.
Width
Field
This field SHALL indicate the width using the metric defined in Metric
M
6.7.5.8.2.
Height
Field
This field SHALL indicate the height using the metric defined in Metric
Video
represents
the
identifying
data
for
a
specific
piece
of
video
content;
6.7.5.8.3.
Metric
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
metric
used
for
example,
"Manchester
by
the
Sea".
defining
Height/Width.
6.7.5.5.
AdditionalInfo
6.7.5.9.
StyleInformationStruct
Type
This
object
defines
additional
name=value
pairs
that
style
information
which
can
be
used
for
identifying
content.
by
content
providers
to
change
the
Media
Player’s
style
related
properties.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
string |
max
|
MS |
|
||
|
1 |
|
string |
|
MS |
| ||
2 | Size | MS | O |
6.7.5.5.1.
Name
6.7.5.9.1.
ImageURL
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
name
URL
of
external
id,
ex.
"musicbrainz".
image
used
for
Styling
different
Video
Player
sections
like
Logo,
Watermark
etc.
6.7.5.5.2.
Value
6.7.5.9.2.
Color
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
color,
in
RGB
or
RGBA,
used
for
styling
different
Video
Player
sections
like
Logo,
Watermark,
etc.
The
value
SHALL
conform
to
the
6-digit
or
8-digit
format
defined
for
external
id,
ex.
"ST0000000666661".
CSS
sRGB
hexadecimal
color
notation
.
Examples:
#76DE19 for R=0x76, G=0xDE, B=0x19, A absent
#76DE1980 for R=0x76, G=0xDE, B=0x19, A=0x80
6.7.5.6.
BrandingInformation
6.7.5.10.
BrandingInformationStruct
Type
This object defines Branding Information which can be provided by the client in order to customize the skin of the Video Player during playback.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
ProviderName |
string |
max 256 |
M |
||
|
1 |
Background |
|
|
O |
||
|
2 |
Logo |
|
|
O |
||
|
3 |
ProgressBar |
|
|
O |
||
|
4 |
Splash |
|
|
O |
||
|
5 |
WaterMark |
|
|
O |
6.7.5.6.1.
6.7.5.10.1.
ProviderName
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
name
of
of
the
provider
for
the
given
content.
6.7.5.6.2.
6.7.5.10.2.
Background
Field
This field SHALL indicate background of the Video Player while content launch request is being processed by it. This background information MAY also be used by the Video Player when it is in idle state.
6.7.5.6.3.
6.7.5.10.3.
Logo
Field
This field SHALL indicate the logo shown when the Video Player is launching. This is also used when the Video Player is in the idle state and Splash field is not available.
6.7.5.6.4.
6.7.5.10.4.
ProgressBar
Field
This field SHALL indicate the style of progress bar for media playback.
6.7.6. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x0000 | AcceptHeader | list[string] | max 100[max 1024] | N | empty | R V | UP |
0x0001 | SupportedStreamingProtocols | N | 0 | R V | UP |
6.7.5.7.
StyleInformation
6.7.6.1.
AcceptHeader
Attribute
This
object
defines
StyleInformation
which
can
be
used
by
attribute
SHALL
provide
a
list
of
content
providers
to
change
types
supported
by
the
Media
Player’s
style
related
properties.
Video
Player
or
Content
App
in
the
form
of
entries
in
the
HTTP
"Accept"
request
header.
6.7.7. Commands
| ID | Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 | LaunchContent | Client ⇒ Server | LauncherResponse | O | CS |
0x01 | LaunchURL | Client ⇒ Server | LauncherResponse | O | UP |
0x02 | LauncherResponse | Server ⇒ Client | N | CS | UP |
6.7.7.1. LaunchContent Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL launch the specified content with optional search criteria.
This command returns a Launch Response.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
O |
6.7.5.7.1.
ImageUrl
6.7.7.1.1.
Search
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
URL
of
image
used
for
Styling
different
Video
Player
sections
like
Logo,
Watermark
etc.
content
to
launch.
6.7.5.7.2.
Color
6.7.7.1.2.
AutoPlay
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
color,
in
RGB
or
RGBA,
used
for
styling
different
Video
Player
sections
like
Logo,
Watermark,
etc.
The
value
SHALL
conform
whether
to
the
6-digit
or
8-digit
format
defined
for
CSS
sRGB
hexadecimal
color
notation
.
Examples:
automatically
start
playing
content,
where:
-
#76DE19 for R =0x76, G =0xDE, B =0x19, A absentTRUE means best match should start playing automatically. -
#76DE1980FALSE means matches should be displayed on screen forR =0x76, G =0xDE, B =0x19, A =0x80user selection.
6.7.5.8.
Dimension
6.7.7.2.
LaunchURL
Command
This
object
defines
dimension
which
can
be
used
for
defining
Size
of
background
images.
Upon
receipt,
this
SHALL
launch
content
from
the
specified
URL.
TODO
:
Evaluate
if
Dimension
should
be
part
of
common
data
types.
As
of
Apr
2021
adding
it
The
content
types
supported
include
those
identified
in
ContentLauncher
because
we
don’t
have
any
other
usecases
which
require
this
datatype.
the
AcceptHeader
and
SupportedStreamingProtocols
attributes.
A check SHALL be made to ensure the URL is secure (uses HTTPS).
This command returns a Launch Response.
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
any |
|
M |
|
|
1 |
|
|
any |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
any |
MS |
|
6.7.5.8.1.
Width
6.7.7.2.1.
ContentURL
Field
This
indicates
the
width
using
field
SHALL
indicate
the
metric
defined
in
Metric
URL
of
content
to
launch.
6.7.5.9.
MetricTypeEnum
6.7.7.3.
LauncherResponse
Command
MetricTypeEnum
Data
Type
is
derived
from
enum8.
This
command
SHALL
be
generated
in
response
to
LaunchContent
and
LaunchURL
commands.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
all | M |
||
|
1 |
|
|
| O |
6.7.5.9.1.
Pixels
6.7.7.3.1.
Status
Field
This
value
is
used
for
dimensions
defined
in
a
number
field
SHALL
indicate
the
status
of
Pixels.
the
command
which
resulted
in
this
response.
6.7.5.9.2.
Percentage
6.7.7.3.2.
Data
Field
This
value
is
for
dimensions
defined
as
a
percentage
of
the
overall
display
dimensions.
For
example,
if
using
a
Percentage
Metric
type
for
a
Width
measurement
of
50.0,
against
a
display
width
of
1920
pixels,
then
the
resulting
value
used
would
be
960
pixels
(50.0%
of
1920)
for
that
dimension.
Whenever
a
measurement
uses
this
Metric
type,
the
resulting
values
field
SHALL
be
rounded
("floored")
towards
0
if
the
measurement
requires
an
integer
final
value.
indicate
Optional
app-specific
data.
6.8. Keypad Input Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for key code based input and control on a device like a Video Player or an endpoint like a Content App. This may include text or action commands such as UP, DOWN, and SELECT.
This cluster would be supported on Video Player devices as well as devices that support remote control input from a keypad or remote. This cluster provides the list of supported keypad inputs and provides a command for sending them.
The cluster server for Keypad Input is implemented by a device that can receive keypad input, such as a Video Player, or an endpoint that can receive keypad input, such as a Content App.
The key codes used are those defined in the HDMI CEC specification (see HDMI ).
Devices MAY understand a subset of these key codes. Feature flags are used to indicate a specific subset that is supported. Device MAY support additional codes beyond what is indicated in feature flags.
6.8.1.1.
6.8.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial Release |
6.8.1.2.
6.8.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
KEYPADINPUT |
6.8.2.
6.8.4.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NV |
|
Supports UP, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT, SELECT, BACK, EXIT, MENU |
|
1 |
LK |
|
Supports CEC keys 0x0A (Settings) and 0x09 (Home) |
|
2 |
NK |
|
Supports numeric input 0..9 |
6.8.6. Commands
|
|
Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
SendKey |
Client ⇒ Server |
SendKeyResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
SendKeyResponse |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
M |
6.8.3.1.
6.8.6.1.
SendKey
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL process a keycode as input to the media device.
If a second SendKey request with the same KeyCode value is received within 200ms, then the endpoint will consider the first key press to be a press and hold. When such a repeat KeyCode value is not received within 200ms, then the endpoint will consider the last key press to be a release.
|
|
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
KeyCode |
uint8 |
all |
M |
6.9. Media Input Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for controlling the Input Selector on a media device such as a Video Player.
This cluster would be implemented on TV and other media streaming devices, as well as devices that provide input to or output from such devices.
This cluster provides the list of available inputs and provides commands for selecting and renaming them.
The cluster server for Media Input is implemented by a device that has selectable input, such as a Video Player device.
6.9.1.1.
6.9.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial Release |
6.9.1.2.
6.9.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
MEDIAINPUT |
6.9.2.
6.9.4.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
NU |
|
Supports updates to the input names |
6.9.3.
6.9.5.
Data
Types
6.9.5.1. InputTypeEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Internal | Indicates content not coming from a physical input. | M |
1 | Aux | M | |
2 | Coax | M | |
3 | Composite | M | |
4 | HDMI | M | |
5 | Input | M | |
6 | Line | M | |
7 | Optical | M | |
8 | Video | M | |
9 | SCART | M | |
10 | USB | M | |
11 | Other | M |
6.9.5.2. InputInfoStruct Type
This contains information about an input.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Index | uint8 | all | M | |||
1 | InputType | desc | M | ||||
2 | Name | string | M | ||||
3 | Description | string | M |
6.9.6. Attributes
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
InputList |
|
R V |
M |
|||
|
0x0001 |
CurrentInput |
uint8 |
all |
R V |
M |
6.9.3.1.
6.9.6.1.
InputList
Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
provide
a
list
provides
of
the
media
inputs
supported
by
the
device.
6.9.3.2.
6.9.6.2.
CurrentInput
Attribute
This
field
contains
attribute
SHALL
contain
the
value
of
the
index
field
of
the
currently
selected
InputInfo
.
InputInfoStruct
.
6.9.4.
6.9.7.
Commands
|
|
Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
SelectInput |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
ShowInputStatus |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x02 |
HideInputStatus |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
O |
M |
|
0x03 |
RenameInput |
Client ⇒ Server |
Y |
M |
NU |
6.9.4.1.
6.9.7.1.
SelectInput
Command
Upon receipt, this command SHALL change the media input on the device to the input at a specific index in the Input List.
|
|
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Index |
uint8 |
all |
M |
6.9.4.1.1.
6.9.7.1.1.
Index
Field
This
field
SHALL
indicate
the
index
field
of
the
InputInfo
InputInfoStruct
from
the
InputList
attribute
in
which
to
change
to.
6.9.4.2.
6.9.7.2.
ShowInputStatus
Command
Upon receipt, this command SHALL display the active status of the input list on screen.
6.9.5.
Data
Types
6.10.
Media
Playback
Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for controlling Media Playback (PLAY, PAUSE, etc) on a media device such as a TV, Set-top Box, or Smart Speaker.
This cluster server would be supported on Video Player devices or endpoints that provide media playback, such as a Content App. This cluster provides an interface for controlling Media Playback.
6.9.5.1.
InputInfo
6.10.1.
Revision
History
This
contains
information
about
an
input.
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
be
the
highest
revision
number
in
the
table
below.
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
uint8
6.10.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role | Scope | PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
M
6.10.4.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
AdvancedSeek |
|
|
|
|
VariableSpeed |
|
6.9.5.1.4.
Description
This
SHALL
indicate
the
user
editable
input
description,
such
as
“Living
room
Playstation”.
This
field
may
be
blank,
but
SHOULD
be
provided
when
known.
6.10.5.
Data
Types
6.9.5.2.
InputTypeEnum
6.10.5.1.
PlaybackStateEnum
Type
InputType
Data
Type
This
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
| Value | Name |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
M |
|
2 |
|
|
M |
|
3 |
|
|
M |
INPUT
6.10.5.2.
StatusEnum
Type
Status Data Type is derived from enum8.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
M |
|
1 |
|
|
M |
|
2 |
|
|
M |
|
3 |
|
|
M |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
6.10.
Media
Playback
Cluster
6.10.5.3.
PlaybackPositionStruct
Type
This
cluster
provides
an
interface
for
controlling
Media
Playback
(PLAY,
PAUSE,
etc)
on
structure
defines
a
media
device
such
as
playback
position
within
a
TV,
Set-top
Box,
or
Smart
Speaker.
6.10.1.
Overview
This
cluster
server
would
be
supported
on
Video
Player
devices
or
endpoints
that
provide
media
playback,
such
as
a
Content
App.
This
cluster
provides
an
interface
for
controlling
Media
Playback.
6.10.1.1.
Revision
History
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
be
the
highest
revision
number
in
the
table
below.
stream
being
played.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
1 |
|
|
|
| M |
6.10.5.3.2. Position Field
This field SHALL indicate the associated discrete position within the media stream, in milliseconds from the beginning of the stream, being associated with the time indicated by the UpdatedAt field. The Position SHALL not be greater than the duration of the media if duration is specified. The Position SHALL not be greater than the time difference between current time and start time of the media when start time is specified.
A value of null SHALL indicate that playback position is not applicable for the current state of the media playback (For example : Live media with no known duration and where seek is not supported).
6.10.3.
6.10.6.
Attributes
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
CurrentState |
desc |
R V |
M |
|||
|
0x0001 |
StartTime |
epoch-us |
desc |
X |
null |
R V |
AS |
|
0x0002 |
Duration |
uint64 |
desc |
X |
null |
R V |
AS |
|
0x0003 |
SampledPosition |
|
desc |
X |
null |
R V |
AS |
|
0x0004 |
PlaybackSpeed |
single |
desc |
0 |
R V |
AS |
|
|
0x0005 |
SeekRangeEnd |
uint64 |
desc |
X |
null |
R V |
AS |
|
0x0006 |
SeekRangeStart |
uint64 |
desc |
X |
null |
R V |
AS |
6.10.3.1.
6.10.6.1.
CurrentState
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the current playback state of media.
During fast-forward, rewind, and other seek operations; this attribute SHALL be set to PLAYING.
6.10.3.2.
6.10.6.2.
StartTime
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the start time of the media, in case the media has a fixed start time (for example, live stream or television broadcast), or null when start time does not apply to the current media (for example, video-on-demand). This time is a UTC time. The client needs to handle conversion to local time, as required, taking in account time zone and possible local DST offset.
6.10.3.3.
6.10.6.3.
Duration
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the duration, in milliseconds, of the current media being played back or null when duration is not applicable (for example, in live streaming content with no known duration). This attribute SHALL never be 0.
6.10.3.4.
6.10.6.4.
SampledPosition
Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
position
of
playback
(
Position
(Position
field)
at
the
time
(
UpdateAt
(UpdateAt
field)
specified
in
the
attribute.
The
client
MAY
use
the
SampledPosition
attribute
to
compute
the
current
position
within
the
media
stream
based
on
the
PlaybackSpeed
,
PlaybackPosition.UpdatedAt
PlaybackSpeed,
PlaybackPositionStruct.UpdatedAt
and
PlaybackPosition.Position
PlaybackPositionStruct.Position
fields.
To
enable
this,
the
SampledPosition
attribute
SHALL
be
updated
whenever
a
change
in
either
the
playback
speed
or
the
playback
position
is
triggered
outside
the
normal
playback
of
the
media.
The
events
which
MAY
cause
this
to
happen
include:
-
Starting or resumption of playback
-
Seeking
-
Skipping forward or backward
-
Fast-forwarding or rewinding
-
Updating of playback speed as a result of explicit request, or as a result of buffering events
6.10.3.5.
6.10.6.5.
PlaybackSpeed
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the speed at which the current media is being played. The new PlaybackSpeed SHALL be reflected in this attribute whenever any of the following occurs:
-
Starting of playback
-
Resuming of playback
-
Fast-forwarding
-
Rewinding
The PlaybackSpeed SHALL reflect the ratio of time elapsed in the media to the actual time taken for the playback assuming no changes to media playback (for example buffering events or requests to pause/rewind/forward).
-
A value for PlaybackSpeed of 1 SHALL indicate normal playback where, for example, playback for 1 second causes the media to advance by 1 second within the duration of the media.
-
A value for PlaybackSpeed which is greater than 0 SHALL indicate that as playback is happening the media is currently advancing in time within the duration of the media.
-
A value for PlaybackSpeed which is less than 0 SHALL indicate that as playback is happening the media is currently going back in time within the duration of the media.
-
A value for PlaybackSpeed of 0 SHALL indicate that the media is currently not playing back. When the CurrentState attribute has the value of
PAUSED ,PAUSED, NOT_PLAYING orBUFFERING ,BUFFERING, the PlaybackSpeed SHALL be set to 0 to reflect that the media is not playing.
Following examples illustrate the PlaybackSpeed attribute values in various conditions.
| Seconds of Media Played | Actual Time Taken in Seconds | Direction of playback | PlaybackSpeed |
|---|---|---|---|
|
2 |
2 |
Forward |
1.0 |
|
2 |
1 |
Forward |
2.0 |
|
1 |
2 |
Forward |
0.5 |
|
2 |
2 |
Reverse |
-1.0 |
|
2 |
1 |
Reverse |
-2.0 |
|
1 |
2 |
Reverse |
-0.5 |
6.10.3.6.
6.10.6.6.
SeekRangeStart
Attribute
This attribute SHALL indicate the earliest valid position to which a client MAY seek back, in milliseconds from start of the media. A value of Nas SHALL indicate that seeking backwards is not allowed.
6.10.3.7.
6.10.6.7.
SeekRangeEnd
Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
indicate
the
furthest
forward
valid
position
to
which
a
client
MAY
seek
forward,
in
milliseconds
from
the
start
of
the
media.
When
the
media
has
an
associated
StartTime
,
StartTime,
a
value
of
null
SHALL
indicate
that
a
seek
forward
is
valid
only
until
the
current
time
within
the
media,
using
a
position
computed
from
the
difference
between
the
current
time
offset
and
StartTime
,
StartTime,
in
milliseconds
from
start
of
the
media,
truncating
fractional
milliseconds
towards
0.
A
value
of
Nas
when
StartTime
is
not
specified
SHALL
indicate
that
seeking
forward
is
not
allowed.
6.10.4.
6.10.7.
Commands
|
|
Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
Play |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x01 |
Pause |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x02 |
Stop |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
M |
|
0x03 |
StartOver |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
O |
|
0x04 |
Previous |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
O |
|
0x05 |
Next |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
O |
|
0x06 |
Rewind |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
VS |
|
0x07 |
FastForward |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
VS |
|
0x08 |
SkipForward |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
O |
|
0x09 |
SkipBackward |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
O |
|
|
PlaybackResponse |
Server ⇒ Client |
N |
M |
|
|
|
Seek |
Client ⇒ Server |
PlaybackResponse |
O |
AS |
6.10.4.1.
6.10.7.1.
Play
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL play media. If content is currently in a FastForward or Rewind state. Play SHALL return media to normal playback speed.
6.10.4.3.
6.10.7.3.
Stop
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL stop playback of the media. User-visible outcome is context-specific. This MAY navigate the user back to the location from where the media was originally launched.
6.10.4.4.
6.10.7.4.
StartOver
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL Start Over with the current media playback item.
6.10.4.5.
6.10.7.5.
Previous
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL cause the handler to be invoked for "Previous". User experience is context-specific. This will often Go back to the previous media playback item.
6.10.4.6.
6.10.7.6.
Next
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL cause the handler to be invoked for "Next". User experience is context-specific. This will often Go forward to the next media playback item.
6.10.4.7.
6.10.7.7.
Rewind
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL start playback of the media backward in case the media is currently playing in the forward direction or is not playing. If the playback is already happening in the backwards direction receipt of this command SHALL increase the speed of the media playback backwards.
Different
"rewind"
speeds
MAY
be
be
reflected
on
the
media
playback
device
based
upon
the
number
of
sequential
calls
to
this
function
and
the
capability
of
the
device.
This
is
to
avoid
needing
to
define
every
speed
(multiple
fast,
slow
motion,
etc).
If
the
PlaybackSpeed
attribute
is
supported
it
SHALL
be
updated
to
reflect
the
new
speed
of
playback.
If
the
playback
speed
cannot
be
changed
for
the
media
being
played(for
example,
in
live
streaming
content
not
supporting
seek),
the
status
of
NOT_ALLOWED
SHALL
be
returned.
If
the
playback
speed
has
reached
the
maximum
supported
speed
for
media
playing
backwards,
the
status
of
SPEED_OUT_OF_RANGE
SHALL
be
returned.
6.10.4.8.
6.10.7.8.
FastForward
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL start playback of the media in the forward direction in case the media is currently playing in the backward direction or is not playing. If the playback is already happening in the forward direction receipt of this command SHALL increase the speed of the media playback.
Different
"fast-forward"
speeds
MAY
be
be
reflected
on
the
media
playback
device
based
upon
the
number
of
sequential
calls
to
this
function
and
the
capability
of
the
device.
This
is
to
avoid
needing
to
define
every
speed
(multiple
fast,
slow
motion,
etc).
If
the
PlaybackSpeed
attribute
is
supported
it
SHALL
be
updated
to
reflect
the
new
speed
of
playback.
If
the
playback
speed
cannot
be
changed
for
the
media
being
played(for
example,
in
live
streaming
content
not
supporting
seek),
the
status
of
NOT_ALLOWED
SHALL
be
returned.
If
the
playback
speed
has
reached
the
maximum
supported
speed
for
media
playing
forward,
the
status
of
SPEED_OUT_OF_RANGE
SHALL
be
returned.
6.10.4.9.
6.10.7.9.
SkipForward
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL Skip forward in the media by the given number of milliseconds, using the data as follows:
|
|
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
DeltaPositionMilliseconds |
uint64 |
all |
M |
6.10.4.9.1.
6.10.7.9.1.
DeltaPositionMilliseconds
Field
This field SHALL indicate the duration of the time span to skip forward in the media, in milliseconds. In case the resulting position falls in the middle of a frame, the server SHALL set the position to the beginning of that frame and set the SampledPosition attribute on the cluster accordingly. If the resultant position falls beyond the furthest valid position in the media the client MAY seek forward to, the position should be set to that furthest valid position. If the SampledPosition attribute is supported it SHALL be updated on the cluster accordingly.
6.10.4.10.
6.10.7.10.
SkipBackward
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL Skip backward in the media by the given number of milliseconds, using the data as follows:
|
|
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
DeltaPositionMilliseconds |
uint64 |
all |
M |
6.10.4.10.1.
6.10.7.10.1.
DeltaPositionMilliseconds
Field
This field SHALL indicate the duration of the time span to skip backward in the media, in milliseconds. In case the resulting position falls in the middle of a frame, the server SHALL set the position to the beginning of that frame and set the SampledPosition attribute on the cluster accordingly. If the resultant position falls before the earliest valid position to which a client MAY seek back to, the position should be set to that earliest valid position. If the SampledPosition attribute is supported it SHALL be updated on the cluster accordingly.
6.10.4.11.
6.10.7.11.
Seek
Command
Upon receipt, this SHALL change the playback position in the media to the given position using data as follows:
|
|
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Position |
uint64 |
all |
M |
6.10.4.11.1.
6.10.7.11.1.
Position
Field
This field SHALL indicate the position (in milliseconds) in the media to seek to. In case the position falls in the middle of a frame, the server SHALL set the position to the beginning of that frame and set the SampledPosition attribute on the cluster accordingly. If the position falls before the earliest valid position or beyond the furthest valid position to which a client MAY seek back or forward to respectively, the status of SEEK_OUT_OF_RANGE SHALL be returned and no change SHALL be made to the position of the playback.
6.10.4.12.
6.10.7.12.
PlaybackResponse
Command
This command SHALL be generated in response to various Playback Commands. The data for this command SHALL be as follows:
|
|
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Status |
desc |
M |
|||
|
1 |
Data |
|
any |
O |
6.11. Target Navigator Cluster
This cluster provides an interface for UX navigation within a set of targets on a device or endpoint.
This cluster would be supported on Video Player devices or devices with navigable user interfaces. This cluster would also be supported on endpoints with navigable user interfaces such as a Content App. It supports listing a set of navigation targets, tracking and changing the current target.
The cluster server for Target Navigator is implemented by endpoints on a device that support UX navigation.
When this cluster is implemented for a Content App endpoint, the Video Player device containing the endpoint SHALL launch the Content App when a client invokes the NavigateTarget command.
6.11.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial Release |
6.10.5.
6.11.4.
Data
Types
6.10.5.1.
PlaybackStateEnum
6.11.4.1.
StatusEnum
Type
PlaybackStateEnum
Data
Type
This
data
type
is
derived
from
enum8.
| Value | Name |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
M |
|
| NotAllowed |
Target
request
is
|
M |
6.11.5. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x0000 |
|
| R V |
M |
|||
|
| CurrentTarget | uint8 | desc | X | null | R V | O |
6.11.5.1. TargetList Attribute
This attribute SHALL represent a list of targets that can be navigated to within the experience presented to the user by the Endpoint (Video Player or Content App). The list SHALL not contain any entries with the same Identifier in the TargetInfoStruct object.
6.10.5.2.
StatusEnum
6.11.5.2.
CurrentTarget
Attribute
Status
Data
Type
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
Identifier
for
the
target
which
is
derived
from
enum8.
currently
in
foreground
on
the
corresponding
Endpoint
(Video
Player
or
Content
App),
or
null
to
indicate
that
no
target
is
in
the
foreground.
When not null, the CurrentTarget SHALL be an Identifier value contained within one of the TargetInfoStruct objects in the TargetList attribute list.
6.11.6. Commands
|
|
Name |
|
| Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
|
|
|
| M |
|
0x01 |
|
|
|
M |
6.11.6.1.
NavigateTarget
Command
failed:
Requested
playback
command
is
invalid
in
Upon
receipt,
this
SHALL
navigation
the
current
playback
state.
UX
to
the
target
identified.
| ID | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Target | uint8 | all | M |
||
|
1 |
|
|
|
O |
6.11.6.2.
NavigateTargetResponse
Command
failed:
Requested
playback
This
command
is
not
allowed
SHALL
be
generated
in
the
current
playback
state.
For
example,
attempting
response
to
fast-forward
during
a
commercial
might
return
NOT_ALLOWED.
NavigateTarget
command.
| ID | Field | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
1 |
|
|
|
| O |
7. Robots
The
FastForward
or
Rewind
Command
was
issued
but
Cluster
Library
is
made
of
individual
chapters
such
as
this
one.
See
Document
Control
in
the
media
Cluster
Library
for
a
list
of
all
chapters
and
documents.
References
between
chapters
are
made
using
a
X.Y
notation
where
X
is
already
playing
back
at
the
fastest
speed
supported
by
chapter
and
Y
is
the
server
sub-section
within
that
chapter.
7.1. General Description
7.1.1. Introduction
The
clusters
specified
in
this
section
define
the
respective
direction.
operation
of
robotic
devices,
such
as
Robotic
Vacuum
Cleaners
(RVCs).
7.1.2. Cluster List
This section lists the RVC specific clusters as specified in this chapter.
| Cluster ID | Cluster Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0x0054 |
|
|
|
|
|
Commands
and
attributes
for
controlling
the
|
0x0061 |
Commands
and
attributes
for
monitoring
and
controlling
the
|
6.10.5.3.
PlaybackPosition
7.2.
RVC
Run
Mode
Cluster
This
structure
cluster
is
derived
from
the
Mode
Base
cluster
to
define
specifics
for
Robotic
Vacuum
Cleaner
devices.
It
also
defines
a
playback
position
within
a
media
stream
being
played.
namespace
for
the
running
modes
of
these
devices.
7.2.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
7.2.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role | Scope | PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
7.2.4. Data Types
7.2.4.1. ModeOptionStruct Type
The table below lists the changes relative to the Mode Base cluster for the fields of the ModeOptionStruct type. A blank field indicates no change.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
| |||||
1 |
|
M |
|||||
|
2 | ModeTags | 1 to 8 |
|
At least one SupportedMode attribute list entry SHALL include the Idle mode tag in the ModeTags field.
At least one SupportedMode attribute list entry (different from the one above) SHALL include the Cleaning mode tag in the ModeTags field.
The Cleaning and Idle mode tags are mutually exclusive and SHALL NOT both be used together in a mode’s ModeTags.
7.2.6. Derived Cluster Namespace
This namespace includes definitions for data associated exclusively with the derived cluster.
7.2.6.1. ChangeToModeResponse Command Namespace Definitions
The following table defines the derived cluster specific StatusCode values.
| Status Code Value | Name |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
DustBinMissing |
|
| DustBinFull |
0x44 | WaterTankEmpty |
0x45 | WaterTankMissing |
0x46 | WaterTankLidOpen |
0x47 | MopCleaningPadMissing |
0x48 | BatteryLow |
7.2.6.2. Mode Tags
The following table defines the derived cluster specific ModeTag values.
| Mode Tag Value | Name |
|---|---|
0x4000 | Idle |
0x4001 | Cleaning |
6.10.5.3.1.
UpdatedAt
7.2.6.2.1.
Idle
Tag
This
SHALL
indicate
The
device
is
not
performing
any
of
the
time
when
main
operations
of
the
position
was
last
updated.
other
modes.
However,
auxiliary
actions,
such
as
seeking
the
charger
or
charging,
may
occur.
For example, the device has completed cleaning, successfully or not, on its own or due to a command, or has not been asked to clean after a restart.
6.10.5.3.2.
Position
7.2.6.2.2.
Cleaning
Tag
This
SHALL
indicate
the
associated
discrete
position
within
The
device
was
asked
to
clean
so
it
may
be
actively
running,
or
paused
due
to
an
error,
due
to
a
pause
command,
or
for
recharging
etc.
If
currently
paused
and
the
media
stream,
in
milliseconds
device
can
resume
it
will
continue
to
clean.
7.2.7. Mode Examples
Starting
a
cleaning
cycle
is
done
by
switching
from
a
mode
with
the
beginning
of
the
stream,
being
associated
Idle
tag
to
a
mode
with
the
time
indicated
Cleaning
tag.
Stopping
a
cleaning
cycle
is
done
by
switching
from
a
mode
with
the
UpdatedAt
field.
Cleaning
tag
to
a
mode
with
the
Idle
tag.
7.3. RVC Clean Mode Cluster
This cluster is derived from the Mode Base cluster to define specifics for Robotic Vacuum Cleaner devices. It also defines a namespace for the cleaning type for these devices.
7.3.1. Revision History
The
Position
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
not
be
greater
than
the
duration
of
highest
revision
number
in
the
media
if
duration
is
specified.
table
below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial Release |
7.3.4. Data Types
7.3.4.1. ModeOptionStruct Type
The
Position
SHALL
not
be
greater
than
table
below
lists
the
time
difference
between
current
time
and
start
time
changes
relative
to
the
Mode
Base
cluster
for
the
fields
of
the
media
when
start
time
is
specified.
ModeOptionStruct
type.
A
blank
field
indicates
no
change.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Label | M | |||||
1 | Mode | M | |||||
2 | ModeTags | 1 to 8 | M |
A
value
of
null
At
least
one
SupportedMode
attribute
list
entry
SHALL
indicate
that
playback
position
is
not
applicable
for
include
the
current
state
of
Vacuum
and/or
the
media
playback
(For
example
:
Live
media
Mop
mode
tag
in
the
ModeTags
field
list.
7.3.5. Derived Cluster Namespace
This
namespace
includes
definitions
for
data
associated
exclusively
with
no
known
duration
and
where
seek
the
derived
cluster.
7.3.5.1. ChangeToModeResponse Command Namespace Definitions
The following table defines the derived cluster specific StatusCode values.
| Status Code Value | Name |
|---|---|
0x40 | CleaningInProgress |
7.3.6. Mode Examples
A few examples of modes and their mode tags are provided below.
For the "Turbo, Vacuum Only" mode, tags: 0x4000 (Deep Clean), 0x4001 (Vacuum).
For the "Mop Only" mode, tags: 0x4002 (Mop), 0x0003 (Low Noise).
For the "Rapid Vacuum and Mop" mode, tags: 0x0001 (Quick), 0x4001 (Vacuum), 0x4002 (Mop).
Note that the "Low Noise" and "Quick" mode tags are defined in the generic Mode Base cluster specification.
6.11.
Target
Navigator
7.4.
RVC
Operational
State
Cluster
This
cluster
provides
an
interface
for
UX
navigation
within
a
set
monitoring
the
operational
state
of
targets
on
a
device
or
endpoint.
Robotic
Vacuum
Cleaner.
6.11.1.
Overview
7.4.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial release |
7.4.2. Classification
| Hierarchy | Role | Scope | PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
Operational State | Application | Endpoint | RVCOPSTATE |
7.4.4. Data Types
7.4.4.1. OperationalStateEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
The
values
defined
herein
are
applicable
to
this
derived
cluster
would
be
supported
of
Operational
State
only
and
are
additional
to
the
set
of
values
defined
in
Operational
State
itself.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0x40 | SeekingCharger | The device is en route to the charging dock | M |
0x41 | Charging | The device is charging | M |
0x42 | Docked |
The
device
is
on
| M |
7.4.4.2. ErrorStateEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
The
values
defined
herein
are
applicable
to
this
derived
cluster
would
also
be
supported
on
endpoints
with
navigable
user
interfaces
of
Operational
State
only
and
are
additional
to
the
set
of
values
defined
in
Operational
State
itself.
| Value | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0x40 | FailedToFindChargingDock | The device has failed to find or reach the charging dock | M |
0x41 | Stuck | The device is stuck and requires manual intervention | M |
0x42 | DustBinMissing | The device has detected that its dust bin is missing | M |
0x43 | DustBinFull | The device has detected that its dust bin is full | M |
0x44 | WaterTankEmpty | The device has detected that its water tank is empty | M |
0x45 | WaterTankMissing | The device has detected that its water tank is missing | M |
0x46 | WaterTankLidOpen | The device has detected that its water tank lid is open | M |
0x47 | MopCleaningPadMissing | The device has detected that its cleaning pad is missing | M |
8. Home Appliances
The
Cluster
Library
is
made
of
individual
chapters
such
as
this
one.
See
Document
Control
in
the
Cluster
Library
for
a
Content
App.
It
supports
listing
a
set
list
of
navigation
targets,
tracking
all
chapters
and
changing
documents.
References
between
chapters
are
made
using
a
X.Y
notation
where
X
is
the
current
target.
chapter
and
Y
is
the
sub-section
within
that
chapter.
8.1. General Description
8.1.1. Introduction
The
cluster
server
clusters
specified
in
this
section
are
typically
used
in
control
of
home
appliances,
such
as
laundry
washers,
refrigerators
etc.
8.1.2. Cluster List
This section lists the home appliance specific clusters as specified in this chapter.
| Cluster ID | Cluster Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Common Clusters | ||
0x0056 |
Commands
and
attributes
for
| |
Dishwasher Clusters | ||
0x0059 | Commands and attributes for controlling a dishwasher | |
0x005D | Alarm definitions for Dishwasher devices | |
Laundry Washer Clusters | ||
0x0051 | Commands and attributes for controlling a laundry washer | |
0x0053 |
Commands
and
attributes
for
the
control
of
options
on
a
device
that
| |
Refrigerator Clusters | ||
0x0052 |
Commands and attributes for controlling a refrigerator or a temperature controlled cabinet | |
0x0057 | Alarm definitions for Refrigerator devices | |
8.2. Temperature Control Cluster
When
this
This
cluster
provides
an
interface
to
the
setpoint
temperature
on
devices
such
as
washers,
refrigerators,
and
water
heaters.
The
setpoint
temperature
is
implemented
for
the
temperature
to
which
a
Content
App
endpoint,
device
using
this
cluster
would
attempt
to
control
to.
This
cluster
does
not
provide
access
to
the
Video
Player
actual
or
physical
temperature
associated
with
any
device
containing
using
this
cluster.
Access
to
the
endpoint
SHALL
launch
physical
temperature
associated
with
a
device
using
this
cluster
would
be
provided
by
other
clusters
as
part
of
that
devices
device
type
definition.
The
values
and
constraints
of
the
Content
App
when
attributes
communicated
to
clients
SHOULD
match
the
controls
on
any
physical
interface
on
a
client
invokes
device
implementing
this
server.
For
example,
the
NavigateTarget
command.
value
of
the
Step
attribute
SHOULD
match
the
incremental
value
by
which
the
temperature
setpoint
can
be
changed
on
the
physical
device.
6.11.1.1.
8.2.1.
Revision
History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Initial
|
6.11.1.2.
8.2.2.
Classification
| Hierarchy | Role |
|
PICS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Base |
Application |
Endpoint |
|
6.11.1.3.
8.2.3.
Cluster
Identifiers
ID
|
|
Name |
|---|---|
|
|
|
6.11.2.
8.2.4.
Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature |
| Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 | TN | TemperatureNumber | O.a | Use actual temperature numbers |
1 | TL | TemperatureLevel | O.a | Use temperature levels |
2 | STEP | TemperatureStep | [TN] | Use step control with temperature numbers |
8.2.4.1. TemperatureNumber Feature
For
devices
that
use
an
actual
temperature
value
for
the
temperature
setpoint,
such
as
some
water
heaters,
the
feature
TN
SHALL
be
used.
Note
that
this
cluster
provides
and
supports
temperatures
in
degrees
Celsius
via
the
temperature
data
type.
6.11.3.
8.2.5.
Attributes
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x0000 |
|
|
MinTemperature to MaxTemperature |
R V |
|
||
|
0x0001 |
|
| max (MaxTemperature - 1) * | F | R V | TN | |
0x0002 | MaxTemperature | temperature |
desc |
|
| TN | |
0x0003 | Step | temperature |
max (MaxTemperature - MinTemperature) | F | R V |
| |
0x0004 | SelectedTemperatureLevel | uint8 | 0 to 31 | R V | TL | ||
0x0005 | SupportedTemperatureLevels | list[string] | max 32[max 16] | R V | TL |
|
Note
| * See temperature data type, in the data model, for encoding units. |
6.11.3.1.
TargetList
8.2.5.1.
TemperatureSetpoint
Attribute
The
TargetList
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
a
list
of
targets
that
can
be
navigated
the
desired
Temperature
Setpoint
on
the
device.
8.2.5.2. MinTemperature Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
minimum
temperature
to
within
which
the
experience
presented
TemperatureSetpoint
attribute
MAY
be
set.
8.2.5.3. MaxTemperature Attribute
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
maximum
temperature
to
which
the
user
by
TemperatureSetpoint
attribute
MAY
be
set.
If
the
Endpoint
(Video
Player
or
Content
App).
The
list
Step
attribute
is
supported,
this
attribute
SHALL
not
contain
any
entries
with
the
same
Identifier
in
be
such
that
MaxTemperature
=
MinTemperature
+
Step
*
n,
where
n
is
an
integer
and
n
>
0.
If
the
TargetInfo
object.
Step
attribute
is
not
supported,
this
attribute
SHALL
be
such
that
MaxTemperature
\$>\$
MinTemperature.
6.11.3.2.
CurrentTarget
8.2.5.4.
Step
Attribute
The
CurrentTarget
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
Identifier
for
the
target
discrete
value
by
which
the
TemperatureSetpoint
attribute
can
be
changed
via
the
SetTemperature
command.
8.2.5.5. SelectedTemperatureLevel Attribute
When
not
null,
This
attribute
SHALL
represent
the
CurrentTarget
currently
selected
temperature
level
setting
of
the
server.
This
attribute
SHALL
be
an
Identifier
value
contained
within
one
the
positional
index
of
the
TargetInfo
objects
list
item
in
the
TargetList
SupportedTemperatureLevels
list
that
represents
the
currently
selected
temperature
level
setting
of
the
server.
8.2.5.6. SupportedTemperatureLevels Attribute
This
attribute
list.
SHALL
represent
the
list
of
supported
temperature
level
settings
that
may
be
selected
via
the
TargetTemperatureLevel
field
in
the
SetTemperature
command.
Each
string
is
readable
text
that
describes
each
temperature
level
setting
in
a
way
that
can
be
easily
understood
by
humans.
For
example,
a
washing
machine
can
have
temperature
levels
like
"Cold",
"Warm",
and
"Hot".
Each
string
is
specified
by
the
manufacturer.
Each item in this list SHALL represent a unique temperature level. Each entry in this list SHALL have a unique value. The entries in this list SHALL appear in order of increasing temperature level with list item 0 being the setting with the lowest temperature level.
6.11.4.
8.2.6.
Commands
|
|
Name | Direction | Response | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0x00 |
|
|
|
O |
M |
8.2.6.1. SetTemperature Command
The SetTemperature command SHALL have the following data fields:
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| TN |
||
|
1 |
| uint8 | desc | TL |
6.11.4.1.
NavigateTarget
Command
8.2.6.1.1.
TargetTemperature
Field
Upon
receipt,
This
field
SHALL
specify
the
desired
temperature
setpoint
that
the
server
is
to
be
set
to.
The TargetTemperature SHALL be from MinTemperature to MaxTemperature inclusive. If the Step attribute is supported, TargetTemperature SHALL be such that (TargetTemperature - MinTemperature) % Step == 0.
8.2.6.1.2. TargetTemperatureLevel Field
This
field
SHALL
specify
the
index
of
the
list
item
in
the
SupportedTemperatureLevels
list
that
represents
the
desired
temperature
level
setting
of
the
server.
The
value
of
this
field
SHALL
navigation
be
between
0
and
the
UX
length
of
the
SupportedTemperatureLevels
list
-1.
8.2.6.1.3. Effect on Receipt
If
the
TargetTemperature
or
TargetTemperatureLevel
fields
of
the
command
meet
all
constraints
but
the
server
is
unable
to
execute
the
target
identified.
command
at
the
time
the
command
is
received
by
the
server
(e.g.
due
to
the
design
of
a
device
it
cannot
accept
a
change
in
its
temperature
setting
after
it
has
begun
operation),
then
the
server
SHALL
respond
with
a
status
code
of
INVALID_IN_STATE,
and
discard
the
command.
If the TN feature is supported, on receipt of this command,
If the value of the TargetTemperature field meets all constraints, the server SHALL set the TemperatureSetpoint attribute to the value of the TargetTemperature field and the response SHALL have a status code of SUCCESS.
Otherwise (e.g. if the value of the TargetTemperature field falls outside of the constraints of the TemperatureSetpoint attribute or if the Step attribute is supported in the server and the value of the TargetTemperature field is such that (TargetTemperature - MinTemperature) % Step != 0), the status of the response SHALL be CONSTRAINT_ERROR and the value of the TemperatureSetpoint attribute SHALL remain unchanged.
If the TL feature is supported, on receipt of this command,
If value of the TargetTemperatureLevel field meets all constraints, the server SHALL set its SelectedTemperatureLevel attribute to the value of TargetTemperatureLevel field and respond with status SUCCESS.
Otherwise (e.g. if the value of the TargetTemperatureLevel field is out of bounds of the SupportedTemperatureLevels list), the status of the response SHALL be CONSTRAINT_ERROR, and the value of SelectedTemperatureLevel SHALL remain unchanged.
8.3. Dishwasher Mode Cluster
This cluster is derived from the Mode Base cluster, defining additional mode tags and namespaced enumerated values for dishwasher devices.
8.3.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
|
|
|
|---|---|
1 | Initial Release |
8.3.4. Data Types
8.3.4.1. ModeOptionStruct Type
The table below lists the changes relative to the Mode Base cluster for the fields of the ModeOptionStruct type. A blank field indicates no change.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
| M |
|||||
|
|
|
M |
|||||
|
2 | ModeTags | 1 to 8 |
|
At least one SupportedMode attribute list entry SHALL include the Normal mode tag in the ModeTags field list.
8.3.5. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| SupportedModes | M |
|||||
|
0x0001 | CurrentMode |
|
|||||
|
| StartUpMode | P | |||||
0x0003 | OnMode | P |
8.4. Dishwasher Alarm Cluster
This cluster is a derived cluster of the Alarm Base cluster.
8.4.1. Revision History
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
indicate
be
the
Identifier
for
highest
revision
number
in
the
target
table
below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial revision |
8.4.4. Data Types
8.4.4.1. AlarmMap Type
This data type is derived from map32.
| Bit | Name | Summary | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | InflowError | Water inflow is abnormal | P,O.a+ |
1 | DrainError | Water draining is abnormal | P,O.a+ |
2 | DoorError | Door or door lock is abnormal | O.a+ |
3 | TempTooLow | Unable to reach normal temperature | P,O.a+ |
4 | TempTooHigh | Temperature is too high | P,O.a+ |
5 | WaterLevelError | Water level is abnormal | P,O.a+ |
8.5. Laundry Washer Mode Cluster
This
cluster
is
derived
from
the
Mode
Base
cluster,
defining
additional
mode
tags
and
namespaced
enumerated
values
for
UX
navigation.
laundry
washer
devices.
8.5.1. Revision History
The
Target
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
be
an
Identifier
value
contained
within
one
of
the
TargetInfo
objects
highest
revision
number
in
the
TargetList
table
below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial Release |
8.5.4. Data Types
8.5.4.1. ModeOptionStruct Type
The table below lists the changes relative to the Mode Base cluster for the fields of the ModeOptionStruct type. A blank field indicates no change.
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Label | M | |||||
1 | Mode | M | |||||
2 | ModeTags | 1 to 8 | M |
At least one SupportedMode attribute list entry SHALL include the Normal mode tag in the ModeTags field list.
8.5.5. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x0000 | SupportedModes | M | |||||
0x0001 | CurrentMode | M | |||||
0x0002 | StartUpMode | P | |||||
0x0003 | OnMode | P |
8.6. Laundry Washer Controls
This cluster provides a way to access options associated with the operation of a laundry washer device type.
8.6.1. Revision History
The
global
ClusterRevision
attribute
value
SHALL
indicate
Optional
app-specific
data.
be
the
highest
revision
number
in
the
table
below.
| Rev | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial release |
8.6.4. Features
This cluster SHALL support the FeatureMap bitmap attribute as defined below.
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | SPIN | Spin | O | Multiple spin speeds supported |
1 | RINSE | Rinse | O | Multiple rinse cycles supported |
8.6.5. Data Types
8.6.5.1. NumberOfRinsesEnum Type
This data type is derived from enum8.
The
NumberOfRinsesEnum
provides
a
representation
of
the
number
of
rinses
that
will
be
performed
for
a
selected
mode.
NumberOfRinsesEnum
is
derived
from
enum8.
It
is
up
to
NavigateTarget
command.
the
device
manufacturer
to
determine
the
mapping
between
the
enum
values
and
the
corresponding
numbers
of
rinses.
| Value | Name | Conformance | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | None | RINSE | This laundry washer mode does not perform rinse cycles |
1 | Normal | RINSE | This laundry washer mode performs normal rinse cycles determined by the manufacturer |
2 | Extra | RINSE | This laundry washer mode performs an extra rinse cycle |
3 | Max | RINSE | This laundry washer mode performs the maximum number of rinse cycles determined by the manufacturer |
8.6.6. Attributes
| ID |
|
Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
| SPIN |
||
|
0x0001 | SpinSpeedCurrent | uint8 | 0 to 15 | X | desc | RW VO | SPIN |
0x0002 | NumberOfRinses | desc | 1 |
|
|
||
|
|
SupportedRinses |
|
| R V | RINSE |
6.11.4.2.1.
Status
8.6.6.1.
SpinSpeeds
Attribute
This attribute indicates the list of spin speeds available to the appliance in the currently selected mode. The spin speed values are determined by the manufacturer. At least one spin speed value SHALL be provided in the SpinSpeeds list. The list of spin speeds MAY change depending on the currently selected Laundry Washer mode. For example, Quick mode might have a completely different list of SpinSpeeds than Delicates mode.
8.6.6.2. SpinSpeedCurrent Attribute
This attribute indicates the currently selected spin speed. It is the index into the SpinSpeeds list of the selected spin speed, as such, this attribute can be an integer between 0 and the number of entries in SpinSpeeds - 1. If a value is received that is outside of the defined constraints, a CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be sent as the response. If a value is attempted to be written that doesn’t match a valid index (e.g. an index of 5 when the list has 4 values), a CONSTRAINT_ERROR SHALL be sent as the response. If null is written to this attribute, there will be no spin speed for the selected cycle. If the value is null, there will be no spin speed on the current mode.
8.6.6.3. NumberOfRinses Attribute
This
attribute
represents
how
many
times
a
rinse
cycle
SHALL
be
performed
on
a
device
for
the
current
mode
of
operation.
A
value
of
None
SHALL
indicate
that
no
rinse
cycle
will
be
performed.
This
value
may
be
set
by
the
client
to
adjust
the
number
of
rinses
that
are
performed
for
the
command.
current
mode
of
operation.
If
the
device
is
not
in
a
compatible
state
to
accept
the
provided
value,
an
INVALID_IN_STATE
error
SHALL
be
sent
as
the
response.
6.11.4.2.2.
Data
8.6.6.4.
SupportedRinses
Attribute
This
attribute
represents
the
amount
of
rinses
allowed
for
a
specific
mode.
Each
entry
SHALL
indicate
Optional
app-specific
data.
a
NumberOfRinsesEnum
value
that
is
possible
in
the
selected
mode
on
the
device.
The
value
of
this
attribute
MAY
change
at
runtime
based
on
the
currently
selected
mode.
Each
entry
SHALL
be
distinct.
8.7. Refrigerator And Temperature Controlled Cabinet Mode Cluster
This cluster is derived from the Mode Base cluster, defining additional mode tags and namespaced enumerated values for refrigerator and temperature controlled cabinet devices.
8.7.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial Release |
8.7.4. Data Types
6.11.5.1.
TargetInfo
8.7.4.1.
ModeOptionStruct
Type
This
indicates
an
object
describing
The
table
below
lists
the
navigable
target.
changes
relative
to
the
Mode
Base
cluster
for
the
fields
of
the
ModeOptionStruct
type.
A
blank
field
indicates
no
change.
|
|
Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|||||
|
| Mode |
M |
|||||
|
2 | ModeTags | 1 to 8 |
M |
At least one SupportedMode attribute list entry SHALL include the Auto mode tag in the ModeTags field list.
8.7.5. Attributes
| ID | Name | Type | Constraint | Quality | Default | Access | Conformance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x0000 |
|
M |
|||||
|
0x0001 | CurrentMode | M | |||||
0x0002 | StartUpMode | P | |||||
0x0003 | OnMode | P |
8.7.6. Derived Cluster Namespace
This namespace includes definitions for data associated exclusively with the derived cluster.
8.7.6.1. Mode Tags
The following table defines the derived cluster specific ModeTag values.
| Mode Tag Value | Name |
|---|---|
0x4000 | RapidCool |
0x4001 | RapidFreeze |
8.7.7. Mode Examples
A
name
string
for
few
examples
of
Refrigerator
and
Temperature
Controlled
Cabinet
modes
and
their
mode
tags
are
provided
below.
For the
TargetInfo."Normal" mode, tags: 0x0000 (Auto)For the "Energy Save" mode, tags: 0x0004 (LowEnergy)
For the "Rapid Cool" mode, tags: 0x4000 (RapidCool)
6.11.5.2.
StatusEnum
8.8.
Refrigerator
Alarm
Cluster
Status
Data
Type
This
cluster
is
a
derived
from
enum8.
cluster
of
Alarm
Base
cluster.
8.8.1. Revision History
The global ClusterRevision attribute value SHALL be the highest revision number in the table below.
| Revision | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Initial revision |
8.8.2. Classification
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Alarm Base |
Application |
|
|
8.8.4. Features
| Bit | Code | Feature | Conformance | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
8.8.6. Attributes
8.8.6.1. Mask Attribute
If the generation of the alarm has not been suppressed at the device itself, then this attribute SHALL have these fixed values.
| Bit | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|
|
| DoorOpen | 1 |
This alarm SHALL be cleared only when the door is closed (manual action).
If the generation of the alarm is suppressed at the device itself, then bit 0 SHALL have a value of 0. It SHALL be re-set to 1 if the alarm is re-enabled at the device itself.